Solid tide phenomenon of cold water source well temperature and its mechanism: Taking Huangcun well as an example
-
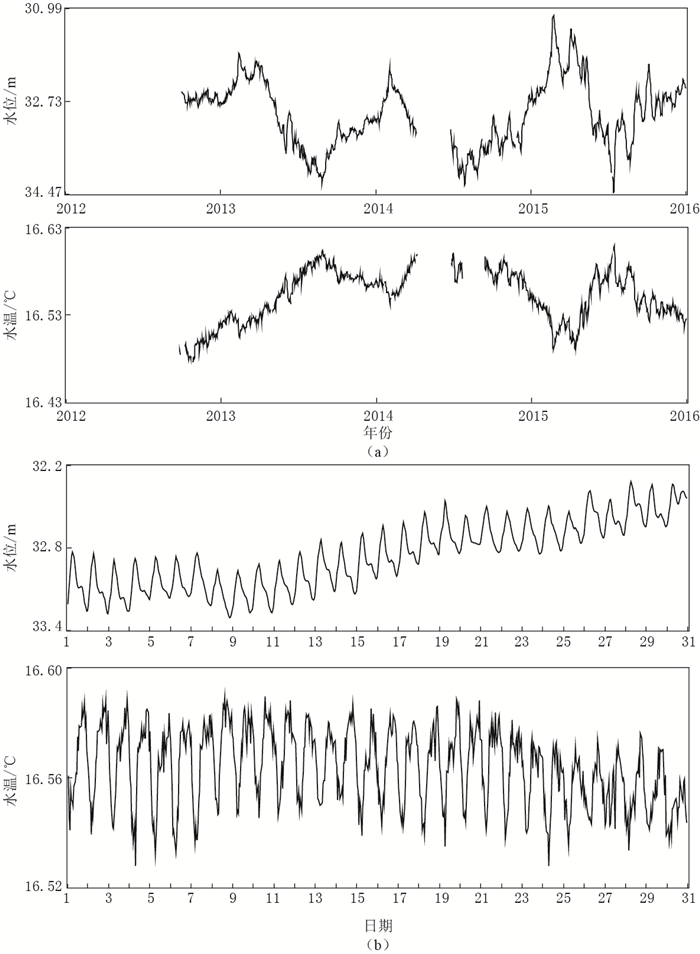
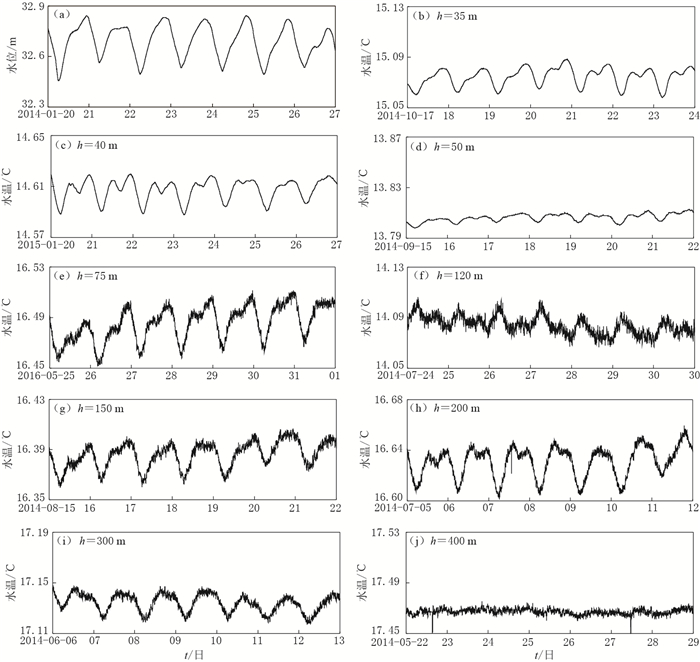
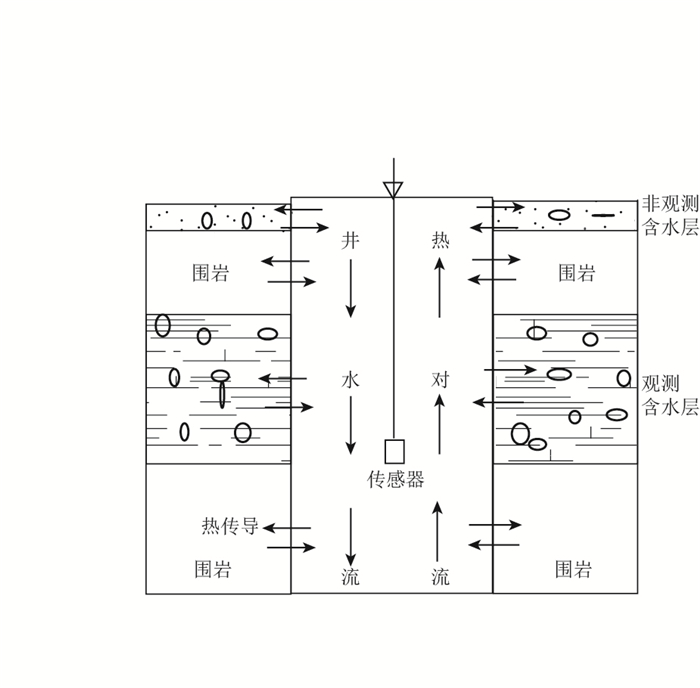
摘要: 该文对黄村冷水源井的水温固体潮现象进行了观测研究,初步解释了冷水源井的水温固体潮汐的形成机理.通过对黄村观测井进行水温梯度的详细观测及不同深度水温的对比观测研究,得到了黄村井水温潮汐现象的观测结果:① 黄村冷水源井的水温固体潮的相位与水位的相位是相反的;② 黄村井水温梯度曲线呈下凹型,特别是在含水层及受含水层进出水影响较大的附近区域下凹程度大,且随着与含水层底板距离逐渐变大,下凹程度也变小;③ 水温传感器的观测值与含水层观测距离存在一定的规律性:距离含水层越远,水温潮汐差越小, 直至潮汐变化消失.这说明冷水源井与热水井的水温潮汐现象是不同的,前者是吸热过程, 后者是放热过程,由此造成二者水-热动力学特征的不同.Abstract: In this study, we conducted an observation to monitor water temperature solid tide phenomenon of cold water source well in Huangcun, and preliminarily interpreted its formation mechanism. Based on detailed monitoring data of water temperature gradient and the comparison of water temperatures in different depths, we concluded the following conclusions: ① The phase of water temperature solid tide of Huangcun well was opposite to that of water level. ② The water temperature gradient of Huangcun well was of concave-down type. The position that was greatly influenced by influent and effluent water of the aquifer or nearby concaved down the most, and the concave degree getting weaker with the increasing of the distance from the aquifer. ③ There is a rule between data from water temperature sensor and the distance from the observation aquifer: Tidal difference of water temperature became smaller with the increasing of distance until tidal variation faded away. It shows that the water temperature tide phenomenon of the cold-water source well is different from that of hot-water source well. One is endothermic process, and the other is exothermic process, which results in the different characteristics of water thermal dynamics.
-
本文在撰写过程中,得到刘耀炜研究员和车用太研究员的悉心指导,并得到徐平、胡平及谷永新等几位领导的支持,作者在此一并感谢!
-
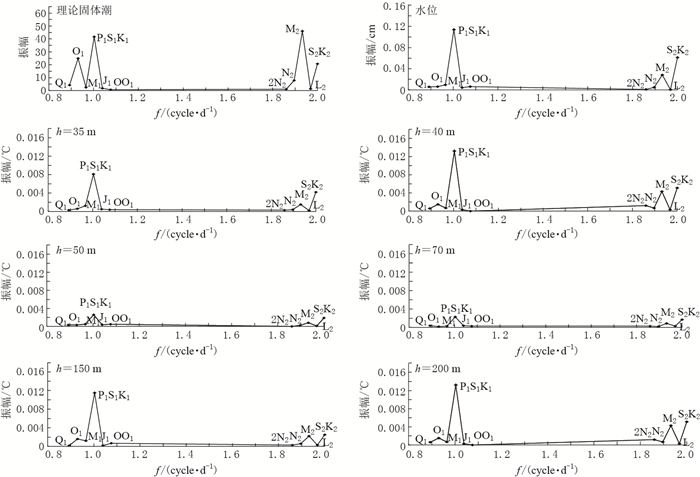
表 1 使用调和分析法得到的黄村井水位、水温潮汐分波振幅
Table 1 Tidal component amplitudes of water level and water temperature for Huangcun well using harmonic analysis method
半月波 水位
/cm理论
固体潮水温/℃ h=35 m h=40 m h=50 m h=70 m h=150 m h=200 m 2N2 0.0010 1.1311 0.0003 0.0004 0 0.0003 0.0003 0.0002 N2 0.0044 7.7826 0.0004 0.0004 0.0002 0.0002 0.0006 0.0012 M2 0.0281 45.9822 0.0015 0.0026 0.0008 0.0009 0.0022 0.0030 L2 0.0015 1.3813 0.0002 0.0002 0.0001 0.0003 0.0003 0.0004 S2K2 0.0661 20.8173 0.0042 0.0057 0.0019 0.0017 0.0025 0.0059 注:h为水温探头埋深. 表 2 距含水层底板距离与水温日潮差变化对比
Table 2 Comparison between distance to observation aquifer floor and water temperature diurnal range
水温探头
埋深/m距含水层底板
距离/m水温日潮差
/℃140 0 0.2857 150 10 0.3349 200 60 0.3743 220 80 0.3546 300 160 0.2364 400 260 0 -
车用太, 鱼金子. 2013.井水温度观测中有待解决的若干基本问题[J].中国地震, 29(3): 306-315. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD201303002.htm Che Y T, Yu J Z. 2013. Some basic problems in well water temperature observation[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 29(3): 306-315 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD201303002.htm
车用太, 何案华, 鱼金子. 2014.水温微动态形成的水-热动力学与地热动力学机制[J].地震学报, 36(1): 106-117. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28929 Che Y T, He A H, Yu J Z. 2014. Mechanisms of water-heat dynamics and earth-heat dynamics of well water temperature micro-behavior[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 36(1): 106-117 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28929
陈沅俊, 姚宝树. 1999.张北6.2级地震地温短临异常特征[J].地震, 19(2): 179-182. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN902.009.htm Chen Y J, Yao B S. 1999. The features of geotemperature in short-term precursory anomalies before the Zhangbei earthquake with MS6.2[J]. Earthquake, 19(2): 179-182 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN902.009.htm
韩志文, 蒙格平. 2004.北京市大兴区岩溶地下水水位变化趋势分析[J].北京水利, (6): 21-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJSL200406010.htm Han Z W, Meng G P. 2004. Analysis of the trend of water level of karst groundwater in Daxing district, Beijing[J]. Beijing Water Resources, (6): 21-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJSL200406010.htm
刘耀炜, 孙小龙, 王世芹, 任宏微. 2008.井孔水温异常与2007年宁洱6.4级地震关系分析[J].地震研究, 31(4): 347-353. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ200804009.htm Liu Y W, Sun X L, Wang S Q, Ren H W. 2008. Relationship of bore-hole water temperature anomaly and the 2007 Ning'er M6.4 earthquake[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 31(4): 347-353 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ200804009.htm
马玉川. 2010. 井水温度潮汐效应及其应变响应能力研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地壳应力研究所: 33-45. Ma Y C. 2010. Tidal Effect of Well Water Temperature and Its Response to Strain[D]. Beijing: Institute of Crustal Dynamics, China Earthquake Administration: 33-45 (in Chinese).
杨竹转. 2011. 地震波引起的井水位水温同震变化及其机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所: 70-76. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92674X/201211/44119188.html Yang Z Z. 2011. Coseismic Variations of Well Water Level and Temperature Caused by Earthquake Waves and Their Generating Mechanisms[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration: 70-76 (in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92674X/201211/44119188.html
赵丹, 王广才. 2013.地下水位气压效应的消除及主要气压影响分波的识别[J].中国科学:技术科学, 43(1): 79-86. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JEXK201301010.htm Zhao D, Wang G C. 2013. Removing barometric pressure effects from groundwater level and identifying main influential constituents[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 56: 129-136. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JEXK201301010.htm
Esipko O A, Rosaev A E. 2007. The temperature monitoring in Vorotilovo deep well and global climate warming[J]. Geophys Res Abstr, 9: 00533. http://meetings.copernicus.org/www.cosis.net/abstracts/EGU2007/00533/EGU2007-J-00533.pdf
Furuya I, Shimamura H. 1988. Groundwater microtemperature and strain[J]. Geophys J Int, 94(2): 345-353. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1988.tb05905.x
Rosaev A E, Esipko O A. 2003. Lithospheric tidal effects from observations in deep wells[J]. Celest Mech Dyn Astr, 87(1/2): 203-207. doi: 10.1023/A:1026160111577
Shimamura H, Ino M, Hikawa H, Iwasaki T. 1984. Groundwater microtemperature in earthquake regions[J]. Pure Appl Geophys, 122(6): 933-946. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226126558_Groundwater_Microtemperature_in_Earthquake_Regions
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 颜永逸,林俊平,高珂,翁顺,赵丹阳,张景琪. 基于图像场景分类和包络线提取的桥梁重车识别. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(03): 73-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 戴世坤,朱德祥,张莹,李昆,陈轻蕊,凌嘉宣,田红军. 任意起伏地形下重力异常三维正演及并行计算. 地球物理学报. 2024(02): 768-780 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘中宪,孟思博,张妤,乔云帆,陈龙伟. 考虑建筑群-沉积盆地动力相互作用的建筑群震害评估方法. 地震学报. 2024(01): 129-143 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 熊超,王欣,王鑫杰,吴和喜. 基于CUDA的航空γ能谱数据小波降噪并行加速算法. 核技术. 2024(04): 23-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王文静,王健,周红. 基于多破裂方式的三河—平谷地震震级研究. 地震学报. 2023(05): 903-918 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 周红,王文静. 夏垫断裂M_W≥7.5地震动的预测. 地震学报. 2022(05): 853-867 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载: