The characteristics of Lg waves induced by the underground nuclear explosions in the waveguides using frequency-wavenumber algorithm
-
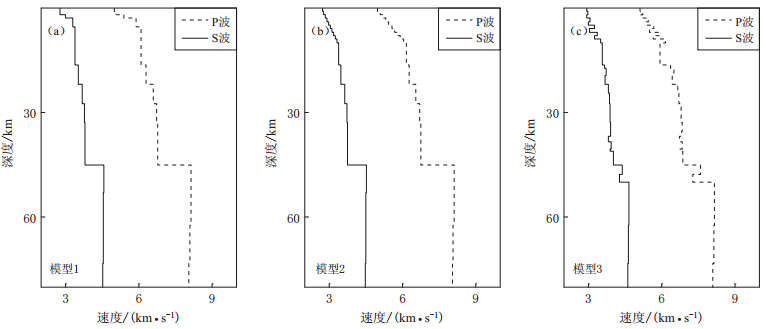
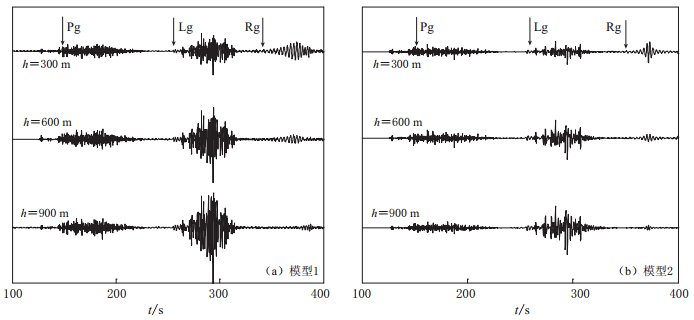
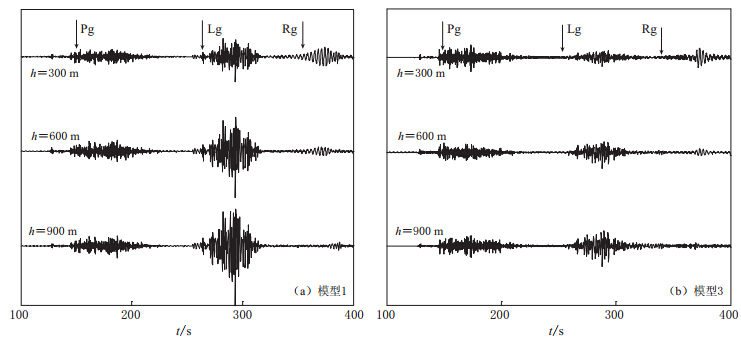
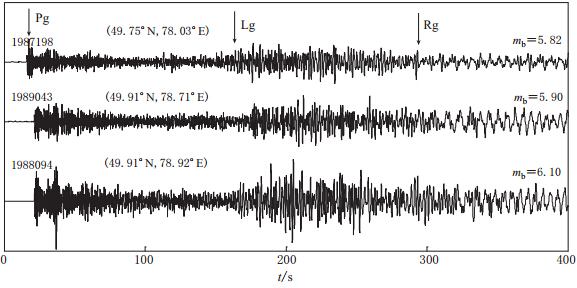
摘要: 基于频率-波数域算法的理论地震波形图方法, 可以数值模拟频率达到10 Hz、 震中距达1000 km的区域理论地震波形图. 该算法适用于计算大量分层地壳结构中激发的导波Lg波. 本文在前苏联东哈萨克斯坦地下核试验场至我国乌鲁木齐台站间的地球介质速度模型中, 引入速度梯度结构、 速度扰动分布的薄叠加层结构、 降低Q值结构以及速度扰动与Q值变化的综合结构来模拟实际地壳波导结构, 较好地模拟出东哈萨克斯坦地下核爆炸地震在乌鲁木齐台站记录的宽频带地震波形图, 模拟出完整的Lg波序列, 该序列符合Lg波能量分布特征, 且能够解释Lg波波尾的特征. 结果表明, Lg波的形状和峰值结构均依赖于地壳的不同波导结构.Abstract: Based on the frequency-wavenumber algorithm,we can simulate high frequency (10 Hz) regional seismograms (up to a distance of more than 1000 km). The algorithm is used to synthesize the regional waveguides on Lg waves in a medium consisting of a large number of crustal layers. Based on the crustal velocity model from a former Soviet nuclear test site located in eastern Kazakhstan to WMQ station in China, this paper build up a modified model consisting of thin layers with an alternating high and low-velocity, a velocity gradient near the surface, the lower Q values, and the composite structure of velocity perturbation and different Q values so as to match the real crustal structure. And then we simulate very well the regional seismograms in WMQ station by underground nuclear explosions of the test site in eastern Kazakhstan. The synthetic results conform to the energy distribution characteristics of Lg waves, and explain the feature of the coda. The numerical results suggest that the shapes and peak amplitudes of Lg waves all depend on the different crustal waveguides.
-
-
表 1 东哈萨克斯坦地区地下核试验场区速度模型
Table 1 Seismic velocity model of underground nuclear test site at eastern Kazakhstan region
层号 界面深度/km 密度/(g·cm-3) S波速度/(km·s-1) P波速度/(km·s-1) QS QS-修正 QP 1 0 2.700 2.790 5.020 100 80 2000 2 2.000 2.700 3.000 5.400 150 120 2000 3 3.000 2.700 3.300 5.900 200 160 2000 4 5.488 2.700 3.400 6.100 600 480 2000 5 16.464 2.702 3.541 6.308 525 420 2000 6 21.952 2.807 3.703 6.597 500 400 2000 7 27.440 2.858 3.781 6.736 450 360 2000 8 32.928 2.875 3.807 6.782 400 400 2000 9 38.492 2.879 3.814 6.795 350 350 2000 10 44.996 3.372 4.573 8.147 179 179 2000 11 53.002 3.369 4.568 8.138 167 167 2000 12 62.361 3.358 4.550 8.106 159 159 2000 13 73.301 3.343 4.527 8.065 153 153 2000 14 86.081 3.336 4.517 8.047 150 150 2000 15 101.031 3.345 4.530 8.070 148 148 2000 16 118.501 3.361 4.556 8.117 148 148 2000 17 138.921 3.375 4.577 8.154 147 147 2000 18 162.801 3.378 4.581 8.161 147 147 2000 19 190.711 3.372 4.572 8.145 146 146 2000 20 223.341 3.363 4.558 8.120 146 146 2000 21 300.000 3.356 4.547 8.101 145 145 2000 -
McLaughlin K L, Barker T G, Day S M, Shkoller B, Stevens J L. 1988. Effects of Depth of Burial on Explosion and Earthquake Regional Seismograms: Regional Discrimination and Yield Estimation[R]. S-CUBED report No. SSS-R-88-9844, Jolla, California.
Patton H J. 1991. Seismic moment estimation and the scaling of the long-period explosion source spectrum[G]//AGU Geophysical Monograph 65: Explosion Source Phenomenology: 239-252.
Saikia C K, Helmberger D V, Burdick L J. 1992. Regional wave propagation and high-frequency/low-frequency energy level discriminant[C]//Proceedings of 14th Annual PL/DARPA Seismol Res Symp. 16—18 September, Tucson, Arizona: 351-360.
Tolstoy I, Clay C S. 1966. Ocean Acoustics Theory and Experiment in Underwater Sound[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 谭友恒,于湘伟,宋倩,章文波. 基于背景噪声研究青藏高原东缘三维横波速度结构. 地球物理学报. 2023(03): 1050-1069 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴磊. 用PTD方法测定泸县M_s6.0地震序列的深度. 科技资讯. 2023(09): 115-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋倩,梁姗姗,于湘伟,章文波,李春来. 云南2020年巧家M_S5.0地震序列发震构造及其与2014年鲁甸M_S6.5地震的关系. 地球物理学报. 2022(04): 1303-1324 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: