Attenuation and dispersion of saturated rocks in temperature and frequency domains
-
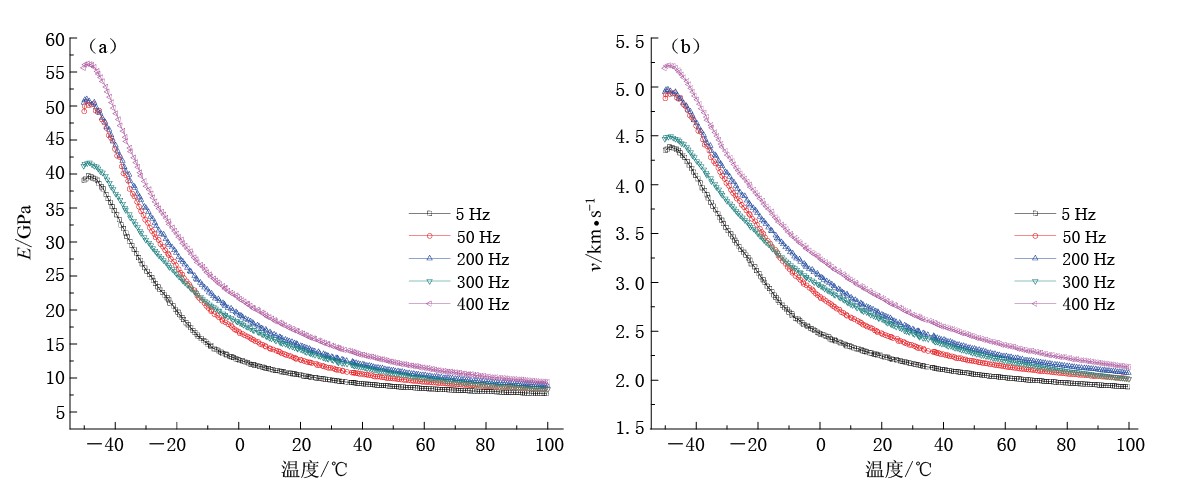
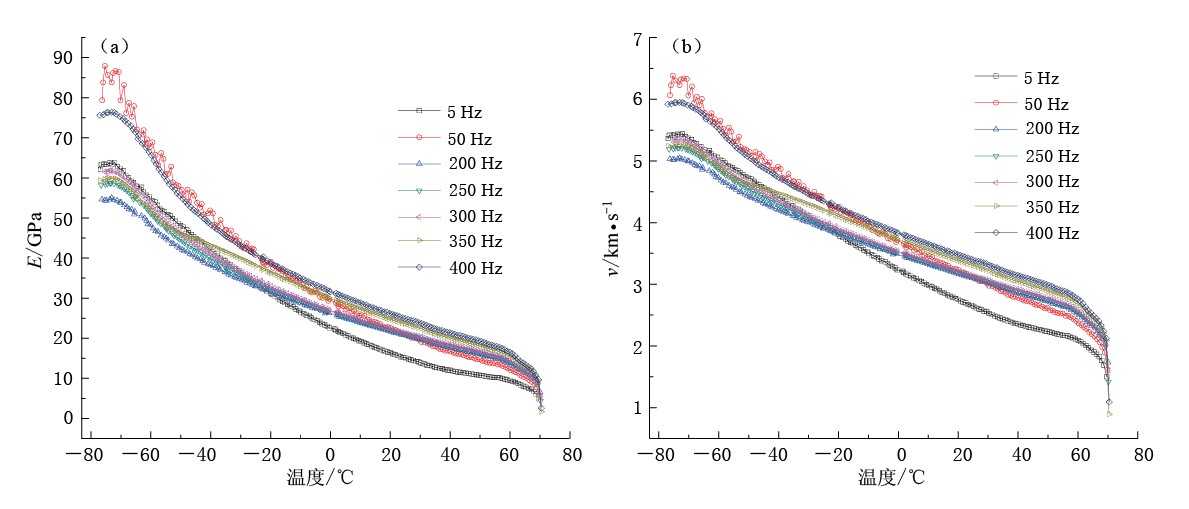
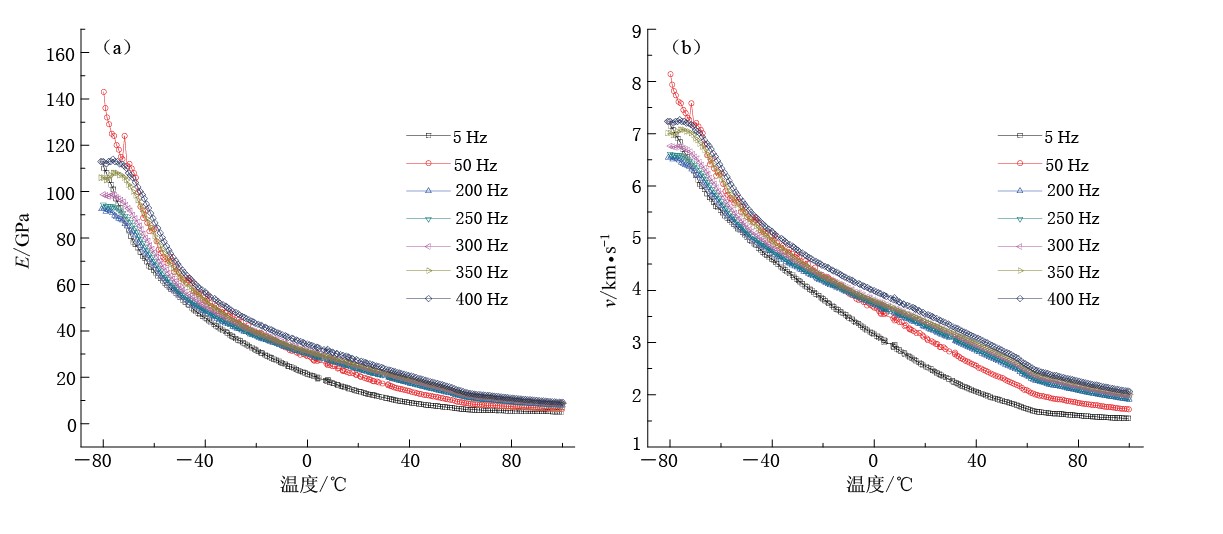
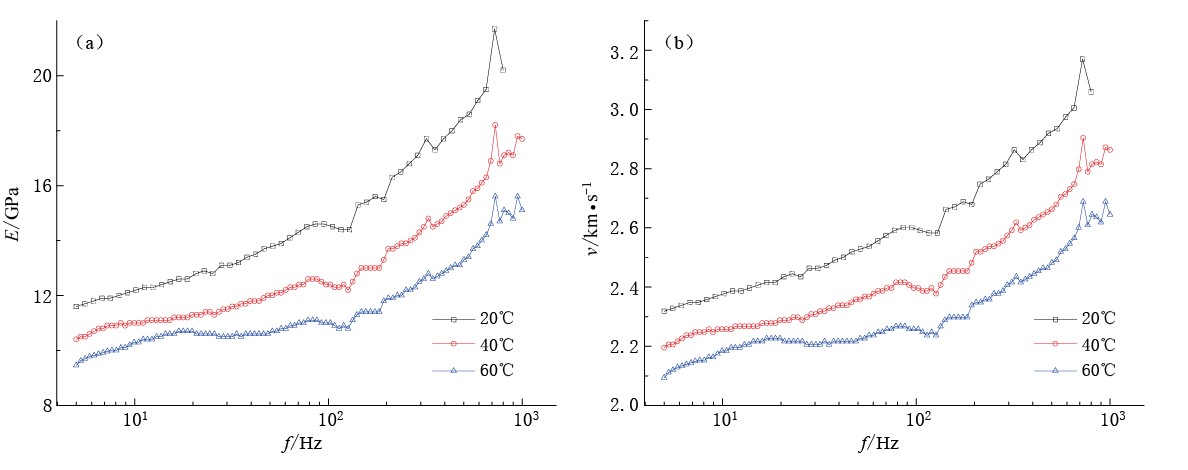
摘要: 利用Metravib热机械分析仪, 在天然地震的频率和温度范围内, 首次对泵油和甘油饱和两种孔隙度的彭山砂岩的衰减和速度频散进行了实验研究. 结果表明, ① 泵油饱和彭山砂岩对频率和温度的依赖呈热激活弛豫规律; ② 杨氏模量和弹性波速度与孔隙度、 温度呈负相关, 与饱和液体的黏滞系数、 频率呈正相关; ③ 频散效应因频率上升而增强, 因温度增高而减弱. 这一规律性的结果为地震波理论研究提供了实验基础.Abstract: Experiments are performed by Metravib dynamic mechanical analyzer about the attenuation and dispersion of pump-oil and glycerol saturated Peng-shan sandstones with two kinds of porosities. The frequency and temperature of tests are natural earthquake. The results show: ① The attenuation peak of pump-oil saturated Pengshan sandstone appears to be thermo-activated relaxation. ② Young’s modulus and elastic wave velocity of saturated Pengshan sandstones reduce with porosity and temperature increasing, and rise with viscosity coefficient of saturated liquid and frequency increasing. ③ Frequency dispersion attenuates as temperature increases, enhances as frequency rises. The data provides the experiment foundation for theoretical research of seismic waves.
-
Keywords:
- saturated rock /
- attenuation /
- modulus /
- dispersion of velocity
-
-
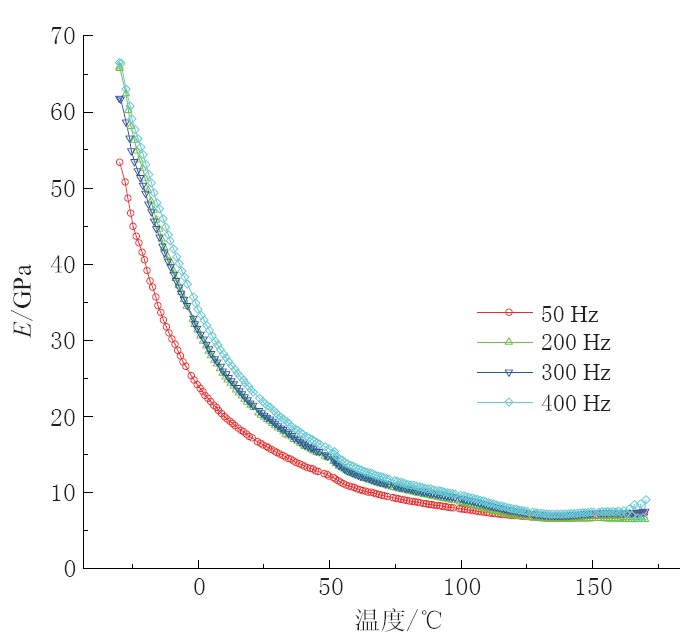
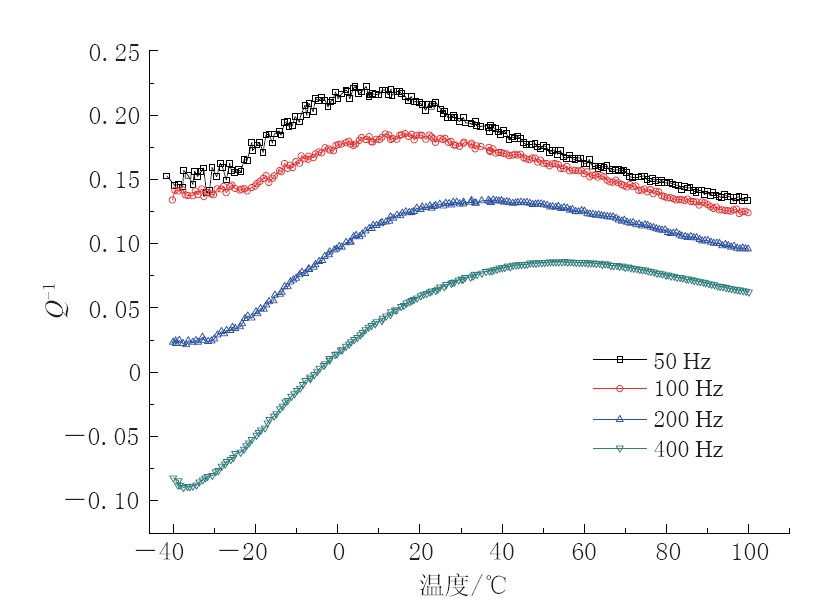
表 1 弛豫衰减峰的峰位和峰值强度
Table 1 The location and strength of the relaxed attenuation peak
频率/Hz 峰位温度/℃ 1/Q峰值强度 50 6.5 0.22 100 17 0.18 200 36 0.13 400 57 0.08 表 2 在相同实验条件下泵油饱和不同孔隙度的彭山砂岩的杨氏模量(E)
Table 2 Young’s moduli of bump-oil saturated Penshan sandstones with different porosity on the same experiment condition
标本 编号 孔隙度 E值(20 ℃各 频率平均)/GPa E总平均值 /GPa A-1 12.84% 22.0 22.0 PⅠ -20 16.08% 14.0 PⅠ -11 16.08% 17.5 PⅠ -10 16.08% 22.0 17.8 PⅡ -15 17.07% 16.0 PⅡ -13 17.07% 14.0 PⅡ -14 17.07% 19.5 16.5 -
杜赟 , 席道瑛, 徐松林, 易良坤. 2009. 多孔岩石波传播的热弛豫模型修正[J]. 地球物理学报, 52 (12): 3051-3060. 葛瑞, 塔潘, 杰克, 德沃金(编著). 1998. 徐海滨戴建春(译). 2008. 岩石物理手册: 孔隙介质中地震分析工具[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社: 166-171. 葛庭燧. 2000. 固体内耗理论基础-晶界弛豫与晶界结构[M].北京: 科学出版社: 29. 席道瑛, 徐松林, 席军, 易良坤, 杜赟. 2011. 饱和砂岩的粘弹行为的实验研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 54 (9): 2302-2308. 席道瑛, 周城光, 徐松林, 杜赟, 席军. 2012. 饱和砂岩滞弹性弛豫衰减机理的探索[J]. 地球物理学报, 55 (7): 2362-2370. Batzle M, Wang Z J. 1992. Seismic properties of pore fluids[J]. Geophysics, 57 (11): 1396-1408.
Batzle M, Hofmann R, Han D H, Castagna J. 2001. Fluids and frequency dependent seismic velocity of rocks[J]. The Leading Edge, 20 (2): 168-171.
Batzle M L, Han D H, Hofmann R. 2006. Fluid mobility and frequency-dependent seismic velocity: Direct measurements[J]. Geophysics, 71 (1): N1-N9, doi:10.1190/1.2159053.
Dvorkin J, Nur A. 1993. Dynamic poroelasticity: A unified model with the squirt and the Biot mechanisms[J]. Geophysics, 58 (4): 524-533.
Gist G A. 1994a. Interpreting laboratory velocity measurements in partially gas-saturated rocks[J]. Geophysics, 59 (7): 1100-1109.
Gist G A. 1994b. Fluid effect on velocity and attenuation in sandstone[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 96 (2): 1158-1173.
Kan T K, Batzle M L, Gaiser J E. 1983. Attenuation measured from VSP: Evidence of frequency-dependent Q[C]//Proceedings of the 53rd SEG Meeting. Las Vegas, USA: 589-590.
Messner R. 1983. Attenuation of seismic waves in sediments[C]//Proceedings of the 11th World Petroleum Congress. London: 363-381.
Pennington W D. 1997. Seismic petrophysics: An applied science for reservoir geophysics[J]. The Leading Edge, 16 (3): 241-246.
Pride S R, Harris J M, Johnson D L, Mateeva A, Nihei K T, Nowack R L, Rector J W, Spetzler H, Wu R, Yamomoto T, Berryman J G, Fehler M. 2003. Permeability dependence of seismic amplitudes[J]. The Leading Edge, 22 (6): 518-525.
Spencer J W. 1981. Stress relaxation at low frequencies in fluid-saturated rocks: Attenuation and modulus dispersion[J]. J Geophys Res, 86 (B3): 1803-1812.
Xi D Y, Liu B, Liu W, Yi L K. 2000. The dependence relationship of relaxation attenuation on time and temperature of saturated rocks[J]. Chinese J Geophys, 43 (6): 873-880.
Xi D Y, Liu B, Tian X Y. 2002. Anisotropy and nonlinear viscoelastic behavior of saturated rocks[J]. Chinese J Geophys, 45 (1): 101-111.
Xi D Y, Liu X Y, Zhang C Y. 2007. The frequency (or time)-temperature equivalence of relaxation in saturated rocks[J]. Pure Appl Geophys, 164 (11): 2157-2173.
Xi D Y, Xu S L, Du Y, Yi L K. 2011. Wave propagation analysis of porous rocks with thermal activated relaxation mechanism[J]. J Appl Geophys, 73 (3): 289-303.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 席军,宛新林,席道瑛. 循环载荷下饱和砂岩的滞弹性衰减与损伤研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2023(05): 1214-1224 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: