Responses of mud volcanoes in the North Tianshan to the 30 June 2012 Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthquake
-
摘要: 2012年6月30日新源-和静MS6.6地震前后, 北天山泥火山出现了喷溢和地球化学异常变化. 该地震前、 后4天内两次观测了北天山泥火山, 采集了两批温泉和泥火山气体样品, 测定了样品的气体组分和He、 Ne同位素及CH4、 CO2的碳同位素组成. 结果表明, 泥火山发生了同震喷发, 气体排放量增加, 温泉和泥火山气体出现了不同程度的微量气体浓度异常, 独山子泥火山震前出现了3He/4He高值异常. 研究结果有利于确定利用泥火山和温泉监测地震活动的方法和指标.Abstract: Eruption and geochemical anomalies of mud volcanoes in the North Tianshan were found before and after the 30 June 2012 Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthquake in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Xinjiang), northwestern China. The mud volcanoes in the Northern Tianshan were surveyed, and the gas samples from the hot springs and mud volcanoes were collected twice in four days before and after the earthquake. Concentrations of gaseous components and isotopic compositions of CH4, CO2 and He, Ne were measured. The data indicated that the mud volcanoes coseismically erupted, amount of gas emissions increased, and anomalies of trace gas concentrations appeared in the hot springs and mud volcanoes in different levels. High-value anomaly of 3He/4He in the Dushanzi mud volcano occurred before the earthquake. Results are favorable to selecting the indicators for monitoring seismic activities in the study area by using hot springs and mud volcanoes.
-
Keywords:
- mud volcanoes /
- earthquake /
- gas /
- isotope /
- Xinjiang
-
引言
地震和泥火山都与地球内部应力和热能作用直接关联. 在区域地应力和热的作用下,封闭在地体内的孔隙流体,当流体压力达到一定值时形成泥火山喷发; 泥火山具有平静、 喷发的准周期性活动特征. 同样,地球内部应力作用下,岩石内发生应力集中、 释放,导致地震的规律性发生. 因此,地震孕育和发生过程常伴有泥火山的异常活动(王道,2000; Kopf et al,2003; Yang et al,2006; Mellors et al,2007; 高小其等,2008; ,Rukavičková Hanžlžl,2008; Bonini,2009; Bonini,Mazzarini,2010; Rudolph,Manga,2010; Jiang et al,2011). 2004年9月5日纪伊半岛MW7.5地震引起日本海沟震中距80 km的泥火山涌出大量甲烷(Tsunogai et al,2012). 地震震级与震中距统计表明,地震能够触发泥火山喷发、 地下水喷涌、 间歇泉活动,在震级和震中距的图解中两参数的点都分散在一条斜率大于零的斜线下. 这表明这些现象可能存在相同的触发机制(Manga et al,2009). 在地震和火山发生前、 发生时和发生后一般会出现流体地球化学异常. 根据这些地球化学异常可以判断未来地震和火山活动(King,1986; Heinicke et al,2000; Yang et al, 2005,2006; Du et al,2008; Tsunogai et al,2012; Mazzini et al,2012). 此外,温泉和泥火山气体同位素地球化学异常也常用来研究地震和泥火山活动趋势(King,1986; Kopf et al,2003; Lavrushin et al,2009; Chao et al,2010; Rudolph et al,2011; Chaudhuri et al,2012).
新疆北天山的石河子—乌苏一带,不仅是泥火山集中分布的地区,而且也是中、 强地震活动频发的地区. 20世纪90年代该地区许多地震前后,均出现了泥火山异常喷溢,喷溢出大量高矿化度水、 泥浆和气体,气体主要成分是CH4、 N2和CO2(王道,2000; 高小其等,2008). 泥火山还原性气体的喷发,导致近地表岩石的蚀变褪色(Fu et al,2007),一些敏感性元素也记录了这种氧化还原反应(Zheng et al,2010a). 同位素和元素地球化学研究表明,烃类气体主要是来自石油伴生气,水主要来自大气降水(Nakada et al,2011; 戴金星等,2012),泥主要来自烃原岩(Nakada et al,2011; Zheng et al, 2010a,b).
2012年6月下旬我们在新疆北天山考察地震断层和泥火山. 6月26—28日采集泥火山流体样品后,6月30日5时7分发生了新源-和静MS6.6地震(43.4°N,84.8°E),7月1日和2日重复采集了泥火山的流体样品. 本文研究了该地震前后泥火山的喷溢和气体地球化学异常变化.
1. 地震地质概况
天山中段是指位于奎屯南的北天山与库车北的南天山间的广大地区,其构造位置是在塔里木古板块与哈萨克斯坦-准噶尔古板块之间,经受了中新生代强烈的陆内造山作用(图 1). 新生代在印度板块与欧亚大陆碰撞汇聚作用下,导致山体强烈隆升,造就了现今的南、 北天山及伊犁盆地、 巴音布鲁克盆地相间以及北天山山前坳陷(左国朝等,2008). 天山中段中部是纳伦—那拉提缝合带,发育了北西西和近东西向的活动断裂和活动褶皱,北天山的断层向南倾,南天山的断层向北倾. 在近南北向强烈挤压作用下,天山北麓发育了具有典型断裂扩展褶皱特征的依连哈比尔尕山山前推覆构造(汪一鹏,沈军,2000).
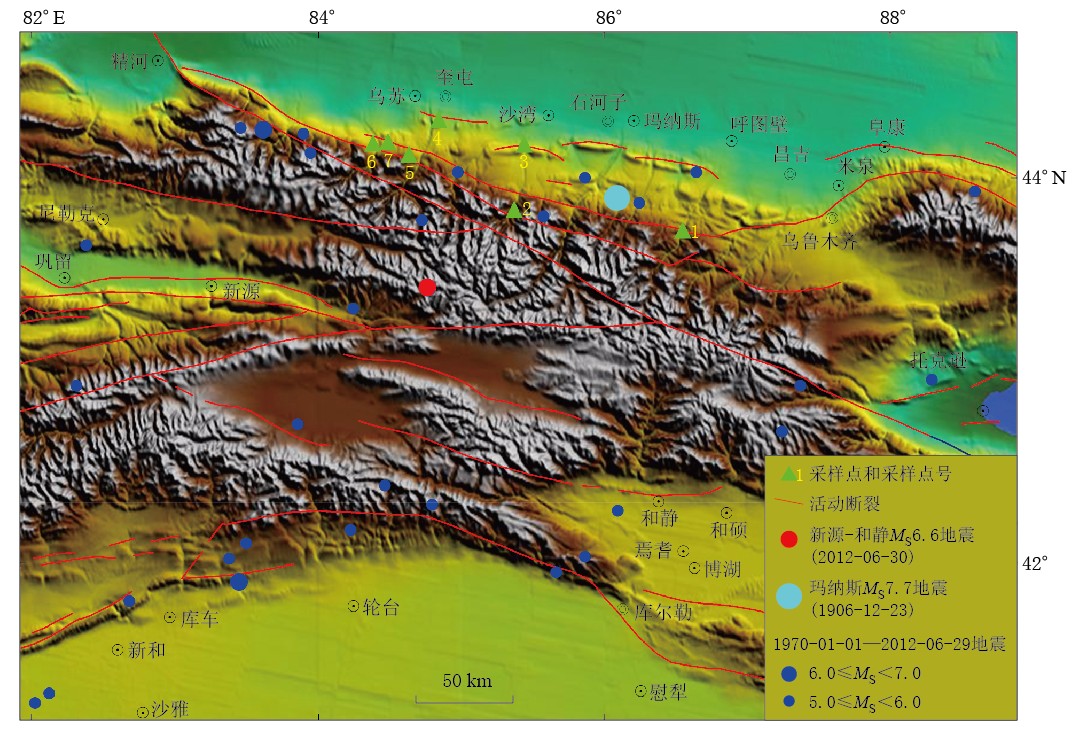
![]() 图 1 图1 天山中段活动断裂和采样点分布略图1. 新疆21号泉; 2. 新疆25号泉; 3. 安集海泥火山; 4. 独山子泥火山; 5. 阿拉山温泉; 6. 乌苏市白杨沟泥火山; 7. 乌苏市艾其沟泥火山Figure 1. Active faults and sampling sites in the middle segment of Tianshan1. Xinjiang spring No.21; 2. Xinjiang spring No.25; 3. Anjihai mud volcano; 4. Dushanzi mud volcano; 5. Alxa hot spring; 6. Baiyanggou mud volcano in Wusu city; 7. Aiqigou mud volcano in Wusu city
图 1 图1 天山中段活动断裂和采样点分布略图1. 新疆21号泉; 2. 新疆25号泉; 3. 安集海泥火山; 4. 独山子泥火山; 5. 阿拉山温泉; 6. 乌苏市白杨沟泥火山; 7. 乌苏市艾其沟泥火山Figure 1. Active faults and sampling sites in the middle segment of Tianshan1. Xinjiang spring No.21; 2. Xinjiang spring No.25; 3. Anjihai mud volcano; 4. Dushanzi mud volcano; 5. Alxa hot spring; 6. Baiyanggou mud volcano in Wusu city; 7. Aiqigou mud volcano in Wusu city天山中段是主要的陆内地震带之一,研究区内1970年以来发生5.0级以上的地震34次,多数分布在天山南北两侧. 1906年12月23日玛纳斯7 3/4 级地震是记录到的最大地震. 2012年6月30日新源-和静MS6.6地震发生在天山中部巴音布鲁克盆地西北附近(图 1).
新疆泥火山所处构造位置是准噶尔—北天山盆山过渡带. 该过渡带走向为北西西,东西延伸长度约350—400 km,南北宽度约50—80 km. 上新世—更新世早期持续的南北向区域挤压作用使准噶尔—北天山盆山过渡带中发生不同形式的构造变形,发育有大量不同尺度的断层和褶皱(漆家福等,2008). 泥火山分布区出露的主要地层有中朱罗—新近纪沉积碎屑岩和第四纪冲洪积物.
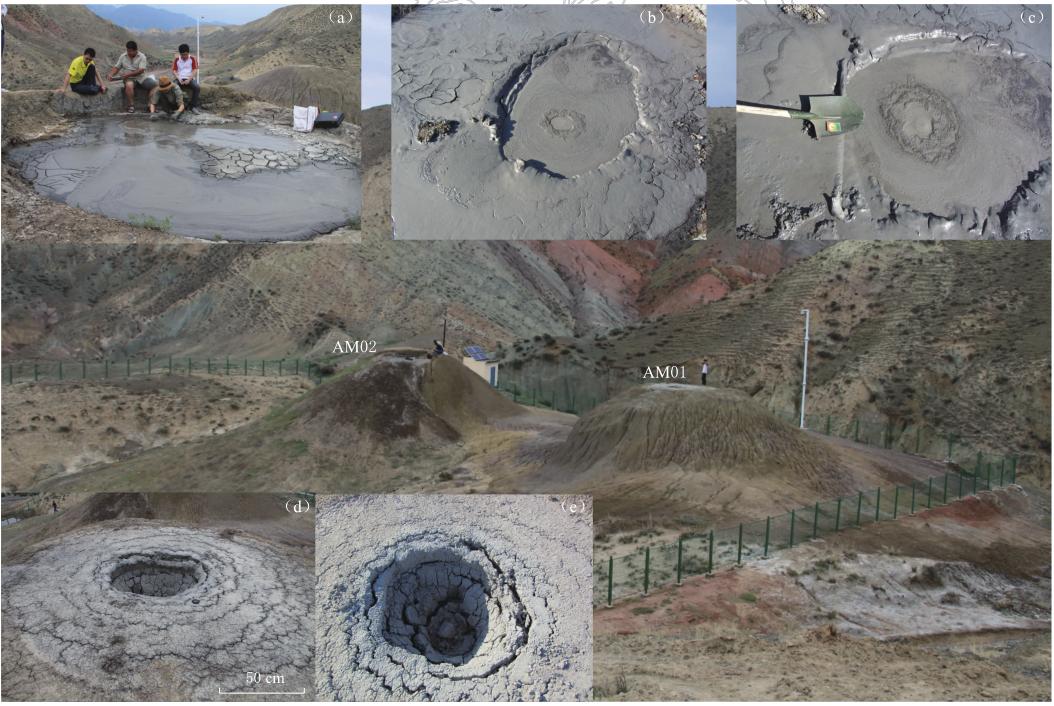
新疆北天山代表性的泥火山分布在沙湾县南霍尔果斯、 独山子油矿、 石河子南紫泥泉子和乌苏白杨沟,每个地方有多个泥火山口. 这些泥火山都处在北天山山前坳陷,坳陷内由南向北发育了3排褶皱—逆断裂带. 泥火山主要分布在背斜的轴部,出露地层多为泥砂质岩层,地层中富含多层地下水,且地下水具有承压高、 矿化度高、 天然气或石油含量高的特点(高小其等,2008). 霍尔果斯泥火山位于霍尔果斯背斜轴部. 独山子泥火山主要有5处,泥火山位于独山子背斜的轴部. 该背斜核部最老的地层为中新统塔西河组(Nt),轴向近东西. 背斜南翼缓,倾角为26°—33°; 北翼陡,倾角为20°—80°. 背斜在全新世还在活动(李锰等,1996). 白杨沟至少有36个泥火山,火山口呈圆形和椭圆形等不同形状,直径从约1—160 cm. 火山口内的喷发物有泥浆、 天然气和石油,有的泥火山口气泡排放速率超过60次/min. 最大的泥火山锥是艾其沟AM02泥火山锥高达15 m,火山口直径为4.6 m. 从1991—2010年,准噶尔盆地南缘泥火山发生气压减小、 排气量减少、 泥浆池口陷落和泥浆池干涸等变化,表明该区泥火山活动渐趋衰弱(戴金星等,2012). 观测的泥火山距新源-和静MS6.6地震震中在66—100 km的范围内(图 1).
2. 观测与样品分析方法
笔者分别于震前(6月26—27日)和震后(7月1—3日)对白杨沟及艾其沟泥火山、 独山子泥火山、 安集海泥火山、 呼图壁雀儿沟21号泉、 沙湾金沟河25号泉(鸡蛋泉)及阿拉山温泉(阿拉山疗养院温泉)进行了现场考察,测量了泥火山与温泉的温度和水位,记录了泥火山气体逸出情况,同时采集了水样和气样. 气体样品容器为玻璃瓶,采样方法为排水取气法(Du et al,2006; 戴金星等,2012).
在中国科学院兰州地质研究所进行了同位素测量. 温泉气体组分用Trace GC型气相色谱仪检测,碳同位素组成用MAT 253型气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-IRMS)测定,测量误差为±0.3‰; 氦和氖同位素分析用MM5400质谱仪检测,实验室标准样为兰州市皋兰山顶的空气(AIRLZ2007)(叶先仁等,2001).
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 泥火山喷溢响应
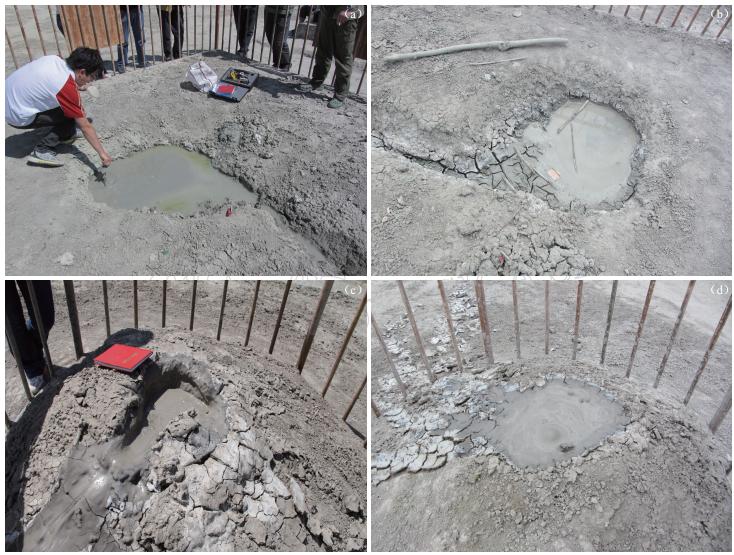
白杨沟泥火山群,震中距为88 km. SM22泥火山口震前泥浆温度为25.0 ℃,1处冒气泡,震后泥浆温度为23.9 ℃,冒气泡处增到10个,气泡直径变大(约10 cm),气泡排放速率为95次/min(图 2). 此外,震前掉进泥火山口的取样玻璃瓶浮出水面,应该是地震时泥浆喷溢将玻璃瓶带出的,这表明同震喷溢较强. 类似的同震喷发的实例也有报道,如在阿塞拜疆的大地震也常触发泥火山异常喷发(Mellors et al,2007).
![]() 图 2 乌苏白杨沟泥火山口震前(2012年6月27日7时6分)(a)和震后(2012年7月1日18时19分)(b)的照片图中泥浆上面有石油形成的晕色, 震后气泡明显变大、 增多, 排气量增加图中泥浆上面有石油形成的晕色, 震后气泡明显变大、 增多, 排气量增加Figure 2. Photos of Baiyanggou mud volcano before the Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthquake (a: 07 h 06 min on 27 June 2012) and after the event (b: 18 h 19 min on 1 July 2012) The iridescence formed by petroleum on mud was colorful. The size and number of bubbles increased obviously after the earthquake, indicating gas discharge increased
图 2 乌苏白杨沟泥火山口震前(2012年6月27日7时6分)(a)和震后(2012年7月1日18时19分)(b)的照片图中泥浆上面有石油形成的晕色, 震后气泡明显变大、 增多, 排气量增加图中泥浆上面有石油形成的晕色, 震后气泡明显变大、 增多, 排气量增加Figure 2. Photos of Baiyanggou mud volcano before the Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthquake (a: 07 h 06 min on 27 June 2012) and after the event (b: 18 h 19 min on 1 July 2012) The iridescence formed by petroleum on mud was colorful. The size and number of bubbles increased obviously after the earthquake, indicating gas discharge increased艾其沟两个泥火山位于背斜轴部断裂带,火山口中心相距约20 m,震中距为86 km. 2012年5月AM01泥火山口停止溢流,AM02泥火山溢流量减少. AM02泥火山口泥浆2012年6月27日的温度为16.5 ℃; 震后2012年7月1日升高到20.5 ℃,气泡直径约15 cm,气泡排放率为50次/min,7月3日温度下降为18.0 ℃,气泡直径约15 cm,排放率为55次/min. 这表明气体排放量增大或泥浆黏度降低了,深层热流体补给量减少了. 2012年7月1日观测该火山口内泥浆增多,将震前干裂的泥淹没,几乎充满火山口,泥浆上面有黑色的石油,2012年7月2日火山口喷溢边缘的泥浆有变干的迹象(图 3). 这表明该泥火山2012年6月30日发生过同震喷发; 2012年7月2号5点发生4.2级余震引起泥火山再次喷发. 艾其沟AM01泥火山锥高约12 m,火山口泥浆液面2012年3月开始下降,5月底停止喷溢,逐渐干涸,地震时未发生泥浆喷发,震后观测还是干的(图 3). 这表明艾其沟AM02与 AM01两个泥火山口可能不是拥有同一个通道.
![]() 图 3 乌苏市艾其沟泥火山锥照片(a) 2012年6月27日18点AM02泥火山口照片; (b)、 (c)分别为7月1日、 7月2日照片; (d), (e)分别为6月27日、 7月1日干涸的AM01泥火山口照片Figure 3. Photos of Aiqigou mud volcanoes in Wusu city(a) Photo of mud volcano AM02 at 18:00 on 27 June 2012; (b) and (c) Photos of mud volcano AM02 on 1 and 2 July respectively; (d) and (e) Photos of mud volcano MA01 taken on 27 June and 1 July respectively
图 3 乌苏市艾其沟泥火山锥照片(a) 2012年6月27日18点AM02泥火山口照片; (b)、 (c)分别为7月1日、 7月2日照片; (d), (e)分别为6月27日、 7月1日干涸的AM01泥火山口照片Figure 3. Photos of Aiqigou mud volcanoes in Wusu city(a) Photo of mud volcano AM02 at 18:00 on 27 June 2012; (b) and (c) Photos of mud volcano AM02 on 1 and 2 July respectively; (d) and (e) Photos of mud volcano MA01 taken on 27 June and 1 July respectively独山子泥火山群的震中距为94 km. 独山子两个泥火山在地震前后的异常变化相反. 独山子1号泥火山震前泥浆温度为24.9 ℃,有2个小的冒气口; 震后泥浆温度稍有降低(22.2 ℃),火山口的泥浆量明显少于震前,出水口出现干裂,约3分钟冒1个气泡(图 4). 但是,2号泥火山地震前泥浆中有1个冒气口,泥浆未充满火山口; 震后泥浆温度为21.2 ℃,出现了2个冒气口,气泡直径增大(约10 cm),气泡排放率明显增大,达到130次/min,排气量明显增大,泥水量明显增多,溢出火山口变干的泥浆表明该泥火山发生过同震喷溢.
![]() 图 4 新源-和静MS6.6地震前后独山子泥火山的照片(a)、 (b)分别为1号泥火山震前(6月27日)和震后(7月2日)照片; (c)、 (d)分别为2号泥火山震前(6月27日)和震后(7月2日)照片Figure 4. Photos of Dushanzi mud volcanoes before and after the Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthqake (a) and (b) are photoes of mud volcano No.1 taken on 27 June and 2 July 2012, respectively; (c) and (d) are those of mud volcano No.2 taken on 27 June and 2 July 2012, respectively
图 4 新源-和静MS6.6地震前后独山子泥火山的照片(a)、 (b)分别为1号泥火山震前(6月27日)和震后(7月2日)照片; (c)、 (d)分别为2号泥火山震前(6月27日)和震后(7月2日)照片Figure 4. Photos of Dushanzi mud volcanoes before and after the Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthqake (a) and (b) are photoes of mud volcano No.1 taken on 27 June and 2 July 2012, respectively; (c) and (d) are those of mud volcano No.2 taken on 27 June and 2 July 2012, respectively安集海泥火山的震中距为98 km. 该泥火山处在黄土山丘上,震前泥火山口的水比较清,水温为22.4 ℃,有1处冒气泡; 震后火山口充满泥浆,泥浆上有许多黑色石油,2012年7月2日火山口内泥浆面略有降低,泥水变黏稠,泥浆温度升高到30.8 ℃,有2处冒气泡,气泡排放率为30次/min(图 5). 这表明该泥火山也发生过同震喷溢,震后排气量增大.
泥火山的同震喷发是由地震波作用引起的. 地震波可以导致地下岩石的动力应变、 流体压力增大、 渗透率增加和水压屏障消失. 地震波触发泥火山同震喷发具有频率效应,长周期地震波触发作用更强. Manga等(2009)评述了地震触发泥火山喷发的机制,指出沙土液化、 岩石强度降低、 气泡成核生长、 渗透率增大、 水压屏障消除和动力应变等机制中,后3种机制更为重要. 2003年台湾成功MW6.8地震引起罗山泥火山同震喷发,喷出水和气体发出响声被认为是局部应力波动导致的,并非区域构造应力场的产物(Jiang et al,2011). 因此,2012年6月30日北天山泥火山的同震喷发应该主要是地震波引起局部应力变化,孔隙流体压力增大导致的.
3.2 地球化学响应
3.2.1 气体组分来源
新疆21号温泉气主要为CH4、 N2和O2,温泉气的He和H2含量远高于大气对流层中的含量(表 1). δ13C1值(-40.97‰)与准噶尔盆地50个二叠系-三叠系储层的石油伴生气样的δ13C1值(-36.7‰— -48.1‰,徐永昌,1994)一致. 这表明甲烷来源于盆地中的沉积有机质(戴金星等,2012). 氦同位素组成(0.02 Ra)也与盆地内天然气中的氦同位素组成(徐永昌,1994)一致,表明He主要是来自地壳,地幔氦贡献少; 与大气组分浓度及比值对比,Ar含量较低,但是N2/O2和O2/Ar值较高,这表明这些气体组分可能主要来自空气,并在水循环过程中发生了不等比例消耗. 另外,鸡蛋泉和阿拉山温泉气体N2含量大于94%,N2/O2值是大气值(3.73)的6.15倍,但是O2/Ar值仅是大气值(22.53)的1/6.86,这表明在水循环过程中O2被消耗了. 此外,高的He和Ar含量表明两个温泉气体组分有岩石圈气体的贡献. 地震前后鸡蛋泉的气体组分的变化说明大气组分相对降低,而深部来源气体相对增加(表 1). 这表明地震促进了深部气体的释放. 温泉气体的一个明显特征是H2、 H2S含量较高以及富集13C的甲烷. 在构造压力作用下,断裂带的岩石破碎,矿物晶体产生新的表面,与水反应产生H2. 当然也不排除有岩石圈深部来源的H2. CO2的碳同位素组成在-16‰与-7‰之间,3He/4He值稍高于地壳氦同位素的均值,4He/20Ne值远大于空气(0.03)的值,地震后H2S和He的浓度增加(表 1). 这意味着温泉气中H2S、 CO2、 CH4及He可能来自岩石圈深部.
表 1 新疆北天山泥火山和温泉气体的组分与同位素组成Table 1. Molecular and isotopic compositions of gases from the mud volcanoes in North Tianshan, Xinjiang名称
纬度/°
经度/°E新疆21号泉
43.730 12
86.556 42鸡蛋泉
43.837 06
85.375 93阿拉山温
泉44.177 38
85.446 69安集海泥火山
44.304 71
84.847 28独山子泥火山
44.124 10
84.639 97白杨沟泥火山
44.182 77
84.387 63艾其沟泥火山
44.188 86
84.493 14采样日期 2012-06-26 06-26 07-03 06-27 07-02 06-27 07-03 06-27 07-02 06-27 07-01 06-27 07-01 07-03 N2 44.81% 94.95% 94.38% 95.50% n 34.00% 1.24% 3.37% 2.54% 3.11% 2.96% 1.52% 2.51% 3.29% O2 5.52% 3.34% 4.12% 3.04% n 1.03% 0.03% 0.12% 0.03% 0.03% 0.04% 0.04% 0.03% 0.06% Ar 0.59% 1.13% 1.26% 1.27% n 0.58% 0.02% 0.03% 0.02% 0.04% 0.02% 0.01% 0.03% 0.04% CO2 0.04% 0.02% 0.02% 0.02% n 2.50% 6.14% 3.92% 4.23% 1.64% 2.31% 15.48% 15.11% 14.90% C1 48.97% 0.28% 0.07% 0.07% n 59.09% 87.58% 88.12% 88.77% 85.25% 94.66% 78.16% 77.26% 76.59% C2 0.02% - - - n 2.81% 4.99% 4.40% 4.39% 9.89% - 4.76% 5.02% 5.08% C3 - - - - n - - 0.03% 0.03% 0.01% - 0.03% 0.03% 0.03% H2S/10-6 13 - 23 - n 27 - - - - - - - - H2/10-6 218 2378 762 - n - - - - 276 - - - - He/10-6 203 495 803 937 n - - - - - - - - - 4He/20Ne 1026.01 325.30 141.92 535.41 529.33 7.76 277.12 3.95 465.18 1345.02 297.89 2362.71 131.93 507.02 
0.0133 0.0352 0.0462 0.0270 0.0268 0.2337 0.0280 0.5557 0.0316 0.0139 0.0192 0.0122 0.0562 0.1345 (3) (5) (10) (7) (7) (175) (6) (140) (7) (5) (7) (3) (11) (31) δ13C1 -40.97‰ 4.84‰ 2.75‰ -13.41‰ -14.81‰ -36.77‰ -37.95‰ -42.58‰ -42.57‰ -45.65‰ -46.03‰ -41.12‰ -41.07‰ -41.24‰ δ13CCO2 -7.30‰ -11.57‰ -10.33‰ -15.81‰ -15.23‰ 31.64‰ 32.11‰ 21.75‰ 19.89‰ 15.78‰ 15.20‰ 29.20‰ 29.14‰ 29.00‰ R/Ra 0.02 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.45 0.04 0.78 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.08 0.19 N2/O2 8.11 28.41 22.93 31.46 n 33.13 36.10 29.12 82.49 108.33 69.33 34.89 74.11 52.38 O2/Ar 9.33 2.96 3.28 2.39 n 1.76 1.93 3.32 2.00 0.76 1.74 5.26 1.19 1.66 T/℃ 36.00 49.50 42.50 43.30 41.90 22.40 30.80 24.90 22.20 25.00 23.90 16.50 20.50 18.00 注: 表中“-”表示未检出, n表示未测(样品废了), R/Ra表示测量的3He/4He值与大气3He/4He值(1.4×10-6)的比, 括弧内的数值表示误差, δ13CCO2和δ13C1分别表示CO2和CH4的碳同位素组成. 北天山泥火山的气体组分以CH4为主,还有部分大气组分和少量乙烷和丙烷. 与安达曼群岛中部Baratang泥火山喷出气体的组成相当,各气体的体积分数: CH4为55.7%、 N2为32.2%、 O2+Ar为9.9%、 CO2为2.0%和He为0.2%(Chaudhuri et al,2012). 北天山泥火山的δ13C1值分布在-36.77‰与-46.03‰之间(表 1),与Nakada等(2011)、戴金星等(2012)报道的数据一致. 烃类气体的碳同位素组成与准噶尔盆地内石油伴生气的碳同位素组成一致,表明这些烃类气体都是来自生油岩(Nakada et al,2011; 戴金星等,2012). 北天山泥火山气体中CO2异常地富集13C,δ13CCO2值在15‰—32‰的范围内,与2008年气体样品的碳同位素值相当(Nakada et al,2011). 富集13C的CO2可能是CO2+H2反应残留的CO2,或是生物化学作用造成的(Nakada et al,2011).
3.2.2 气体地球化学变化
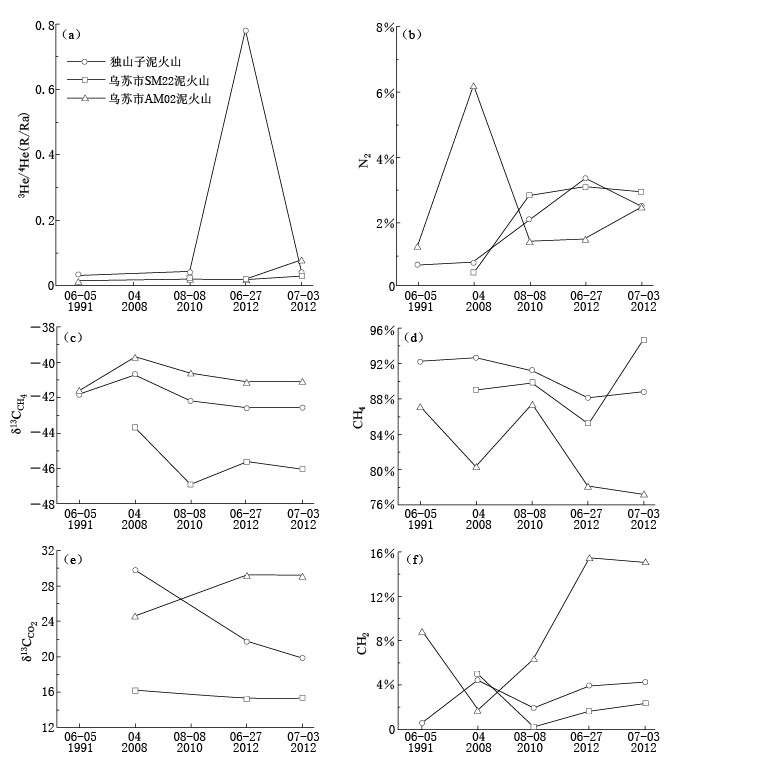
北天山的泥火山处于天山地震带,是中国大陆最典型的泥火山. 因此,北天山泥火山一直倍受关注(李锰等,1996; 高小其等,2008; Nakada et al,2011; 戴金星等,2012). 有关文献和最近测量的泥火山气体地球化学数据表明,从1991年6月5日—2012年7月3日泥火山气体中CH4、 CO2、 N2、 He的浓度和同位素组成都有变化(图 6).
![]() 图 6 泥火山气体中N2、 CO2、 CH4浓度和碳同位素组成及氦同位素组成变化 (a)-(f) 分别为氦同位素比值、 氮气、 甲烷的碳同位素组成、 甲烷浓度、 二氧化碳的碳同位素组成和二氧化碳浓度随时间的变化. 1991年6月和2010年8月数据引自戴金星等(2012), 2008年4月数据引自Nakada等(2011)Figure 6. Diagrams of molecular and isotopic compositions from the mud volcanoes at different dates (a)-(f) show variations of 3He/4He, N2, δ13C of CH4, concentration of CH4, δ13C of CO2and concentration of CO2respectively; data of June 1991 and August 2010 after Dai et al(2012), data of April 2008 after Nakada et al(2011)
图 6 泥火山气体中N2、 CO2、 CH4浓度和碳同位素组成及氦同位素组成变化 (a)-(f) 分别为氦同位素比值、 氮气、 甲烷的碳同位素组成、 甲烷浓度、 二氧化碳的碳同位素组成和二氧化碳浓度随时间的变化. 1991年6月和2010年8月数据引自戴金星等(2012), 2008年4月数据引自Nakada等(2011)Figure 6. Diagrams of molecular and isotopic compositions from the mud volcanoes at different dates (a)-(f) show variations of 3He/4He, N2, δ13C of CH4, concentration of CH4, δ13C of CO2and concentration of CO2respectively; data of June 1991 and August 2010 after Dai et al(2012), data of April 2008 after Nakada et al(2011)1)独山子泥火山. 1991年以来,氦同位素比值在震前出现了显著的高值异常(图 6a),氮气含量总体呈增大的趋势,但是地震后有所降低(图 6b). CH4的浓度和碳同位素组成随时间的变化不大,总体呈降低的趋势,地震前后变化不明显(图 6c,d). CO2浓度呈增大的趋势,6月30日新源-和静MS6.6地震前后变化不明显,但是δ13CCO2值呈明显降低的趋势,6月30日地震后比震前还低(图 6e,f). 这些变化可以归因于地震前深部气体在局部应力作用下加快逸散,也意味着深部流体对地震孕育发生有贡献. 类似的震例也有报道,如意大利北亚平安山脉和西西里岛的泥火山地下压力达到临界值时,地震波会触发泥火山喷发(Bonini,2009).
2)乌苏白杨沟SM22泥火山. 1991年以来,CO2浓度和δ13CCO2值变化不大,地震前后也没有大的变化. 从2008年4月—2012年7月3日,CH4的浓度和δ13C1值随时间出现了降低、 再升高的趋势,但是N2浓度明显增高. 6月30日地震前后CH4浓度明显增高,但是δ13C1和3He/4He值变化不大(图 6). 地震前甲烷浓度的升高是在地应力的作用下地层中石油伴生气排放量增大的结果. 类似现象在台湾泥火山(Jiang et al,2011)和海底泥火山(Tsunogai et al,2012)也出现过. 因此,可以推断在该处测量泥火山的气体流量应该能够获得地震前兆.
3)乌苏艾其沟AM02泥火山. 1991年以来,CO2浓度变化很大,但是δ13CCO2值增大幅度很小,地震前后CO2浓度和δ13CCO2值基本没变化,表明CO2的来源没有变化. 甲烷的浓度随时间出现大的波动,但是δ13C1值变化幅度较小,地震前后变化也不明显(图 6). 同样表明CH4的来源没有变化. 氮浓度呈增大的趋势,2008年4月含量明显增高,地震后浓度明显增高. 氦同位素变化幅度小,但是,地震后略增高. 这些变化说明在该处监测地震应该选择测量N2和CH4浓度与3H/4He指标.
4. 结论
在2012年6月30日新源-和静MS6.6地震前后,北天山几处的泥火山均发生了不同程度的同震喷溢. 多年的地球化学数据(Nakada et al,2011; 戴金星等,2012)与我们获得的气体地球化学数据表明,温泉气中H2S、 CO2、 CH4及He可能来自岩石圈深部. 新疆21号泉的CH4和泥火山气体中CH4主要源于山前坳陷中的沉积有机质,异常富集13C的CO2与He、 Ne主要来自岩石圈. 震后温泉气体中He含量和同位素比值都增高,震前独山子泥火山出现的3He/4He值高值异常可能是地震前兆. 泥火山气体在地震前后变化明显的指标是氦同位素比值、 CH4和CO2浓度,这些指标应该是研究区映震的灵敏指标. 地震活动相伴的泥火山异常喷溢现象和气体地球化学变化表明,深部流体可能对地震孕育有贡献. 但是,由于采样密度低,分析数据有限,所以确定气体地球化学地震前兆尚需更多的监测数据.
作者衷心地感谢塔城地震局王中道、 焦建鹏,沙湾县地震局刘萍丽在野外工作中给予的帮助; 兰州地质研究所贺坚、 李立武、 杜丽、 李中平和陈义林及时分析了样品; 审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵意见.
-
图 1 图1 天山中段活动断裂和采样点分布略图
1. 新疆21号泉; 2. 新疆25号泉; 3. 安集海泥火山; 4. 独山子泥火山; 5. 阿拉山温泉; 6. 乌苏市白杨沟泥火山; 7. 乌苏市艾其沟泥火山
Figure 1. Active faults and sampling sites in the middle segment of Tianshan
1. Xinjiang spring No.21; 2. Xinjiang spring No.25; 3. Anjihai mud volcano; 4. Dushanzi mud volcano; 5. Alxa hot spring; 6. Baiyanggou mud volcano in Wusu city; 7. Aiqigou mud volcano in Wusu city
图 2 乌苏白杨沟泥火山口震前(2012年6月27日7时6分)(a)和震后(2012年7月1日18时19分)(b)的照片图中泥浆上面有石油形成的晕色, 震后气泡明显变大、 增多, 排气量增加图中泥浆上面有石油形成的晕色, 震后气泡明显变大、 增多, 排气量增加
Figure 2. Photos of Baiyanggou mud volcano before the Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthquake (a: 07 h 06 min on 27 June 2012) and after the event (b: 18 h 19 min on 1 July 2012) The iridescence formed by petroleum on mud was colorful. The size and number of bubbles increased obviously after the earthquake, indicating gas discharge increased
图 3 乌苏市艾其沟泥火山锥照片
(a) 2012年6月27日18点AM02泥火山口照片; (b)、 (c)分别为7月1日、 7月2日照片; (d), (e)分别为6月27日、 7月1日干涸的AM01泥火山口照片
Figure 3. Photos of Aiqigou mud volcanoes in Wusu city
(a) Photo of mud volcano AM02 at 18:00 on 27 June 2012; (b) and (c) Photos of mud volcano AM02 on 1 and 2 July respectively; (d) and (e) Photos of mud volcano MA01 taken on 27 June and 1 July respectively
图 4 新源-和静MS6.6地震前后独山子泥火山的照片(a)、 (b)分别为1号泥火山震前(6月27日)和震后(7月2日)照片; (c)、 (d)分别为2号泥火山震前(6月27日)和震后(7月2日)照片
Figure 4. Photos of Dushanzi mud volcanoes before and after the Xinyuan-Hejing MS6.6 earthqake (a) and (b) are photoes of mud volcano No.1 taken on 27 June and 2 July 2012, respectively; (c) and (d) are those of mud volcano No.2 taken on 27 June and 2 July 2012, respectively
图 6 泥火山气体中N2、 CO2、 CH4浓度和碳同位素组成及氦同位素组成变化 (a)-(f) 分别为氦同位素比值、 氮气、 甲烷的碳同位素组成、 甲烷浓度、 二氧化碳的碳同位素组成和二氧化碳浓度随时间的变化. 1991年6月和2010年8月数据引自戴金星等(2012), 2008年4月数据引自Nakada等(2011)
Figure 6. Diagrams of molecular and isotopic compositions from the mud volcanoes at different dates (a)-(f) show variations of 3He/4He, N2, δ13C of CH4, concentration of CH4, δ13C of CO2and concentration of CO2respectively; data of June 1991 and August 2010 after Dai et al(2012), data of April 2008 after Nakada et al(2011)
表 1 新疆北天山泥火山和温泉气体的组分与同位素组成
Table 1 Molecular and isotopic compositions of gases from the mud volcanoes in North Tianshan, Xinjiang
名称
纬度/°
经度/°E新疆21号泉
43.730 12
86.556 42鸡蛋泉
43.837 06
85.375 93阿拉山温
泉44.177 38
85.446 69安集海泥火山
44.304 71
84.847 28独山子泥火山
44.124 10
84.639 97白杨沟泥火山
44.182 77
84.387 63艾其沟泥火山
44.188 86
84.493 14采样日期 2012-06-26 06-26 07-03 06-27 07-02 06-27 07-03 06-27 07-02 06-27 07-01 06-27 07-01 07-03 N2 44.81% 94.95% 94.38% 95.50% n 34.00% 1.24% 3.37% 2.54% 3.11% 2.96% 1.52% 2.51% 3.29% O2 5.52% 3.34% 4.12% 3.04% n 1.03% 0.03% 0.12% 0.03% 0.03% 0.04% 0.04% 0.03% 0.06% Ar 0.59% 1.13% 1.26% 1.27% n 0.58% 0.02% 0.03% 0.02% 0.04% 0.02% 0.01% 0.03% 0.04% CO2 0.04% 0.02% 0.02% 0.02% n 2.50% 6.14% 3.92% 4.23% 1.64% 2.31% 15.48% 15.11% 14.90% C1 48.97% 0.28% 0.07% 0.07% n 59.09% 87.58% 88.12% 88.77% 85.25% 94.66% 78.16% 77.26% 76.59% C2 0.02% - - - n 2.81% 4.99% 4.40% 4.39% 9.89% - 4.76% 5.02% 5.08% C3 - - - - n - - 0.03% 0.03% 0.01% - 0.03% 0.03% 0.03% H2S/10-6 13 - 23 - n 27 - - - - - - - - H2/10-6 218 2378 762 - n - - - - 276 - - - - He/10-6 203 495 803 937 n - - - - - - - - - 4He/20Ne 1026.01 325.30 141.92 535.41 529.33 7.76 277.12 3.95 465.18 1345.02 297.89 2362.71 131.93 507.02 
0.0133 0.0352 0.0462 0.0270 0.0268 0.2337 0.0280 0.5557 0.0316 0.0139 0.0192 0.0122 0.0562 0.1345 (3) (5) (10) (7) (7) (175) (6) (140) (7) (5) (7) (3) (11) (31) δ13C1 -40.97‰ 4.84‰ 2.75‰ -13.41‰ -14.81‰ -36.77‰ -37.95‰ -42.58‰ -42.57‰ -45.65‰ -46.03‰ -41.12‰ -41.07‰ -41.24‰ δ13CCO2 -7.30‰ -11.57‰ -10.33‰ -15.81‰ -15.23‰ 31.64‰ 32.11‰ 21.75‰ 19.89‰ 15.78‰ 15.20‰ 29.20‰ 29.14‰ 29.00‰ R/Ra 0.02 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.45 0.04 0.78 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.08 0.19 N2/O2 8.11 28.41 22.93 31.46 n 33.13 36.10 29.12 82.49 108.33 69.33 34.89 74.11 52.38 O2/Ar 9.33 2.96 3.28 2.39 n 1.76 1.93 3.32 2.00 0.76 1.74 5.26 1.19 1.66 T/℃ 36.00 49.50 42.50 43.30 41.90 22.40 30.80 24.90 22.20 25.00 23.90 16.50 20.50 18.00 注: 表中“-”表示未检出, n表示未测(样品废了), R/Ra表示测量的3He/4He值与大气3He/4He值(1.4×10-6)的比, 括弧内的数值表示误差, δ13CCO2和δ13C1分别表示CO2和CH4的碳同位素组成. -
戴金星, 吴小奇, 倪云燕, 汪泽成, 赵长毅, 王兆云, 刘桂侠. 2012. 准噶尔盆地南缘泥火山天然气的地球化学特征[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学,42 (2): 178-190. 高小其, 王海涛, 高国英, 高歌, 王中道, 陆明勇, 桑丽荣, 杨晓芳, 郭卫英, 许秋龙. 2008. 霍尔果斯泥火山活动与新疆地区中强以上地震活动关系的初步研究[J]. .地震地质,30 (2): 464-472 李锰, 王道, 李茂伟, 戴晓敏. 1996. 新疆独山子泥火山喷发特征的研究[J]. 内陆地震,10 (4): 359-362. 漆家福, 陈书平, 杨桥, 于福生. 2008. 准噶尔-北天山盆山过渡带构造基本特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,29 (2): 252-260. 汪一鹏, 沈军. 2000. 天山北麓活动构造基本特征[J]. 新疆地质,18 (3): 204-211. 王道. 2000. 新疆北天山地区泥火山与地震[J]. 内陆地震,14 (4): 350-353. 徐永昌. 1994. 天然气成因理论与应用[M].北京: 科学出版社: 1-413. 叶先仁, 吴茂炳, 孙明良. 2001. 岩矿样品中稀有气体同位素组成的质谱分析[J]. 岩矿测试,20 (3): 174-178. 左国朝, 张作衡, 王志良, 刘敏, 王龙. 2008. 新疆西天山地区构造单元划分、 地层系统及其构造演化[J]. 地质论评,54 (6): 748-767. Bonini M. 2009. Mud volcano eruptions and earthquakes in the Northern Apennines and Sicily, Italy[J].Tectonophys,474 (3/4): 723-735.
Bonini M, Mazzarini F. 2010. Mud volcanoes as potential indicators of regional stress and pressurized layer depth[J].Tectonophys,494 (1/2): 32-47.
Chao H C, You C F, Sun C H. 2010. Gases in Taiwan mud volcanoes: Chemical composition, methane carbon isotopes, and gas fluxes[J]. Applied Geochem,25 (3): 428-436.
Chaudhuri H, Ghose D, Bhandari R K, Sen P, Sinha B. 2012. A geochemical approach to earthquake reconnaissance at the Baratang mud volcano, Andaman and Nicobar Islands[J].J Asian Earth Sci,46 : 52-60.
Du J, Cheng W, Zhang Y, Jie C, Guan Z, Liu W, Bai L. 2006. Helium and crbon isotopic compositions of thermal springs in earthquake zone of Sichuan, Southwestern China[J].J Asia Earth Sci,26 (5): 533-539.
Du J, Si X, Chen Y, Fu H, Jian C, Guan Z. 2008. Geochemical anomalies connected with great earthquakes in China[M]//Stefánsson Óed. Geochemistry Research Advances. New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc: 57-92.
Fu B H, Zheng G D, Ninomiya Y, Wang C Y, Sun G. 2007. Mapping hydrocarbon-induced mineralogical alterations in the northern Tian Shan using ASTER multispectral data[J].Terra Nova,19 (4): 225-231.
Heinicke J, Italiano F, Lapenna V, Martinelli G, Nuccio P M. 2000. Coseismic geochemical variations in some gas emissions (Central Italy)[J]. Phys Chem Earth (A),25 (3): 289-293.
Jiang G J, Angelier J, Lee J C, Chu H T, Hu J C. 2011. Faulting and mud volcano eruptions inside of the coastal range during the 2003 MW=6.8 Chengkung earthquake in Eastern Taiwan[J]. Terr Atmos Ocean Sci,22 (5): 463-473.
King C Y. 1986. Gas geochemistry applied to earthquake prediction: An overview[J]. J Geophys Res,91 (B12): 12269- 12281.
Kopf A, Deyhle A, Lavrushin V Y, Polyak B G, Gieskes J M, Buachidze G I, Wallmann K, Eisenhauer A. 2003. Isotopic evidence (He, B, C) for deep fluid and mud mobilization from mud volcanoes in the Caucasus continental collision zone[J].Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch),92 (3): 407-425.
Lavrushin V Y, Polyak B G, Pokrovskii B G, Kopp M L, Buachidze G I, Kamenskii I L. 2009. Isotopic-geochemical peculiarities of gases in mud volcanoes of Eastern Geor'gia[J]. Lithol Miner Resour,44 (2): 183-197.
Manga M, Brumm M, Rudolph M L. 2009. Earthquake triggering of mud volcanoes[J]. Marine Petrol Geol,26 (9): 1785-1798.
Mazzini A, Etiope G, Svensen H. 2012. A new hydrothermal scenario for the 2006 Lusi eruption, Indonesia. Insights from gas geochemistry[J]. .Earth Planet Sci Let,317/318:305-318
Mellors R, Kilb D, Aliyev A, Gasanov A, Yetirmishli G. 2007. Correlations between earthquakes and large mud volcano eruptions[J]. J Geophys Res,112 (B4), B04304, doi:10.1029/2006JB004489.
Nakada R, Takahashi Y, Tsunogai U, Zheng G D, Shimizu H, Hattori K H. 2011. A geochemical study on mud volcanoes in the Junggar Basin, China[J]. Appl Geochem,26 (7): 1065-1076.
Rudolph M L, Manga M. 2010. Mud volcano response to the 4 April 2010 El Mayor-ucapah earthquake[J]. J Geophys Res,115 (B12), B12211, doi:10.1029/2010JB007737.
Rudolph M L, Karlstrom L, Manga M. 2011. A prediction of the longevity of the Lusi mud eruption, Indonesia[J].Earth Planet Sci Let,308 (1/2): 124-130.
Rukavičková L, Hanžlžl P. 2008. Mud volcanoes in the Khar Argalantyn Nuruu, NW Gobi Altay, Mongolia as manifestation of recent seismic activity[J].J Geosci,53 : 181-191.
Tsunogai U, Maegawa K, Sato S, Komatsu D D, Nakagawa F, Toki T, Ashi J. 2012. Coseimic massive methane release from a submarine mud volcano[J]. Earth Planet Sci Let,341/344 : 79-85.
Yang T F, Walia V, Chyi L L, Fu C C, Chen C H, Liu T K, Song S R, Lee C Y, Lee M. 2005. Variations of soil radon and thoron concentrations in a fault zone and prospective earthquakes in SW Taiwan[J].Radiat Meas,40 (2/6): 496-502.
Yang T F, Fu C C, Walia V, Chen C H, Chyi L L, Liu T K, Song S R, Lee M, Lin C W, Lin C C. 2006. Seismo-geochemical variations in SW Taiwan: Multi-parameter automatic gas monitoring results[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,163 (4): 693-709.
Zheng G, Fu B, Takahashi Y, Kuno A, Matsuo M, Zhang J. 2010a. Chemical speciation of redox sensitive elements during hydrocarbon leaching in the Junggar Basin, Northwest China[J]. J Asia Earth Sci,39 (6): 713-723.
Zheng G, Fu B, Kuno A, Matsuo M. 2010b. Iron speciation in bleached rocks by hydrocarbon leaching in Dushanzi Mud Volcano, NW China[J].J Physics: Conference Series,217 (1): 012048, doi:10.1088/1742-6596/217/1/012048.
-
期刊类型引用(20)
1. 汪倩,彭莱,蒋雨函,周启超,高小其. 中国泥火山的主要分布及研究进展. 地震地质. 2025(01): 90-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李志海,朱成英,周晓成,张志斌,李慧峰. 新疆北天山地区泥火山变化特征及其在震情跟踪中的应用. 中国地震. 2024(03): 617-629 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马勇,马向贤,张力,胥旺,李小雅,卢昌顺,傅庆州,郑国东. 准噶尔盆地南缘白杨沟泥火山群地质流体的地球化学特征. 地球化学. 2022(04): 492-502 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 万志峰,吴婷婷,张伟,苏丕波,钟思玲,张金锋,罗钧升. 海底泥火山形成机制——南海台西南盆地泥火山钻探建议. 地质学报. 2022(08): 2906-2916 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 麻荣,朱成英,李新勇,汪成国,刘建明,刘代芹,李杰. 新疆乌苏艾其沟泥火山气体排放通量及其前兆异常特征研究. 内陆地震. 2022(03): 218-226 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王玲灵,刘红,孙凤霞,李一闪,刘雷,周晓成. 氦在矿物中的扩散及其在地震研究中的应用前景. 地震. 2022(03): 165-179 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 许世阳,柴少峰,尹光华,王平,蒲小武. 新疆泥火山发育区场地震陷灾害机理探讨. 地震工程学报. 2021(01): 63-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈昊,冀战波,王琼,苏金波. 动态应力触发研究进展. 中国地震. 2020(03): 442-459 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张磊,刘耀炜,任宏微,柯云龙. 水化学分析方法在地下水异常核实中的应用. 地震. 2019(01): 29-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 朱成英,周晓成,麻荣,闫玮,梁卉,张涛,高小其,颜玉聪. 2017年8月9日精河M_S6.6地震前乌苏泥火山群流体地球化学变化特征. 地震地质. 2019(04): 1060-1075 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 梁卉,高小其,向阳,朱成英. 新疆北天山艾其沟泥火山强震前显著喷涌现象及其变化机理分析. 中国地震. 2018(03): 534-544 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 薛治国,许善洋,刘海艳,胡莎莎,木合塔尔·艾买提,郭晓,郭建清. 地震在新疆苏约克泉华地球化学指标中的印记. 科学技术与工程. 2017(05): 152-156+166 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 郭正府,郑国东,孙玉涛,张茂亮,张丽红,成智慧. 中国大陆地质源温室气体释放. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2017(02): 204-212+183 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 张涛,朱成英,梁卉. 2016年12月8日呼图壁M_S6.2地震震前流体异常. 内陆地震. 2017(03): 253-258 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 高小其,梁卉,王海涛,郑黎明,李杰,赵纯青,向阳,张涛. 北天山地区泥火山的地球化学成因. 地震地质. 2015(04): 1215-1224 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 王云,赵慈平,冉华,陈坤华. 地壳流体CO_2的释放与地震关系:回顾与展望. 地震研究. 2015(01): 119-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 陈志,杜建国,李营,周晓成,高小其,刘红,颜龙. 北天山地区泥火山流体特征变化与地震活动的关系初探. 科学技术与工程. 2015(20): 1-7+16 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 陈志,李营,汪成国,颜龙. 新疆温泉县泥火山喷发水的化学特征研究. 四川地震. 2015(02): 12-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 高小其,王海涛,郑黎明,李娜,朱成英,杨晓芳,汪成国,向阳,梁卉,麻荣. 新疆泥火山群地震前兆异常实时监测与预报的研究. 震灾防御技术. 2015(03): 587-597 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 马向贤,郑国东,郭正府,ETIOPE Giuseppe,FORTIN Danielle,佐野有司. 准噶尔盆地南缘独山子泥火山温室气体排放通量. 科学通报. 2014(32): 3190-3196 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: