Location of the Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake sequence of Guangdong and 3D P-wave velocity structure in and around source region
-
摘要: 利用震源位置和速度结构的联合反演, 得到2012年2月16日广东东源MS4.8地震序列的震源位置及震源区速度结构模型, 并进一步采用双差定位法对该序列位置重新定位. 结果显示, 东源MS4.8地震是一次自上而下、 自西向东的单侧破裂过程, 破裂面积约3 km×5 km. 震源区地壳结构复杂, 埋深712 km处为一个速度达6.2 km/s的高速体, 主震的起始破裂位置位于高速体的顶部速度梯度较大的区域, 破裂面穿越整个高速体, 余震止于高速体下方的低速区底部(埋深约16 km). 东源县锡场镇下方的这种高、 低速相间的结构, 表明地壳层间相邻物质性状的差异利于应变能的积累和释放, 因此东源地区具备发生中强地震的构造条件.Abstract: In this paper, we determined the location of Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake sequence on 16 February 2012 and velocity structure of the source region using a simultaneous inversion method. On this basis we relocated the earthquake sequence using the double-difference location algorithm. The results show that the Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake fits a unilateral fracture model, and ruptured down and westward, with a rupture area of 3 km×5 km. A high velocity zone (HVZ) is at the depth of 712 km, with the velocity 6.2 km/s. The source rupture started from the top of the HVZ, where the velocity shows a large gradient. The ruptured area cuts across HVZ. All aftershocks are not beyond the lower bound, at 16 km, of low velocity zone, which is located below the HVZ. Such a structure of high velocity alternating with low velocity is propitious for strain energy accumulation and release. So Dongyuan region has a crust structure favourable to moderate earthquake occurrence.
-
引言
2012年2月16日广东省新丰江水库库区西北缘东源县锡场镇发生了MS4.8地震,距1962年新丰江水库MS6.1地震震中约30 km. 以往对新丰江地区的研究主要集中在水库大坝区,即MS6.1地震的震中附近(王妙月等,1976; 陈益明,1982; 丁原章等,1983; 丁原章1989; 魏柏林,陈庞龙,1991; 郭贵安等,2004; 官幼雄等,2005),东源MS4.8地震在库区边缘,且历史上无大震记录,对于这一地区的地壳速度结构、 构造条件等研究甚少. 以往针对新丰江地区速度结构的研究(郭贵安,冯锐,1992)受制于计算机技术的发展,仅以一维速度模型进行反演,精度低且不包括东源地区. 东源MS4.8地震发生后,震中附近已有成熟的数字地震台网,对序列的记录较为完整,为开展东源地区的速度结构研究提供了基础资料.
在现有条件下,采用高精度地壳速度模型是提高定位精度最有效的方法之一. 随着地震层析成像技术的发展(Aki,Lee,1976; Thurber,1983; 刘福田等,1989; Zhao et al,1992),三维地壳速度结构模型的建立为地震定位提供了研究基础. 在地震层析成像过程中加入震源项,进行震源和速度结构的联合反演(Crosson,1976; Pavlis,Booker,1980; Spencer,Gubbins,1980; 刘福田,1984; Michael,1988; Kissling et al,1994; 周龙泉等,2006),可在提高定位精度的同时得到速度结构. 该方法已经成功应用于诸多地震序列的研究中(刘福田等,1986; 潘素珍等,2007; 周龙泉等, 2007,2009; 马宏生等,2008). 本文采用震源位置和速度结构方法获取东源MS4.8地震震源区速度结构,在得到序列的震源位置后,进一步利用双差定位法对该序列进行重新定位; 并结合震源机制结果讨论该序列的空间分布特征及破裂过程,为今后东源地区乃至整个新丰江地区的震情研判提供深部结构的参考依据.
1. 方法原理
震源位置和速度结构联合反演的基本原理在众多文献中已有详细介绍(刘福田,1984; 周龙泉等,2009; 马宏生等,2008),本文仅作如下简要说明. 在震源位置和速度结构的联合反演过程中,走时残差δt是由于震源参数的扰动和速度的扰动引起的,对于l次地震和j个台站,可写成如下的紧凑形式:

式中,δt是m维走时残差向量,δv是n维节点速度扰动向量,δx是4l维震源参数扰动向量,A是m×n维走时对速度的偏导数矩阵,B是m×4l维走时对震源参数的偏导数矩阵.
由于式(1)中速度参数和震源参数是相互耦合的. 若在同一个方程中同时反演两种不同量纲的参数,将会增加算法的数值不稳定性,消耗大量的计算机资源,因此须进行参数分离. 本文采用刘福田(1984)提出的正交投影算子,将式(1)分解为以下两个分别求解速度参数和震源参数的方程组:


式中,PB为与震源参数有关的从Rm 到B的像空间R(B)上的正交投影算子. 速度参数和震源参数解耦后的分析表明,速度扰动量的确定与震源位置扰动量无直接关系,仅与它的初值有关,而震源位置扰动量则与速度扰动量明显有关. 根据式(2)和式(3),联合反演过程中先确定研究区的速度结构参数,再确定震源参数,从而消除了速度结构的不确定性对定位精度的影响. 因此,通过震源位置和速度结构的联合反演可以有效提高地震定位的精度,并在反演中得到该研究区的速度结构模型.
研究中采用的双差定位法已在众多文献中有详细论述(Waldhauser,Ellaworth,2000; 杨智娴等,2003; Wolfe,2003; 杨智娴,陈运泰,2004; Menke,Schaff,2004; 王新岭等,2005; 张天中等,2007; 黄媛等,2008),本文不再赘述.
2. 地震资料整理和初始速度模型
2.1 地震资料整理
2012年2月16日东源MS4.8地震发生后,8月31日新丰江水库大坝附近又发生MS4.0地震,两次地震后广东省地震局立即布设了现场流动数字地震台,加上新丰江地区原有的数字地震台网,地震序列记录较为完整,ML≥1.0的地震基本不会遗漏.
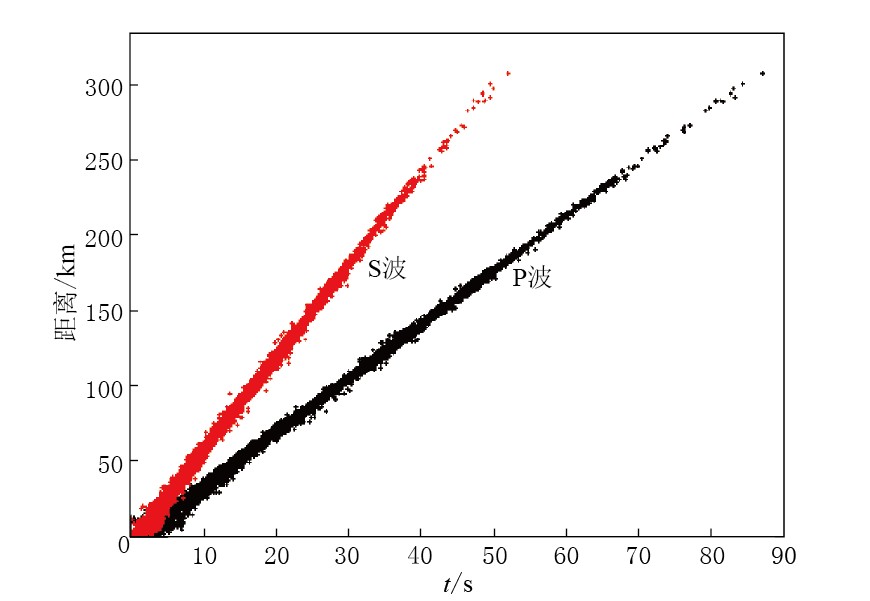
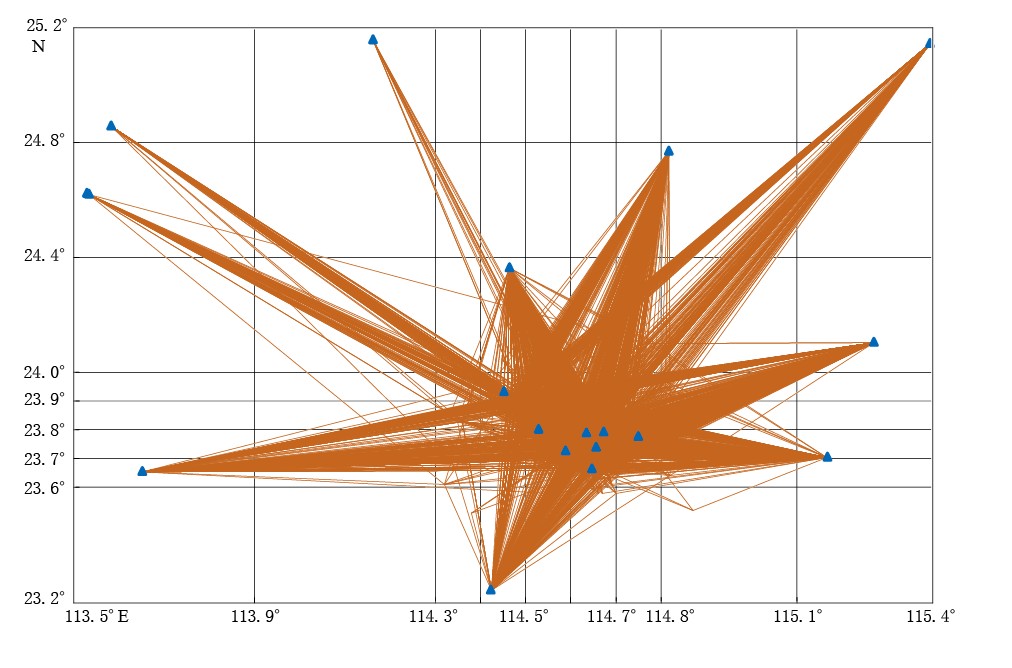
考虑到整个序列地震数量不多,为提高反演精度,进行速度结构反演时扩大了研究时段及研究范围(23.2°—25.2°N,113.5°—115.4°E,图 1). 广东省“十五”期间建设的数字地震台网自2007年6月开始运行,本文使用了2007年6月—2012年10月共计6750次地震的36547条P波走时记录作为基本数据集进行速度结构的反演(图 2). 地震与台站射线分布图(图 3)显示,研究区内只有新丰江地区(23.6°—24.0°N,114.3°—114.8°E)射线密度较高,为此进行速度结构反演时不能等间距进行网格划分,而需根据射线密度进行适当调整,射线密集的区域按0.1°×0.1°划分,其余地区按0.4°×0.4°划分(图 3).
2.2 初始速度模型
进行反演计算前,笔者查阅了相关文献玉兰等. 1988. 华南地区走时表.(江西省地质矿产局,1984; 姚伯初等,1994; 郑圻森等, 2003,2004; 赵明辉等,2004; 闻则刚等,2005; 徐辉龙等,2006),得到了研究区域地壳各深度上的S波速度及部分深度上的P波速度,对于未能查找到部分深度上的P波速度使用插值法,最终确定了研究区地壳速度结构模型(表 1).
表 1 本文使用的初始地壳速度模型Table 1. Initial crustal velocity model in this study深度/km S波速度 /km · s -1 P波速度 /km · s -1 纵横波速比 深度/km S波速度 /km · s -1 P波速度 /km · s -1 纵横波速比 0 3.25 4.92 1.51 20 3.67 6.40 1.74 5 3.48 5.50 * 1.58 * 25 3.73 6.50 1.74 10 3.65 5.80 1.59 31 3.92 6.82 1.74 15 3.66 5.98 1.63 40 4.58 7.98 1.74 注: 带*为插值法估算的地壳速度数据, 其它为汇总相关文献得到的地壳速度数据. 2.3 分辨率分析
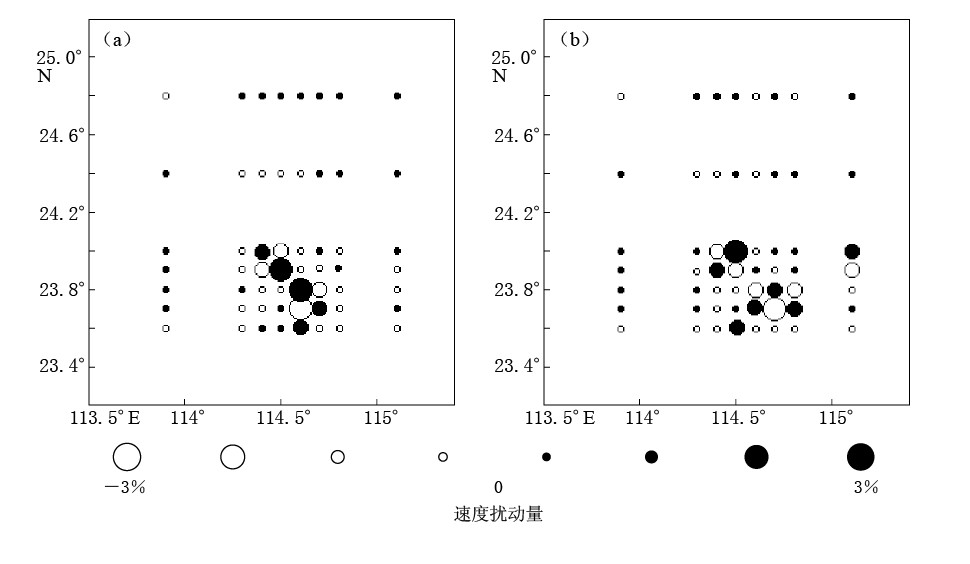
本文采用检测板方法来估算解的分辨率和可靠性. 根据实际射线分布,通过正演计算得到理论走时数据,将理论走时数据加上一定随机误差(本文采用的扰动值取正常值±3%)后作为观察数据进行反演,比较反演结果与检测板的相似程度,作为解的可靠性估计. 结果表明(图 4),从新丰江水库大坝至东源县锡场镇北西向区域,由于地震和台站密度较高,在上地壳5和10 km深度解的分辨率符合预期,其它地区检测板结果不理想.
3. 地震序列定位结果
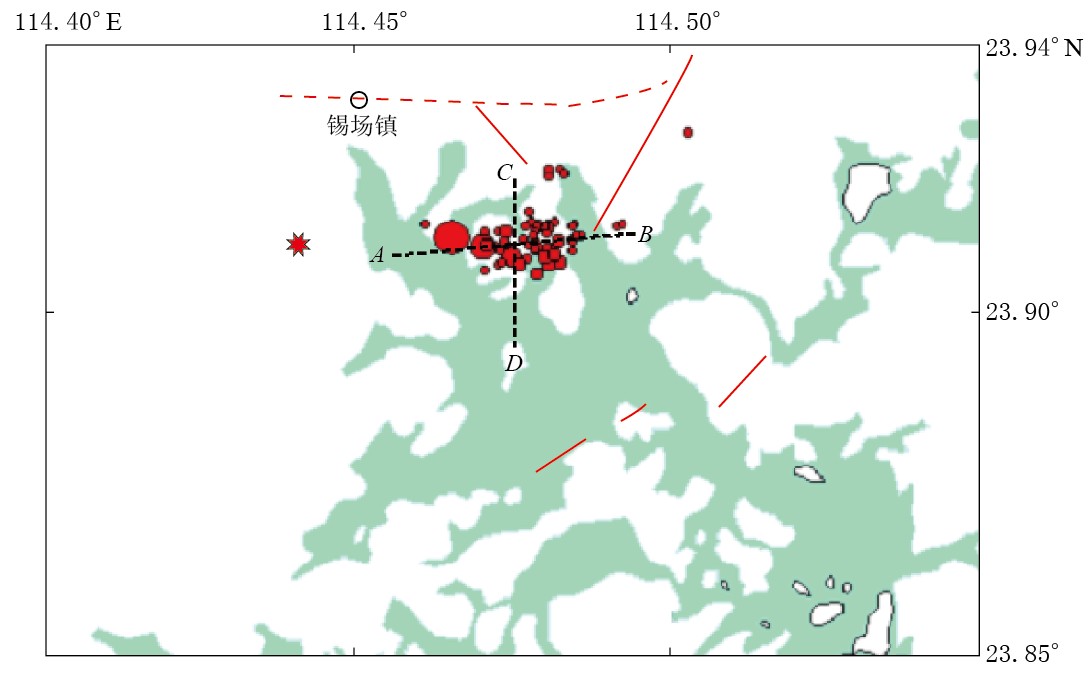
为了避免常规地震定位方法使用一维速度模型定位可能带来较大的初始模型误差,本文参考了吴建平等(2009)的方法,采用联合反演得到的地震定位结果作为初始位置,在此基础上再采用双差定位法对地震序列进行高精度定位. 结果显示(图 5、 表 2),此序列空间分布呈北东东向展布,余震主要分布在主震的东侧,是一个单侧破裂的过程.
![]() 图 5 东源MS4.8地震序列重新定位后的震中分布图Figure 5. Distribution of the relocated Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake sequence The star stands for macroseismic epicenter, circles for microseismic epicenters (ML≥1.0) during February 16 through March 31, 2012. AB and CD stand for NS-trending profile and ENE-WSW-trending profile, respectively表 2 东源MS4.8地震震中位置Table 2. Epicentral location of the Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake
图 5 东源MS4.8地震序列重新定位后的震中分布图Figure 5. Distribution of the relocated Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake sequence The star stands for macroseismic epicenter, circles for microseismic epicenters (ML≥1.0) during February 16 through March 31, 2012. AB and CD stand for NS-trending profile and ENE-WSW-trending profile, respectively表 2 东源MS4.8地震震中位置Table 2. Epicentral location of the Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake震中类型 定位方法 纬度/°N 经度/°E 震源深度/km 微观震中 震源位置和速度联合反演后再采用双差定位 23.911 1 114.465 3 6.8 宏观震中 现场调查 23.909 114.435 东源MS4.8地震发生后半小时,广东省地震局派出了现场工作组赴地震现场进行宏观调查. 工作组实地调查了11个村镇,电话落实了8个村镇的震害及人、 物反应情况,根据现场调查情况确定宏观震中位于东源县锡场镇西南约3 km处(图 5、 表 2)(钟贻军等,2012). 重新定位确定的微观震中位于现场调查确定的宏观震中东侧,两者距离约2.5 km. 这种差异可能是由于宏观震中东侧为水域,无法进行宏观调查,宏观震中有可能偏西.
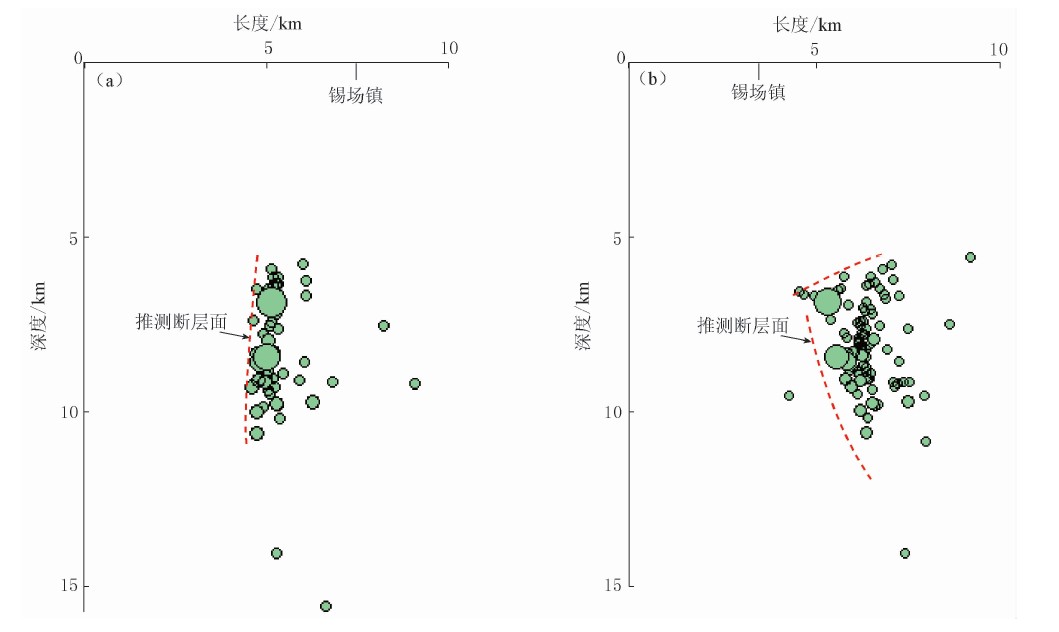
分别沿北东东向(AB)、 南北向(CD)(图 5)作剖面图可见,主震位于该地震序列的上方,余震震源深度较主震深,余震分布在主震的东侧下方,余震展布区域约3 km×5 km(图 6).
4. 震源区速度结构特征
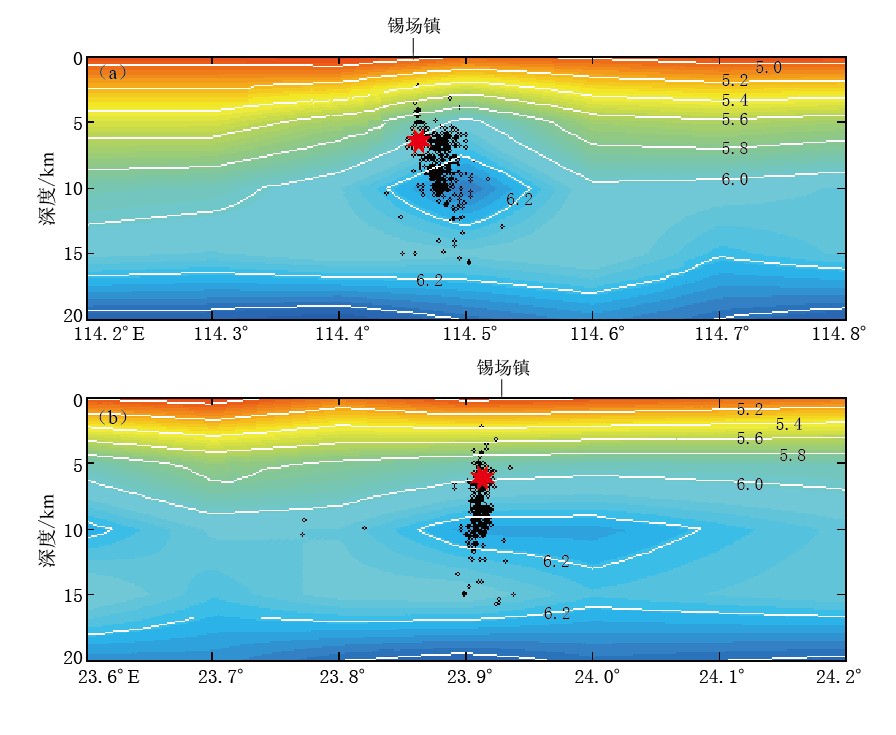
图 7分别给出了沿东西向和南北向的P波速度剖面图. 锡场镇下方的震源区地壳结构较为复杂,在3—12 km处有一相对高速区,主震及余震主要集中在高低速交界带的低速区(5—10 km)一侧. 再往下,13—17 km为相对低速区,余震的分布截止于低速区的底部,余震最大深度不超过16 km.
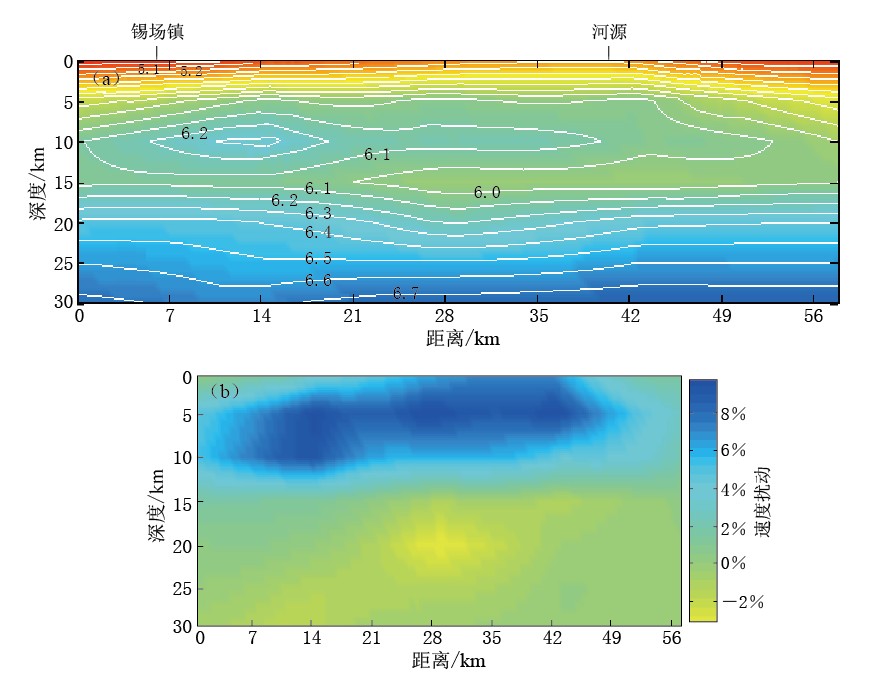
在得到序列重新定位结果后,为了更清晰反映0—20 km发震层间的速度结构,笔者缩小研究区域重新对新丰江地区进行速度结构反演. 反演范围为23.2°—24.4°N、 114.4°—114.8°E,水平向网格0.03°—0.05°,垂直向网格3—4 km. 从反演结果看(图 8),深度约3 km开始从河源往北西向一直延伸到东源县锡场镇(图 8虚线框内),为一高速区域; 深度达到7 km后,高速区域的东南端(河源附近)逐渐消失,西北端(东源县锡场镇附近)依然存在; 深度达到10 km后高速体逐渐消失. 高速体往深部的延伸在西北端要深于东南端.
![]() 图 8 新丰江地区不同深度P波速度水平面分布图(a, b, c)及检测板结果(d, e, f)图a, b, c中虚线椭圆表示高速区; 图b中星号表示东源MS4.8地震Figure 8. P-wave velocity distribution (a, b, c) and checkboard resolution tests (d, e, f) in Xinfengjiang area Dashed ellipse represents high velocity zone (HVZ) in Figs.8a, b, c, and the star represents Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake in Fig.8b
图 8 新丰江地区不同深度P波速度水平面分布图(a, b, c)及检测板结果(d, e, f)图a, b, c中虚线椭圆表示高速区; 图b中星号表示东源MS4.8地震Figure 8. P-wave velocity distribution (a, b, c) and checkboard resolution tests (d, e, f) in Xinfengjiang area Dashed ellipse represents high velocity zone (HVZ) in Figs.8a, b, c, and the star represents Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake in Fig.8b5. 讨论与结论
1)重新定位后结果显示,东源MS4.8地震序列呈北东东向展布,且主震位于序列西侧顶部. 震源机制结果表明http://www.gdsin.net/dizhenzt/dzztxw.asp?id=674. 查阅日期:[2012-09-20].,东源MS4.8地震为走滑兼少量正断倾滑分量的错动,表现为北西向挤压和北东向拉张,与区域构造应力场方向相一致(魏柏林等,2000). 节面Ⅰ走向北北西,节面Ⅱ走向北东东. 其中节面Ⅱ走向82.5°,倾角65.9°,与序列空间分布特征基本一致. 据此可以推断MS4.8主震是一次自上而下、 自西向东的单侧破裂过程,从余震空间分布范围估算该震源破裂尺度约3 km×5 km.
东源MS4.8地震的起始破裂位于高速体的顶部速度梯度较大的区域,破裂面穿越了整个高速体,余震截止于高速体之下的低速区的底部(约16 km). 东源MS4.8地震虽然震源较浅(6.8 km),但与同等量级的地震相比,地表灾害较轻(钟贻军等,2012),这与地震序列空间分布揭示的东源MS4.8地震是一次自上而下的破裂过程是相符合的.
2)杨卓欣等(2011)利用主动源深地震探测获得了沿英德—河源—陆河剖面(北西—南东)速度结构,显示在河源—东源间存在一个相对高速体,速度达6.1 km/s. 河源这一端深度为3.5—8.5 km,东源县锡场镇一端略深,深度延伸至10 km左右. 在22—28 km埋深处存在一相对低速体,速度为6.4 km/s. 本文采用天然地震反演得到的结果与杨卓欣等(2011)结果基本一致. 东源县锡场镇下方约5 km开始出现6 km/s的高速体,埋深7 km处速度达6.2 km/s,高速体底部止于12 km深处(图 7a、 图 9a); 河源一端的高速体埋深略浅,速度略低. 对20 km以下的下地壳反演效果不如主动震源得到的结果理想,仅从速度扰动图(图 9b)能看到在深度为18—30 km间存在相对低速区域. 由于本文反演的数据是Pg震相的记录,且新丰江地区震源较浅,因而对上地壳反演结果要好于下地壳.
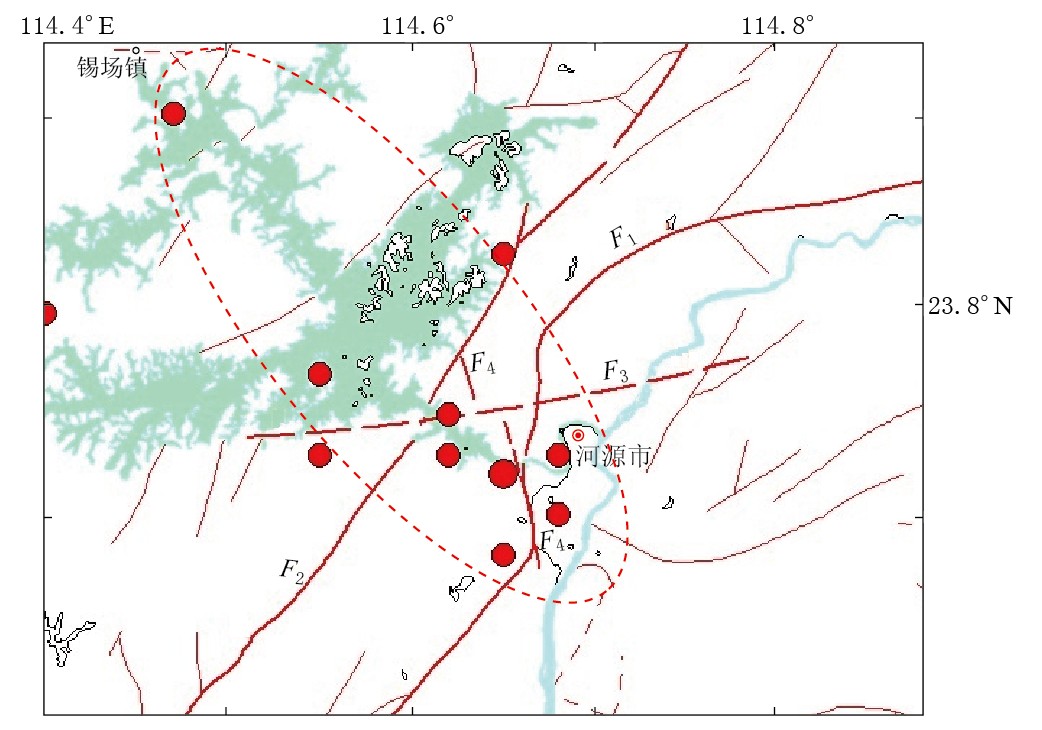
3)新丰江1962年MS6.1地震以及大部分ML≥5.0地震位于高速体的东南端,东源MS4.8地震位于高速体的西北端. 1960年5月至今新丰江地区ML≥5.0地震主要分布区域从新丰江水库大坝往西北方向延伸到东源县锡场镇附近,与高速体在地面的投影位置(图 10虚线框)基本吻合. 从1959年10月新丰江水库建成蓄水开始,新丰江大坝区域开始出现密集有感地震活动(丁原章,1989). 虽然1962年新丰江MS6.1地震的发生与水库建成蓄水存在一定的关系,但其构造条件是强震发生的物理基础,水库蓄水只是外部诱发因素.
![]() 图 10 新丰江地区地震震中分布图(1960-05—2012-10, ML≥5.0)F1: 河源—绍武断裂; F2: 人字石断裂; F3: 南山—坳头断裂; F4: 石角—新港—白田断裂Figure 10. Distribution of earthquakes (ML≥5.0) in Xinfengjiang area during May of 1960 through October of 2012 F1: Heyuan-Shaowu fault; F2: Renzishi fault; F3: Nanshan-Aotou fault; F4: Shijiao-Xingang-Baitian fault
图 10 新丰江地区地震震中分布图(1960-05—2012-10, ML≥5.0)F1: 河源—绍武断裂; F2: 人字石断裂; F3: 南山—坳头断裂; F4: 石角—新港—白田断裂Figure 10. Distribution of earthquakes (ML≥5.0) in Xinfengjiang area during May of 1960 through October of 2012 F1: Heyuan-Shaowu fault; F2: Renzishi fault; F3: Nanshan-Aotou fault; F4: Shijiao-Xingang-Baitian fault4)速度模型反演结果显示,新丰江地区速度结构复杂,埋深5—12 km处存在一高速体,速度达6.1 km/s. 高速体河源一端1962年发生了新丰江MS6.1水库地震,东源县锡场镇一端高速体速度更高,最大达6.2 km/s. 锡场镇下方的这种高、 低速多层相间的结构显示了地壳层间相邻物质性状的差异,这种差异导致层间滑动,有利于应变能的积累和释放,地震多发于这种速度梯度大的区域(刘福田等,1986). 因此,东源地区具备发生中强地震的构造条件.
中国地震台网中心周龙泉博士为本研究提供速度结构和震源位置联合反演计算程序,广东省地震监测中心提供高质量的震相报告,审稿专家为本文提出了宝贵修改意见,在此一并表示感谢.
-
图 5 东源MS4.8地震序列重新定位后的震中分布图
Figure 5. Distribution of the relocated Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake sequence The star stands for macroseismic epicenter, circles for microseismic epicenters (ML≥1.0) during February 16 through March 31, 2012. AB and CD stand for NS-trending profile and ENE-WSW-trending profile, respectively
图 8 新丰江地区不同深度P波速度水平面分布图(a, b, c)及检测板结果(d, e, f)图a, b, c中虚线椭圆表示高速区; 图b中星号表示东源MS4.8地震
Figure 8. P-wave velocity distribution (a, b, c) and checkboard resolution tests (d, e, f) in Xinfengjiang area Dashed ellipse represents high velocity zone (HVZ) in Figs.8a, b, c, and the star represents Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake in Fig.8b
图 10 新丰江地区地震震中分布图(1960-05—2012-10, ML≥5.0)F1: 河源—绍武断裂; F2: 人字石断裂; F3: 南山—坳头断裂; F4: 石角—新港—白田断裂
Figure 10. Distribution of earthquakes (ML≥5.0) in Xinfengjiang area during May of 1960 through October of 2012 F1: Heyuan-Shaowu fault; F2: Renzishi fault; F3: Nanshan-Aotou fault; F4: Shijiao-Xingang-Baitian fault
表 1 本文使用的初始地壳速度模型
Table 1 Initial crustal velocity model in this study
深度/km S波速度 /km · s -1 P波速度 /km · s -1 纵横波速比 深度/km S波速度 /km · s -1 P波速度 /km · s -1 纵横波速比 0 3.25 4.92 1.51 20 3.67 6.40 1.74 5 3.48 5.50 * 1.58 * 25 3.73 6.50 1.74 10 3.65 5.80 1.59 31 3.92 6.82 1.74 15 3.66 5.98 1.63 40 4.58 7.98 1.74 注: 带*为插值法估算的地壳速度数据, 其它为汇总相关文献得到的地壳速度数据. 表 2 东源MS4.8地震震中位置
Table 2 Epicentral location of the Dongyuan MS4.8 earthquake
震中类型 定位方法 纬度/°N 经度/°E 震源深度/km 微观震中 震源位置和速度联合反演后再采用双差定位 23.911 1 114.465 3 6.8 宏观震中 现场调查 23.909 114.435 -
陈益明. 1982. 新丰江水库地震及其小震震源机制的研究[J]. 华南地震, 2 (3): 64-71. 丁原章. 1989. 水库诱发地震[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 42-51. 丁原章, 潘健雄, 肖安予, 沈立英, 马汉雄, 繆维城. 1983. 新丰江水库诱发地震的构造条件[J]. 地震地质, 5 (3): 61-74. 官幼雄, 李亚林, 颜玉定. 2005. 1962年3月19日新丰江6.1级水库诱发地震时的构造应力[J]. 华南地震, 25 (3): 83 - 86. 郭贵安, 冯锐. 1992. 新丰江水库三维速度结构和震源参数的联合反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 35 (3): 331-342. 郭贵安, 刘特培, 秦乃岗, 陈丽芬. 2004. 新丰江水库1961-1999年小震综合机制解结果分析[J]. 地震学报, 26 (3): 261-268. 黄媛, 吴建平, 张天中, 张东宁. 2008. 汶川8.0级大地震及其余震序列重新定位研究[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 38 (10): 1242-1249. 江西省地质矿产局. 1984. 江西省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 703. 刘福田. 1984. 震源位置和速度结构的联合反演(Ⅰ): 理论和方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 27 (2): 167-175. 刘福田, 李强, 吴华, 胡戈, 刘建华. 1989. 用于速度图像重建的层析成像法[J]. 地球物理学报, 32 (1): 46-61. 刘福田, 曲克信, 吴华, 李强, 刘建华, 胡戈. 1986. 华北地区的地震层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 29 (5): 442-449. 马宏生, 张国民, 周龙泉, 刘杰, 邵志刚, 夏红. 2008. 川滇地区中小震重新定位与速度结构的联合反演研究[J]. 地震, 28 (2): 29-38. 潘素珍, 张先康, 杨卓欣, 张成科, 赵金仁, 王帅军, 段玉玲. 2007. 伽师强震群区上地壳三维速度层析成像: 人工爆破和天然地震的联合反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 50 (5): 1456-1463. 王妙月, 杨懋源, 胡毓良, 李自强, 杨真荣, 王大均, 罗学海. 1976. 新丰江水库地震的震源机制及其成因初步讨论[J]. 地球物理学报, 19 (1): 1-17. 王新岭, 刘杰, 张国民, 赵翠萍. 2005. 姚安地震序列与永胜地震序列的高精度定位[J]. 中国地震, 21 (3): 386-397. 魏柏林, 陈庞龙. 1991. 新丰江地震震源机制解及构造应力场[J]. 地震学报, 13 (4): 462-470. 魏柏林, 陈仁发, 黄日恒. 2000. 广东省地震构造概论[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 161-183. 闻则刚, 杨马陵, 叶秀薇, 康英, 王正尚. 2005. 广东省东部地区的S波速度结构[J]. 西北地震学报, 27 (2): 154-157. 吴建平, 黄媛, 张天中, 明跃红, 房立华. 2009. 汶川MS8.0级地震余震分布及周边区域P波三维速度结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52 (2): 320-328. 徐辉龙, 丘学林, 赵明辉, 孙金龙, 朱俊江. 2006. 南海东北部南澳大地震(M=7.5)震中区的地壳结构特征与震源构造[J]. 科学通报, 51 (增刊Ⅱ): 83-91. 杨智娴, 陈运泰. 2004. 用双差地震定位法再次精确测定1998年张北-尚义地震序列的震源参数[J]. 地震学报, 26 (2): 115-120. 杨智娴, 陈运泰, 郑月军, 于湘伟. 2003. 双差地震定位法在我国中西部地区地震精确定位中的应用[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 33 (增刊): 129-134. 杨卓欣, 刘宝峰, 王勤彩, 王洪体, 原世豪. 2011. 新丰江库区二维P波速度结构: 英德-河源-陆河深地震测深剖面探测结果[J]. 地球物理学进展, 26 (6): 1968-1975. 姚伯初, 曾维军, Hayes D E, Spangler S. 1994. 中美合作调研南海地质专报GMSCS[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社: 75-88. 张天中, 武巴特尔, 黄媛, 蒋长胜. 2007. 近台资料对近震相对定位算法的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 50 (4): 1123-1130. 赵明辉, 丘学林, 叶春明, 夏戡原, 黄慈流, 谢剑波, 王平. 2004. 南海东北部海陆深地震联测与滨海断裂带两侧地壳结构分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 47 (5): 845-852. 郑圻森, 朱介寿, 曹家敏, 蔡学林. 2004. 华南地区岩石圈地壳速度结构数据处理[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 26 (2): 97-100. 郑圻森, 朱介寿, 宣瑞卿, 蔡学林. 2003. 华南地区地壳速度结构分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 23 (12): 9-13. 钟贻军, 陈庞龙, 王维亮, 叶秀薇. 2012. 2012年2月16日东源县4.8级地震[J]. 华南地震, 32 (2): 9-19. 周龙泉, 刘福田, 陈晓非. 2006. 三维介质中速度结构和界面的联合成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 49 (4): 1062-1067. 周龙泉, 刘杰, 张晓东. 2007. 2003年大姚6.2和6.1级地震前三维波速结构的演化[J]. 地震学报, 29 (1): 20-30. 周龙泉, 刘杰, 马宏生, 周俊杰. 2009. 2003年大姚 6.2级、 6.1级地震序列震源位置及震源区速度结构的联合反演[J]. 地震, 29 (2): 12-24. Aki K, Lee W H K. 1976. Determination of three-dimensional velocity anomalies under a seismic array using P arrival times from local earthquakes. 1. A homogeneous initial model[J]. J Geophys Res, 81 : 4381-4399.
Crosson R S. 1976. Crustal structure modeling of earthquake data: 1. Simultaneous least squares estimation of hypocenter and velocity parameters[J]. J Geophys Res, 81 : 3036-3046.
Kissling E, Ellsworth W L, Eberhard-Phillips D, Kradolfer U. 1994. Initial reference models in local earthquake tomography[J]. J Geophys Res, 99 : 19635-19646.
Menke W, Schaff D. 2004. Absolute earthquake location with differential data[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 94 : 2254-2264.
Michael A J. 1988. Effects of three-dimensional velocity structure on the seismicity of the 1984 Morgan Hill, California, aftershock sequence[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 78 : 1199-1221.
Pavlis L G, Booker J R. 1980. The mixed discrete-continuous inverse problem: application to the simultaneous determination of earthquake hypocenters and velocity structure [J]. J Geophys Res, 85 : 4801- 4810.
Spencer C, Gubbins D. 1980. Travel time inversion for simultaneous earthquake location and velocity structure determination in laterally varying media[J]. Geophys J R astr Soc, 63 (1): 95-116.
Thurber C H. 1983. Earthquake locations and three-dimensional crustal structure in the Coyote Late area, Central California[J]. J Geophys Res, 88 : 8226-8236.
Waldhauser F, Ellaworth W L. 2000. A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: Method and application to the Northern Hayward fault, California[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 90 (6): 1353-1368.
Wolfe C J. 2003. On the mathematics of using difference operations to relocate earthquakes[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 93 : 1875-1889.
Zhao D, Hasegawa A, Horiuchi S. 1992. Tomographic imaging of P and S wave velocity structure beneath northeastern Japan[J]. J Geophys Res, 97 : 19909-19928.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. Peng Zhang,Xinlei Sun,Yandi Zeng,Zhuo Xiao,Runqing Huang. South China Sea Typhoon Hagibis enhanced Xinfengjiang Reservoir seismicity. Earthquake Science. 2024(03): 210-223 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. Xing Yan,Zhihui Deng,Jiping Liu,Shishan Ye,Zhiqun Chen,Tianren Zhong. Numerical simulation of deep-hole resistivity anomaly caused by drilling construction in Xinfengjiang geoelectric station. Earthquake Research Advances. 2022(03): 25-36 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 王力伟,吴国瑞,黄柳芳. CAP方法反演新丰江锡场地区M_L4.0级以上地震震源机制解. 华南地震. 2018(03): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王力伟,黄柳芳,吴国瑞. 锡场地区5次M_L4.0级以上地震的静态库仑应力触发研究. 华南地震. 2018(S1): 18-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 叶东华,陈大庆,杨马陵,刘吉平. 2012年和2013年广东东源4.8和4.7级地震和异常特征. 华南地震. 2018(04): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. Ye Xiuwei,Huang Yuanmin,Liu Jiping. 3D P-wave Velocity Structure and Active Tectonics in the Xinfengjiang Area of Guangdong. Earthquake Research in China. 2017(04): 441-454 .  必应学术
必应学术
7. 叶秀薇,黄元敏,刘吉平. 新丰江地区地壳P波三维速度结构及活动构造研究. 中国地震. 2016(03): 465-476 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵小艳,孙楠. 2014年云南鲁甸6.5级地震震源位置及震源区速度结构联合反演. 地震研究. 2014(04): 523-531 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: