Research of tidal water level amplitude and phase and application to causation analysis of well water level changes
-
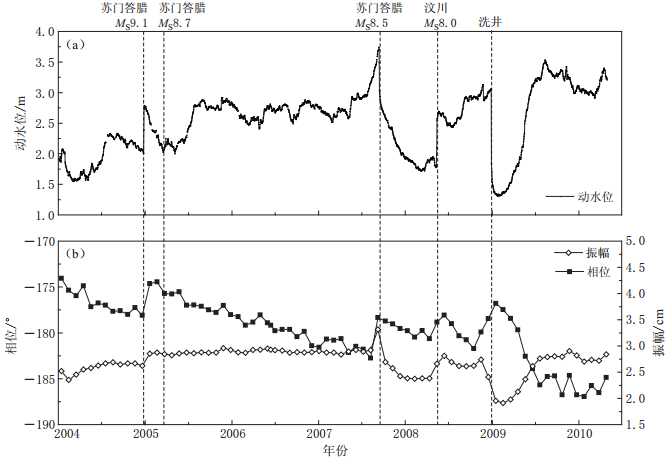
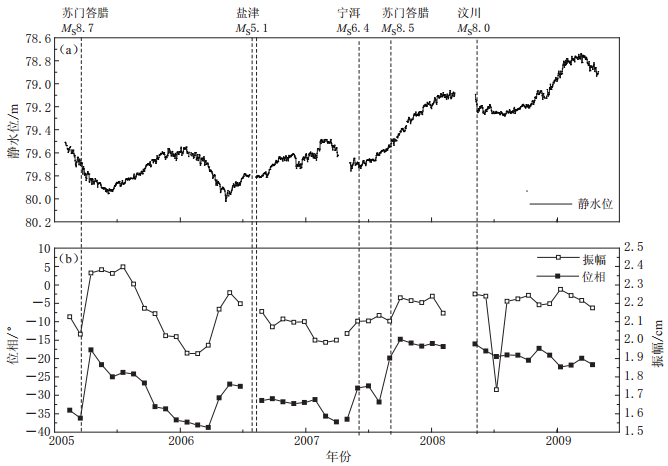
摘要: 将多孔介质中井-含水层-隔水层的潮汐水位振幅和位相的计算公式推广到裂隙饱水岩体潮汐分析中, 分析了裂隙含水层中井与裂隙, 裂隙与微裂隙的潮汐孔压响应原理和水流交换过程, 提取了影响裂隙含水层潮汐水位振幅和位相的主要因素, 应用井-裂隙排水产生的井水位-引潮高的振幅比A和位相差α2主要随径向等效导水系数T同向变化, 裂隙和微裂隙(孔隙)排水产生的孔压-引潮高的振幅比D和位相差α1主要随不排水条件下微裂隙与裂隙间振幅比E'/E反向变化的规律, 提出了潮汐井水位振幅和位相的8种不同变化类型, 分析了不同类型所反映的含水层形变, 并用于分析东川、 弥勒和西昌川03等3口井井水位振幅和位相变化的成因.Abstract: The theory of the amplitude and phase shift of tidal well water-level variation in well-aquifer-aquiclude system (WAAS) is introduced to study hydraulic flow among the well, fractures and micro-fractures (porosity) in the well-fracture-micro-crack fracture (porosity) system (WFMS). While analyzing the tide induced pore pressure and the hydraulic flow process in WFMS, the main factors affecting amplitude and phase shift in WFMS were drawn up. The amplitude ratio A and phase α2 of the tide water-lever caused by hydraulic flow between the well and fractures vary with the same tendency as equivalent transmissivity (T). The amplitude ratio D and phase α1 of tidal water-lever caused by hydraulic flow between fracture and micro-crack (porosity) vary in opposite trend with the tidal amplitude ratio (E'/E) between fracture and micro-crack under undrained condition. An analysis table on aquifer deformation is listed in this paper according to the changes of well water level, tidal amplitude and phase ratio. And is used to analyze abnormal causes of water level changes in Dongchuan, Mile and Xichangchuan 03 three wells.
-
Keywords:
- tide /
- phase /
- amplitude /
- fracture /
- aquifer-zone
-
-
表 1 潮汐井水位振幅和位相的变化形态、因及所反映的裂隙含水层形变
Table 1 hanges of phase shift and amplitude of tide water-level,causes and deformation of aquifer zone

-
刘春平, 唐彦东, 廖欣, 万飞, 石云. 2011a. 线弹性含水层井水位、 孔压对引潮位响应的研究及其应用[J]. 地震地质, 33(1): 133-140. 刘春平, 唐彦东, 廖欣. 2011b. 垂向和径向排水的潮汐水位振幅和位相变化研究[J]. 地震, 31(4): 68-76. 刘春平, 石云, 万飞. 2011c. 不排水条件下裂隙流体压力对引潮高的振幅比和位相差的响应[J]. 中国地震, 27(3): 300-308. Biot M A. 1962. Mechanics of deformation and acoustic propagation in porous media[J]. J Appl Phys, 33(4): 1482-1498.
Bower D R. 1983. Bedrock fracture parameters from the interpretation of well tides [J]. J Geophys Res, 88(B6): 5025-5035.
Bredehoeft J D. 1967. Response of well-aquifer systems to earth tides[J]. J Geophys Res, 72(12): 3075-3087.
Burbey T J. 2010. Fracture characterization using earth tide analysis[J]. J Hydrol, 380(3-4): 237-246.
Elkhoury J E, Brodsky E E, Agnew D C. 2006. Seismic waves increase permeability[J]. Nature, 441(7097): 1135-1138.
Hanson J M, Owen L B. 1982. Fracture orientation analysis by the solid earth tidal strain method[C]//The 57th Annual Fall Technical Conference and Exhibition of the Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME. Louisiana: New Orleans: 26-29.
Hsieh P A, Bredehoeft J D, Farr J M. 1987. Determination of aquifer transmissivity from earth tide analysis[J]. Water Resour Res, 23(10): 1824-1832.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王秀娟,周璇. 江苏睢宁苏02、03井水位异常变化机理探讨. 四川地震. 2023(03): 31-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王俊,何康,李军辉,陈德兴. 定远皖04井水位映震特征分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(S1): 283-285 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王俊,刘耀炜,孙小龙,方震,黎哲君,陶媛. 苏皖交界北部井水位群体性异常综合分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2021(S1): 93-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孙小龙,向阳,李源. 深井水位对地震波、固体潮和气压的水力响应——以范县井为例. 地震学报. 2020(06): 719-731 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 钱建秀,刘春平,樊春燕,石云,廖欣. 地震前后井-含水层系统潮汐参数变化特征分析——以云南弥勒井为例. 中国地震. 2019(01): 169-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王俊,周振贵,李军辉,何康,郑海刚,王雪莹. 安庆皖23井水位破年变异常浅析. 高原地震. 2019(S1): 46-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 唐彦东,刘春平,廖欣,石云,万飞. 小江断裂带中段和南段井水位变化与形变分析. 地震地质. 2013(03): 553-564 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 唐彦东,刘春平,石云,廖欣,万飞. 滇中、滇南部分井水位下降的构造作用因素分析. 地震研究. 2013(04): 443-449+553 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: