Sedimentary basin structure of the Bohai Bay from teleseismic receiver functions
-
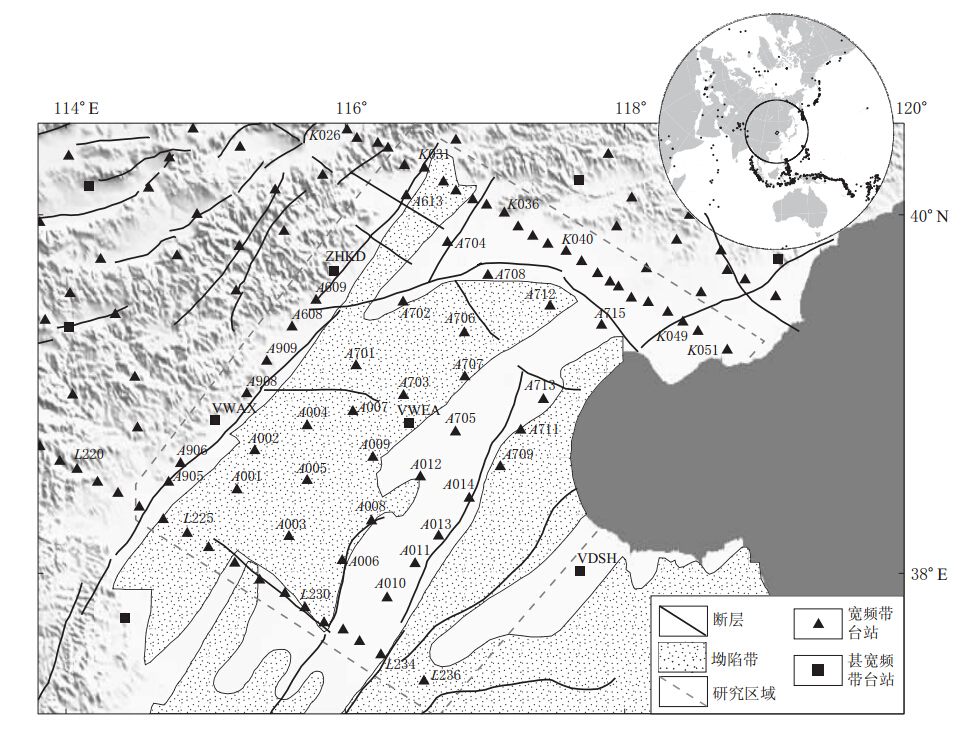
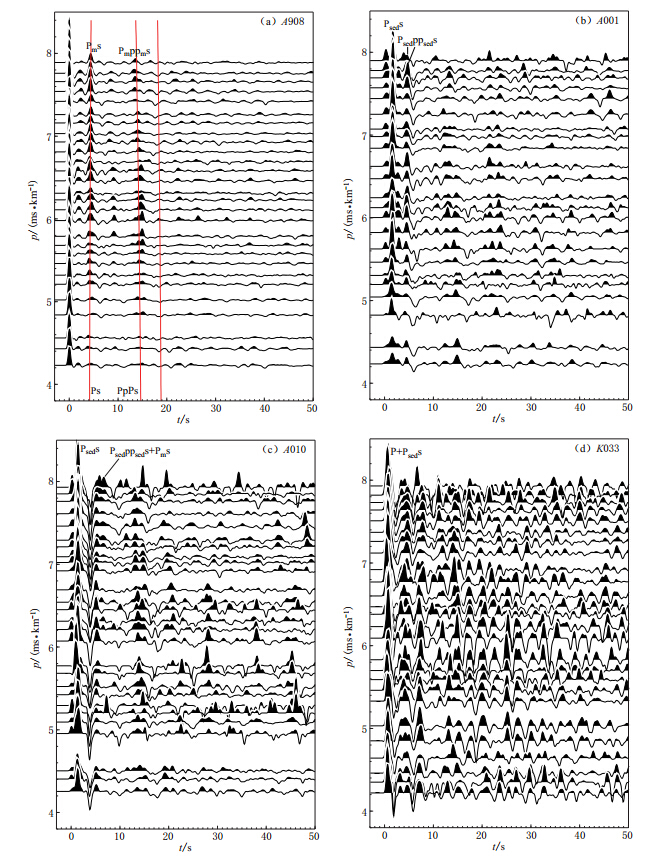
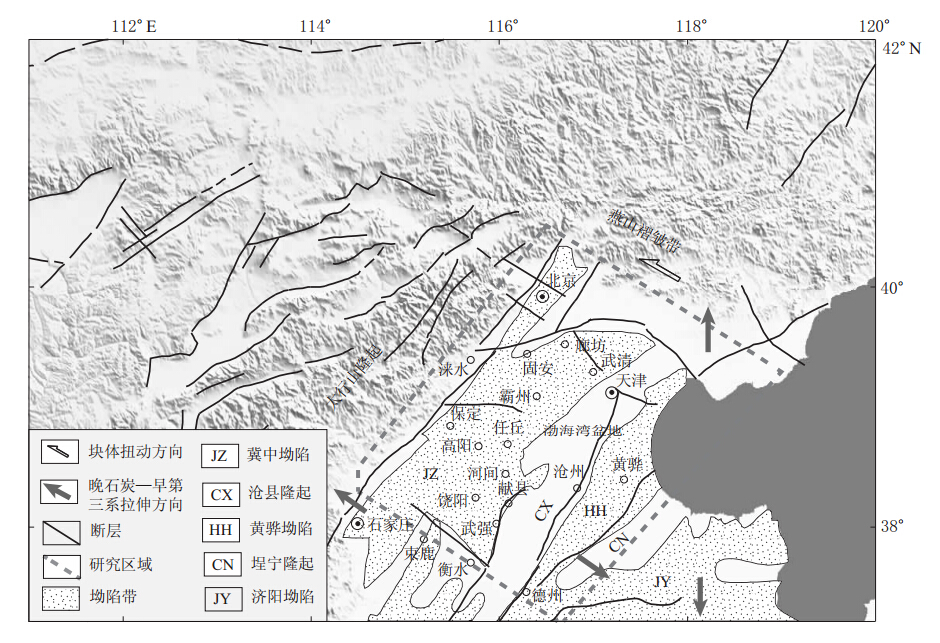
摘要: 对布设于渤海湾盆地地区的70个台站2006年9月—2009年9月记录到的895个远震数据进行接收函数计算,发现位于沉积层上的台站记录的接收函数震相较为复杂,由沉积层基底的转换波、多次波及莫霍面转换波、多次波共同构成,且随着沉积层厚度的增加,沉积层基底转换波、多次波与莫霍面转换波、多次波震相相互叠加,使之无法分辨出莫霍面转换波及多次波到时.为此,本文利用相邻算法对沉积层模型进行搜索, 以获取与实际波形误差最小的波形相对应的模型,即台站下方的沉积层结构.结果显示:① 渤海湾盆地由NNE向展布的坳陷带与隆起带组成,冀中坳陷带的沉积层厚度为3—6 km, 坳陷带内沿NE-NNE向分布着带状凹陷带与凸起带相间的次级构造,而且其东侧靠近沧县隆起区的凹陷带沉积层基底埋深最大,体现了渤海湾盆地基底受正断层控制而形成的半地堑(地堑)-半地垒(地垒)构造;② 隆起带的波速比vP/vS大于坳陷带的波速比,推测与隆起带下第三系地层的缺失有关, 坳陷带内高波速比地区与地热田的分布相对应, 说明沉积层内高温环境下波速比较高;③ 隆起带内的S波平均速度较坳陷带内的S波平均速度小,且冀中坳陷带内沉积层较厚地区对应的S波平均速度比其它地区更大, 说明渤海湾地区沉积层厚度与沉积层内的S波平均速度成反比关系,推测与下第三系地层的厚度有关,且下第三系地层越厚的地区,S波平均速度越大.以上结果表明,利用接收函数研究的结果与通过地质、地热等方面的研究结果存在着良好的对应关系.Abstract: We calculated P wave receiver functions using 895 teleseismic events from September 2006 to September 2009 recorded by 70 temporary stations located in the Bohai Bay basin.We found that it is difficult to identify the P to S converted phases from the Moho discontinuity.The first few seconds after the direct P arrival are mainly controlled by the sedimentary structure response which includes the Ps phase generated by the bottom of the basin and its multiple reverberations in the basin.Based on these characteristics, we used the neighborhood algorithm to invert the data and try to find the best basin velocity model that produces the best fit between the theoretical receiver functions and observed ones in the least-squares sense.The results show that there is a series of depressions and uplifts orienting in the NNE direction in the Bohai Bay basin.The sedimentary depth in the Jizhong Depression is about 3-6 km.There are several secondary depressions and uplifts alternating in the NNE or NE direction in the Jizhong depression.The thickest sedimentary layer is located in the eastern Jizhong depression.The above shows the characteristics of a half rift valley (rift valley)-half horst (horst) structure.The ratio of the P velocity to S velocity in the uplifts is larger than that in the depressions, which may be caused by the lack of the Paleogene stratum in the uplifts.The proximity of geothermal fields to the high vP/vS ratio depressions shows a close relationship between the high temperatures of the stratum and the large vP/vS ratios .The average of S velocity of the sedimentary in the uplift is smaller than that in the depression, and the thicker sedimentary area always has a higher average S velocity.These characteristics show a relationship between thick sedimentary and high average S velocity.It may be because that the thicker sedimentary area has a thicker Paleogene stratum and the S velocity of the Paleogene stratum is much higher than that of the Neogene and Quaternary stratums.The sedimentary structure provides a base to determine crustal structure beneath the Bohai Bay basin.
-
Keywords:
- receiver function /
- Bohai Bay basin /
- sedimentary structure /
- neighborhood algorithm
-
-
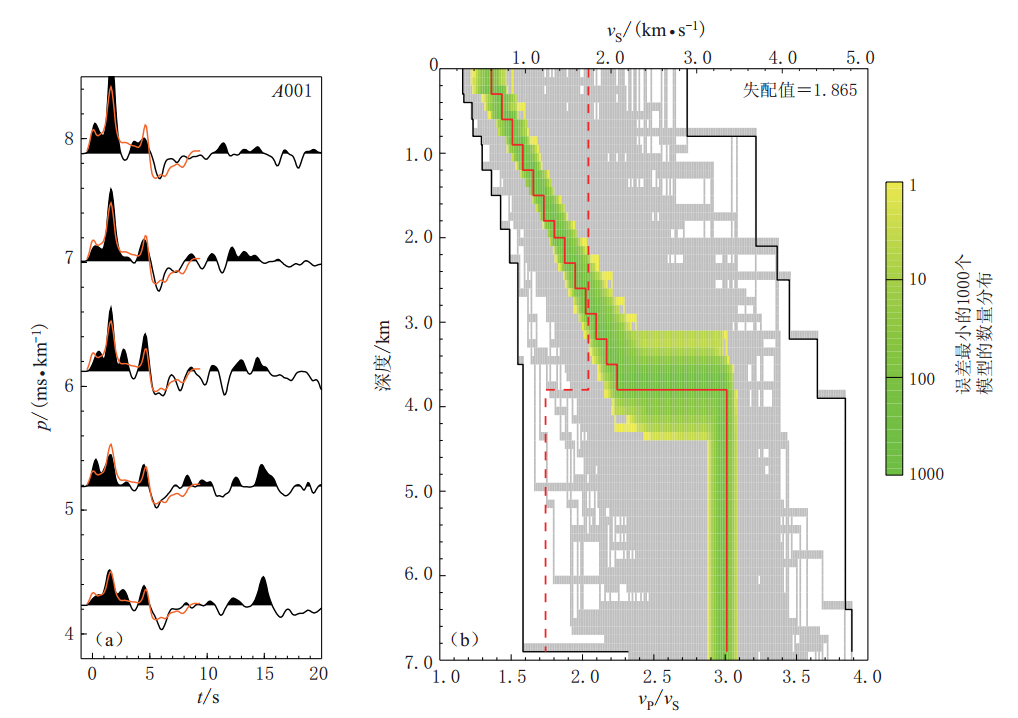
图 4 利用相邻算法得到的波形模拟结果(a)及S波速度模型与波速比(b)图(a)中红色波形为利用最佳模型计算出的波形;图(b)中灰色区域为整个模型参数的搜索范围,绿色区域为误差最小的1 000个模型的分布区域,红色实线为最佳模型,红色虚线为基于IASP91模型得到的波速比vP/vS
Figure 4. The results of waveform fitting by the neighboring algorithm method (a)Waveform comparison,where the red waves are the synthetic wave calculated by the best-fitting model; (b)S-velocity velocity models and vP/vS ratios where the gray shaded area shows the entire sampled model space,and the green area represents the best 1 000 models that have the lowest misfit,red trace represents the model with lowest misfit,red dashed trace represents vP/vS from IASP91 model
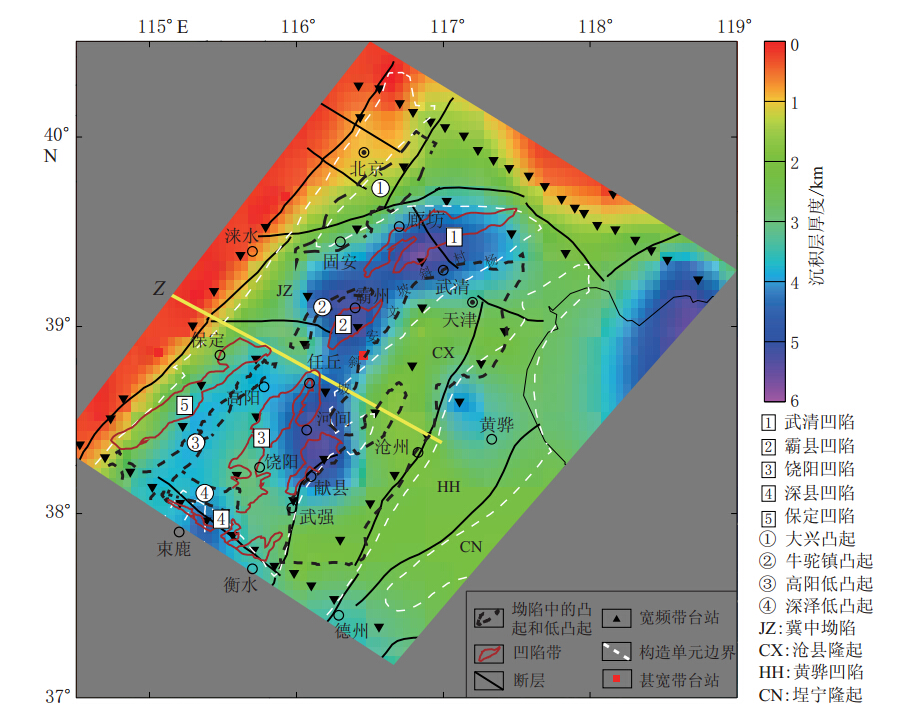
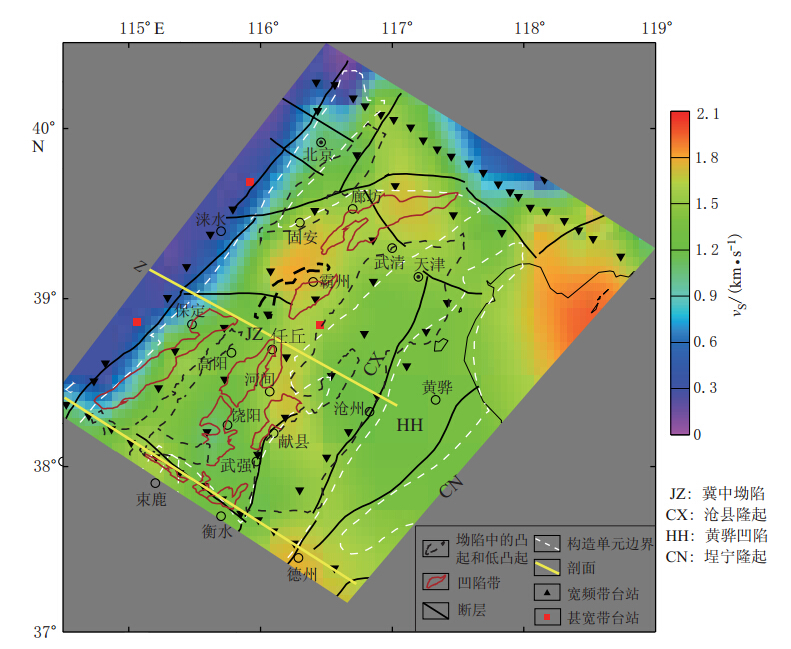
图 5 渤海湾盆地沉积层厚度分布地质结构据林世辉,龚育龄,(2005)修改;Z测线引自Zheng等(2005)
Figure 5.
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
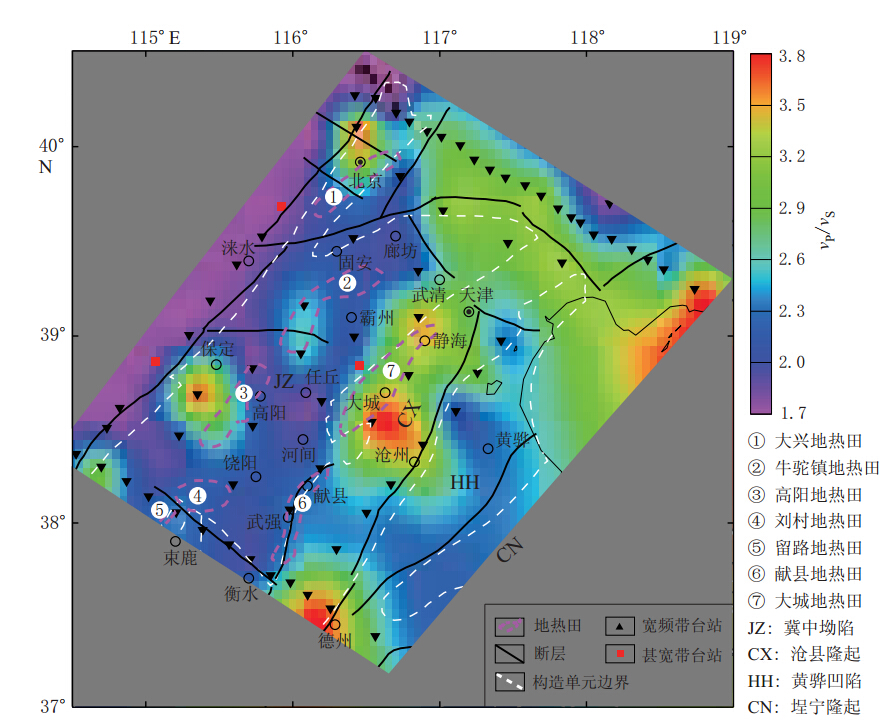
图 6 渤海湾盆地沉积层波速比分布(地热田根据梁宏斌等(2010)修改)
Figure 6. Distribution of the vP/vS ratioin the sedimentary of Bohai Bay basin where the geothermal field is modified from Liang et al(2010) ①Daxing geothermal field; ② Niutuozheng eothermal field; ③Gaoyang geothermal field;④ Liucun geothermal field; ⑤ Liulu geothermal field; ⑥ Xianxian geothermal field; ⑦ Dacheng geothermal field;JZ: Jizhong depression; CX: Cangxian uplift; HH: Huanghua depression; CN:Chengning uplift
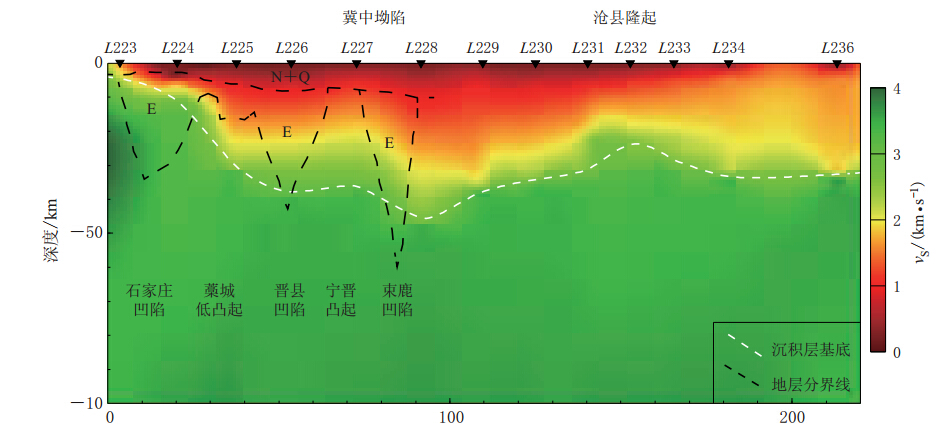
图 8 测线L纵剖面的S波速度分布(地质结构陆克政等(1997))
Figure 8. The S wave velocity structure of the profile L where the tectonic structure is from Lu et al(1997)
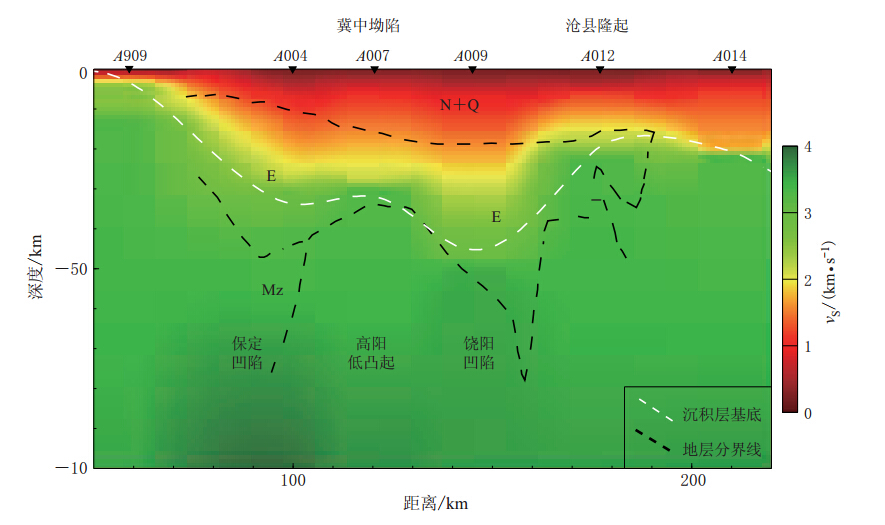
图 9 测线Z的纵切面沉积层分布测线Z选取与Zheng等(2005)的测线位置相同,地质结构引自陆克政等(1997)
Figure 9. The S velocity structure of the profile Z The location of profile Z is from Zheng et al(2005),and the tectonic structure is from Lu et al(1997)
表 1 各台站最佳沉积层结构模型参数
Table 1 The best sedimentary model of eachstation

-
嘉世旭, 齐诚, 王夫运, 陈棋福, 张先康, 陈颙. 2005. 首都圈地壳网格化三维结构[J]. 地球物理学报,48 (6): 1316-1324. Jia S X, Qi C, Wang F Y, Chen Q F, Zhang X K, Chen Y. 2005. Three dimensional crustal gridded structure of the Capital area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,48 (6): 1316-1324 (in Chinese).
李三忠, 索艳慧, 戴黎明, 刘丽萍, 金宠, 刘鑫, 郝天珧, 周立宏, 刘保华, 周均太, 焦倩. 2010. 渤海湾盆地形成与华北克拉通破坏[J]. 地学前缘,17 (4): 64-89. Li S Z, Suo Y H, Dai L M, Liu L P, Jin C, Liu X, Hao T Y, Zhou L H, Liu B H, Zhou J T, Jiao Q. 2010. Development of the Bohai Bay Basin and destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,17 (4): 64-89 (in Chinese).
梁宏斌, 钱铮, 辛守良, 赵克镜, 朱连儒. 2010. 冀中坳陷地热资源评价及开发利用[J]. 中国石油勘探,15 (5): 63-68. Liang H B, Qian Z, Xin S L, Zhao K J, Zhu L R. 2010. Assessment and development of geothermal resources in Jizhong Depression [J]. China Petroleum Exploration,15 (5): 63-68 (in Chinese).
林世辉, 龚育龄. 2005. 冀中坳陷现今地温场分布特征[J]. 东华理工学院学报,28 (4): 359-364. Lin S H, Gong Y L. 2005. Distribution characteristics of geotemperature field in Jizhong Depression, North China[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology,28 (4): 359-364 (in Chinese).
陆克政, 漆家福, 戴俊生, 杨桥, 童亨茂. 1997. 渤海湾新生代含油气盆地构造模式[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 72-141. Lu K Z, Qi J F, Dai J S, Yang Q, Tong H M. 1997. The Structural Model of Cenozoic Hydrocarbon Basin in Bohai Bay[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 72-141 (in Chinese).
罗艳, 崇加军, 倪四道, 陈棋福, 陈颙. 2008. 首都圈地区莫霍面起伏及沉积层厚度[J]. 地球物理学报,51 (4): 1135-1145. Luo Y, Chong J J, Ni S D, Chen Q F, Chen Y. 2008. Moho depth and sedimentary thickness in Capital region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,51 (4): 1135-1145 (in Chinese).
Allen M B, Macdonald D I M, Zhao X, Vincent S J, Brouet-Menzies C. 1997. Early Cenozoic two-phase extension and Late Cenozoic thermal subsidence and inversion of the Bohai Basin, northern China[J]. Mar Petrol Geol,14 (7/8): 951-972.
Chen L, Wang T, Zhao L, Zheng T Y. 2008. Distinct lateral variation of lithospheric thickness in the Northeastern North China Craton[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,267 (1/2): 56-68.
Chen L. 2009. Lithospheric structure variations between the eastern and central North China Craton from S- and P-receiver function migration[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,173 (3/4): 216-227.
Haskell N A. 1964. Radiation pattern of surface waves from point sources in a multi-layered medium[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,54 (1): 377-393.
Kikuchi M, Kanamori H. 1982. Inversion of complex body waves[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,72 (2): 491-506.
Li J, Tian B F, Wang W M, Zhao L F, Yao Z X. 2007. Lateral variation in the sedimentary structure of the west Bohai Bay Basin inferred from P-multiple receiver functions[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,97 (4): 1355-1363.
Ligorría J P, Ammon C J. 1999. Iterative deconvolution and receiver-function estimation[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,89 (5): 1395-1400.
Sambridge M. 1999. Geophysical inversion with a neighbourhood algorithm: I. Searching a parameter space[J]. Geophys J Int,138 (2): 479-494.
Zhao L, Zheng T Y. 2005. Seismic structure of the Bohai Bay Basin, northern China: Implications for basin evolution[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,231 (1/2): 9-22.
Zheng T Y, Zhao L, Chen L. 2005. A detailed receiver function image of the sedimentary structure in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,152 (3): 129-143.
Zheng T Y, Chen L, Zhao L, Xu W W, Zhu R X. 2006. Crust-mantle structure difference across the gravity gradient zone in North China Craton: Seismic image of the thinned continental crust[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,150 (1/2): 43-58.
Zhou J X, Zhou J S. 2006. Mechanisms of Cenozoic deformation in the Bohai Basin, Northeast China: Physical modeling and discussions[J]. Science in China: Series D,49 (3): 258-271.
Zhu L P. 2004. Refining the Southern California 3D Model in the Los Angeles Area[R/OL]. [2013-12-18]. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/research/external/reports/03HQGR0100.pdf.
Zhu L P, Mitchell B J, Akyol N, Cemen I, Kekovali K. 2006. Crustal thickness variations in the Aegean region and implications for the extension of continental crust[J]. J Geophys Res,111 (B1): B01301. doi:10.1029/2005JB003770.
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 朱冰清,王伟涛,谢俊举,李志伟,姚新强,黄翔,卞真付,林逸. 利用近震Sp转换波到时和远震接收函数P波峰值延迟研究华北盆地浅部结构. 地球物理学报. 2024(06): 2172-2190 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王秋实,李永华,武岩. 使用接收函数自相关约束渤海湾北部沉积层结构. 地球物理学报. 2024(06): 2191-2203 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张瑞青,况春利,张笑晗,李永华. 沉积层结构被动源探测方法及其在典型盆地的应用. 地球与行星物理论评(中英文). 2023(01): 12-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. Jinkai An,Song Huang,Xiangyang Chen,Tao Xu,Zhiming Bai. Research progress in geophysical exploration of the Antarctic ice sheet. Earthquake Research Advances. 2023(03): 72-84 .  必应学术
必应学术
5. 刘嘉栋,丁志峰,武岩,姜磊. 利用远震接收函数研究华北克拉通北部造山带地壳厚度及泊松比. 地震学报. 2022(03): 357-373 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 姜磊,丁志峰,高天扬,黄翔. 利用背景噪声和接收函数研究华北克拉通地壳结构. 地球物理学报. 2021(05): 1585-1596 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王文才,杨晓鹏,苏小芸,陈丽君,王燕,刘红玫. 基于强震记录的唐山5.1级地震强地面运动特征及局部场地效应分析. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2021(10): 1063-1068 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 马海超,储日升,盛敏汉,危自根. 利用深源近震高频Ps转换波震相研究松辽盆地沉积层结构. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2020(02): 214-220 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵珊,刘华,蒋有录,王永诗,郝雪峰,张聪. 渤海湾盆地缓坡带类型及其油气分布特征. 石油与天然气地质. 2019(02): 223-235 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 齐玉妍,孙丽娜,吕国军,李慧. 2012年唐山4.8级地震强震动记录特征及场地相关特性分析. 地震. 2019(04): 172-180 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 邓莉,谭毅培,刘双庆,马婷,卞真付,曹井泉. 天津滨海爆炸事件检测与相对定位研究. 地震. 2018(03): 158-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 武岩,丁志峰,王兴臣,朱露培. 华北克拉通地壳结构及动力学机制分析. 地球物理学报. 2018(07): 2705-2718 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 余大新,耿冠世. 利用背景噪声估计华北地区场地放大效应. 地震工程学报. 2017(04): 719-724 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 高占永,张瑞青,吴庆举,张广成. 中国东北地区下方660km间断面研究. 地震学报. 2015(05): 711-721+885 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(12)




 下载:
下载: