Analysis of terrain effect on the properties of ground motion
-
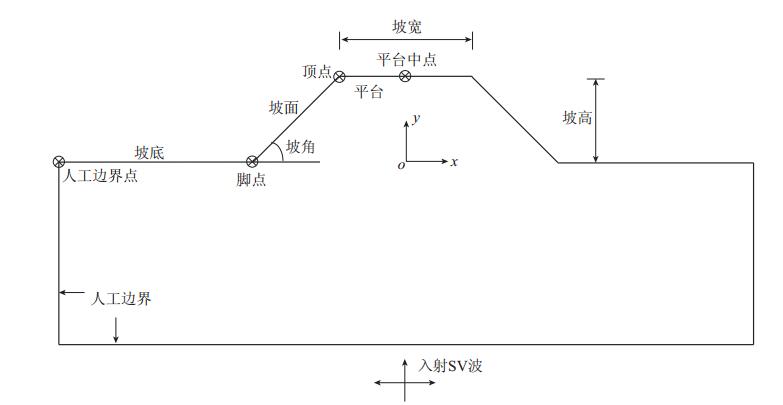
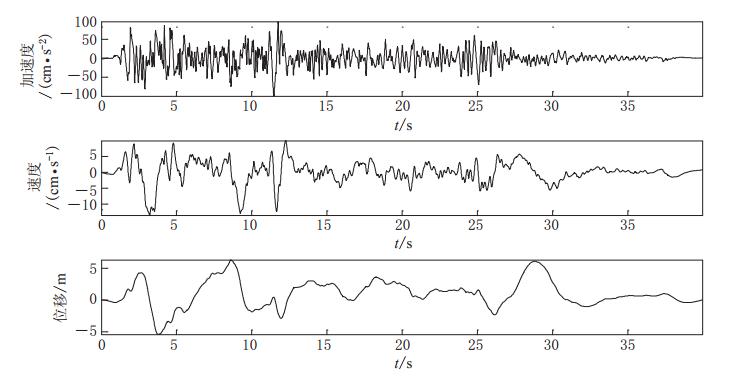
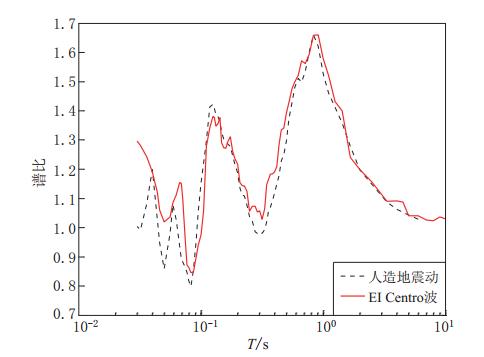
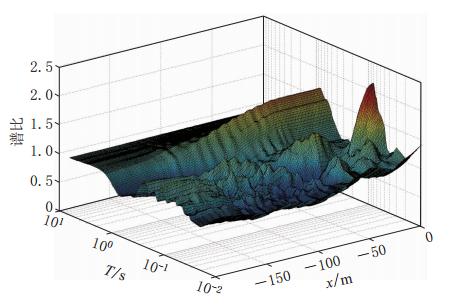
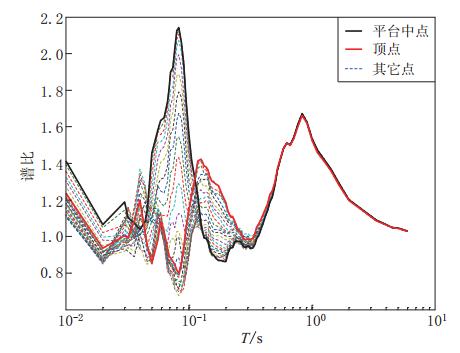
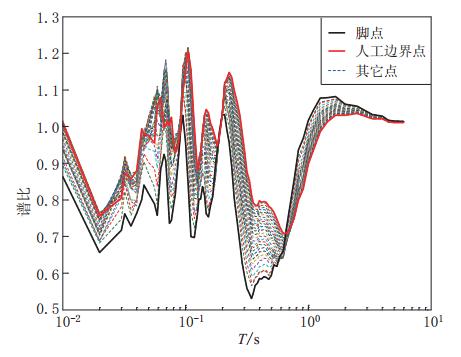
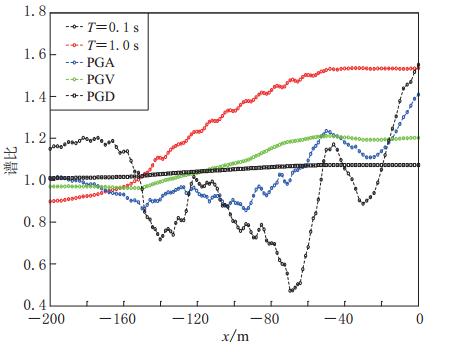
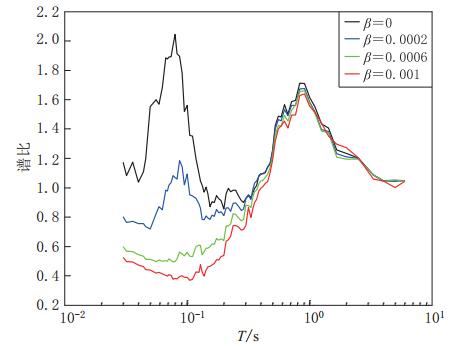
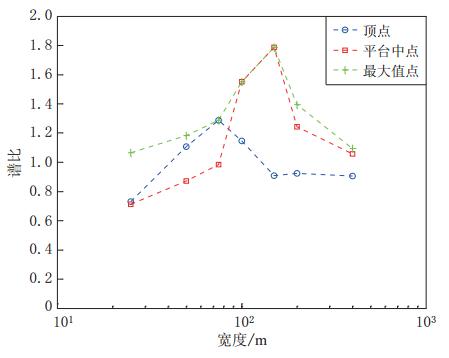
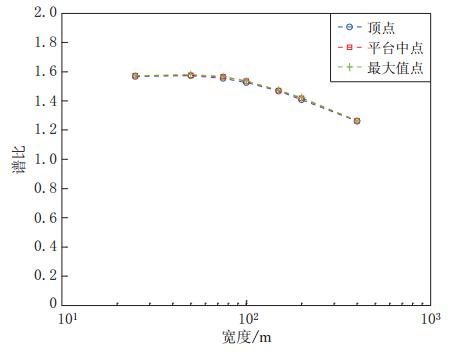
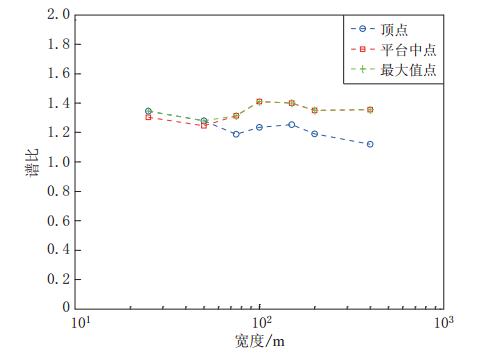
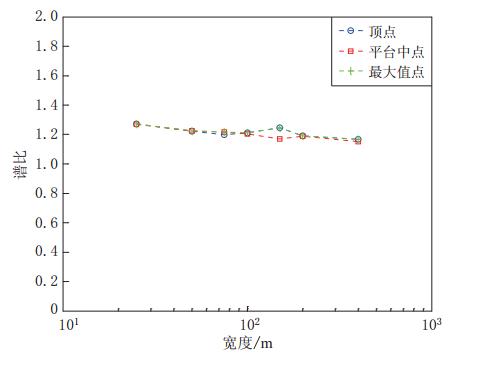
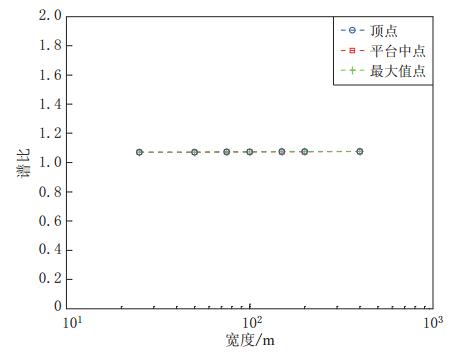
摘要: 采用基于ABAQUS平台的显式有限元动力学分析方法,结合人工黏弹性边界理论,研究了局部凸起地形对地震动特性(包括反应谱、峰值加速度、峰值速度和峰值位移等)的影响,分析了台地宽度对地形放大效应的影响.结果表明:凸起地形平台段空间点地震动受地形效应影响较大,在零阻尼条件下,其谱比曲线呈双峰特点,.8—0.9s的中长周期段谱比达到一个较大值1.6,在0.08—0.09s的高频段谱比超过2.0,且最大值出现在平台中点;对于凸起地形斜坡段,在大部分周期点处,顶点的谱比高于其它斜坡点,而且在周期超过0.4s的频段,斜坡段观测点的谱比表现出较明显的规律性,即越靠近顶点的观测点,其谱比值越大;坡底段地表不同观测点的谱比基本在脚点与计算边界点(人工边界点)对应的谱比值之间变化,在不同的频段均表现出较明显的规律性.凸起地形平台段宽度对地震动高频成分的放大效应具有较大影响,但只局限在一定的宽度范围内,随着宽度的增大,其对地形放大效应的影响逐渐减弱. 此外,台地宽度的变化对地震动峰值加速度的放大效应有一定的影响,而对峰值速度、峰值位移的放大效应的影响则不明显.Abstract: The explicit finite element analysis method combined with the artificial viscous-elastic boundary theory based on the platform ABAQUS is performed to evaluate the terrain effects on ground motion (such as the response spectrum, peak acceleration, peak velocity and peak displacement), and the influence of the terrain width on its amplification effects is studied. The results show that the ground motions on the platform are affected most seriously by the topography; in the zero damping conditions, the spectral ratio curves present the characteristics of double peaks,with their values being a higher value of 1.6 in the long period range of 0.8—0.9 s and exceeding 2 in the high-frequency range of 0.08—0.09 s, and the maximum ratio appearing at the midpoint of the platform. For the slope section, as to most natural periods of response spectrum, the spectral ratios of the vertices are higher than the other surface points on theslope.Inaddition,inthenatural period beyond 0.4 s, the spectral ratios of the spatial points on the slope show some regularity: the closer to the vertex the observation point, the greater the spectral ratio.Spectral ratios of different observation points on the bottom change between spectral ratios corresponding to basic foot point and those to the boundary point,ortheartificial boundary point, which is obvious in different frequency bands. The width of terrain imposes significant influence on its amplification effects on high-frequency componentsofgroundmotion.However, such influenceislimited in some range of width, and with the increase of width, the influence of width on the topographic amplification effects becomes weak. In addition, the width of terrain influences the amplification effect on the peak acceleration of ground motion to some extent, while its influences on the amplification effects on thepeakground velocity and peak ground displacement are not distinct.
-
本文在收集整理分析中国大陆1902—2014年132次板内浅源地震事件的相关数据(包括震级、 发震时间、 地点、 断层类型、 地震矩、 地表破裂长度、 余震分布长度、 波谱反演得到的震源处破裂长度等)的基础上,给出了震级与震源破裂长度和余震分布长度的经验公式,并对震级与破裂长度之间的相关性进行了分析. 表 1给出了本文所用部分地震序列的相关参数.
表 1 本文所用部分地震序列及其相关参数Table 1. Partial earthquake sequences of China and related parameters used in this paper序号 发震时刻 地点 北纬/° 东经/° M0/(1018 N·m) 中国MS 美国MS MW L1/km L2/km L3/km 断层类型 来源 年-月-日 时:分 1 1988-11-06 21:03 云南澜沧 22.9 99.8 36.6 7.6 7.3 7.0 70 70 右旋 邓起东等(1992) 2 1996-02-03 19:14 云南丽江 27.3 100.2 9.94 7.0 6.5 6.6 42 41 正 蒋海昆等(2007) 3 2008-03-21 06:33 新疆于田 35.6 81.6 54.3 7.3 7.3 7.1 31 正 徐锡伟等(2011) 4 2008-05-12 14:28 四川汶川 31.0 103.4 897 8.0 8.1 7.9 300 逆 张勇等(2008) 5 2010-04-14 07:49 青海玉树 33.2 96.6 7.1 6.9 65 65 走滑 陈立春等(2010) 6 2013-04-20 08:02 四川芦山 30.3 103.0 10.2 7.0 6.8 6.6 40 逆 苏金蓉等(2013) 7 2014-08-03 16:30 云南鲁甸 27.1 103.3 2.12 6.5 6.2 6.2 22 走滑 张广伟等(2014) 8 2014-10-07 21:49 云南景谷 23.4 100.5 1.89 6.6 6.1 6.1 20 左旋 徐甫坤等(2015) 注: M0为地震矩,L1表示地表破裂长度,L2表示余震长度,L3表示基于波谱方法得到的震源处破裂长度. 本文所用面波震级有两种: 一种是采用中国记录的面波震级(下文简称为中国面波震级)MS-China,另一种是采用美国地质调查局(USGS)和全球地震矩张量(global centroid moment tensor,简写为GCMT)目录所记录的面波震级(下文简称为美国面波震级)MS-US,数据均从USGS和GCMT网站上下载所得,其中1976年以前的MS-US引自USGS,1976年以后的MS-US引自GCMT. 所用矩震级也分为两部分: 1976年以后的地震事件矩震级MW引自GCMT,1976年之前的矩震级MW引自USGS,GCMT和相关文献. 所有矩震级均保留一位小数,参与回归分析.
图 1a给出了美国面波震级MS-US与矩震级MW的回归关系,可以看出: MS-US为5.5—7.7时,其值与MW基本相等; MS-US为4.5—5.5时,其值较MW整体偏小; MS-US>7.7时,其值较MW整体偏大. 图 1b给出了中国面波震级MS-China与矩震级MW的回归关系,可以看出,MS-China为4.5—8.6时,MS-China>MW,但随着震级的增大,这种差距在减小. 图 1c给出了MS-China与MS-US的对比,可以看出,二者的相对平均偏差为5.5%,最大绝对偏差为0.19,而且相对偏差大于10%的MS-China主要集中在4.5—6.0之间.
震源破裂长度的估算方法中,有两种应用得较多. 其一,采用余震空间分布的方法来确定; 其二,采用地震波资料反演震源参数,通过P波或S波的时频特性来求解震源的破裂参数(沈建文等,1990). 鉴于MS<6.0地震所造成的破裂不明显或位移不显著,本文选取MS6.0—8.6地震事件用于拟合震级与断层破裂长度的关系.
针对不同的断层类型,利用最小二乘法计算分析了中国面波震级(MS-China)、 美国面波震级(MS-US)、 平均面波震级(
S)、 矩震级与地表破裂长度、 余震破裂长度和基于波谱分析所获取的地下破裂长度之间的关系. 因MS-China与MS-US的偏差不大,这里仅给出平均面波震级 S与地表破裂长度和地下破裂长度之间的拟合表达式,具体列于表 2. 本文参考Wells和Coppersmith(1994)的方法,通过改变数组的大小来评估各种相关关系的稳定性,并通过在每组数据中抽出两组数据后观察其相关系数的变化来检测数据拟合的稳定性. 结果显示: 数据点为10个或10个以上时,震级与破裂长度之间的相关性较好,两组数据的回归系数在95%的置信水平下无明显区别,其相关系数的差值基本上都在小数点后两位; 8个数据点以下的回归则视为不稳定. 因此在地表破裂长度以及由波谱反演得到的地下破裂长度回归方程中仅分析走滑断层和所有断层两种情况下的回归公式,以便根据各个回归关系式的相关系数来评估震级与破裂长度之间的相关性. 表 2 震级与破裂长度的回归关系式Table 2. Regression relationship between magnitude and rupture length经验公式 断层类型 a b 相关系数 标准差 震级范围 样本数 MS=a+blgL1 走滑 5.7040 0.9871 0.774 0.2699 6.9—8.6 20 所有 5.9024 0.8954 0.823 0.2803 6.4—8.6 30 MW=a+blgL1 走滑 5.0865 1.2114 0.731 0.3766 6.4—8.6 21 所有 5.3162 1.1201 0.753 0.3906 6.0—8.6 29 MS=a+blgL2 走滑 3.7380 1.9259 0.899 0.3589 5.0—8.1 37 逆 4.2191 1.3478 0.786 0.4363 4.9—8.1 26 正 3.5181 1.7882 0.543 0.5912 4.9—7.3 10 所有 3.8235 1.7325 0.817 0.4594 4.9—8.1 78 MW=a+blgL2 走滑 3.7505 1.7830 0.898 0.3373 5.1—7.8 38 逆 4.2674 1.2002 0.816 0.3393 5.1—7.9 28 正 3.4062 1.8221 0.880 0.2941 5.0—7.0 16 所有 3.8005 1.6414 0.853 0.3746 5.0—7.9 82 MS=a+blgL3 走滑 3.5189 2.0049 0.833 0.5492 5.1—8.0 16 所有 3.5577 2.0162 0.812 0.5548 4.9—8.0 21 MW=a+blgL3 走滑 3.6598 1.8143 0.848 0.4343 5.2—7.7 20 所有 3.7433 1.7899 0.836 0.4259 5.2—7.7 25 注: 第一列经验公式中,L1表示地表破裂长度,L2表示余震破裂长度,L3表示基于波谱反演所得的地下破裂长度. 从表 2可以看出: 地表破裂长度与面波震级的相关性优于其与矩震级的相关性; 余震破裂长度和基于波谱反演所得地下破裂长度与矩震级的相关性优于其与面波震级相关性. 图 2a比较了本文所得经验公式与邓起东等(1992)给出的经验公式(以下简称邓式),可以看出,当MS为6.4—8.6时邓式所对应的地表破裂长度L1始终小于本文结果,并且随着震级的增大,由邓式计算出的破裂长度增大的速率大于本文公式,这可能是由于本文仅使用了1902年以后的地震数据并增加了最新的地震数据所致; 图 2b中,当MS>5.3时,本文结果大于龙锋等(2006)的经验公式所确定的地下破裂长度; 图 2c为本文结果与Wells和Coppersmith(1994)经验公式所得结果的比较,可以看出,本文经验公式所对应的由余震确定的地下破裂长度总体比Wells和Coppersmith(1994)所得结果大,但是随着震级的增大,这种差距在逐渐减小.
通过比较不同断层类型的回归方程来评估断层类型对破裂长度的影响,其结果表明,震级与破裂长度的回归方程在95%的置信水平上与断层类型无关,这与Wells和Coppersmith(1994)的结果相一致.
-
-
中华人民共和国建设部. 2010. GB50011-2010建筑抗震设计规范[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 21. Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. 2010. GB50011-2010 Code for Seismic Design of Buildings[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 21 (in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 胡祎石,钟菊芳,谢星. 里龙断裂最大潜在M_W7.4地震模拟地震动特征分析. 震灾防御技术. 2024(04): 639-650 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘启方,李家祥,温瑞智. SV波入射下斜坡地形对上覆土层地震动放大的影响研究. 防灾减灾工程学报. 2022(01): 92-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 丁佳龙,郝冰,李远东,周港圣,周正华. 典型斜坡地形地震动特征分析. 震灾防御技术. 2022(03): 473-480 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 巴振宁,赵靖轩,吴孟桃,梁建文,塔拉. 基于逆断层动力学模型的三维山体地震动谱元法模拟. 地震工程与工程振动. 2021(03): 32-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郝明辉,张郁山,赵凤新. 坡地地形对地震动特性的影响分析. 震灾防御技术. 2021(02): 229-236 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. Liu Zhongxian,Shang Ce,Huang Lei,Liang Jianwen,Li Jie. Scattering of seismic waves by three-dimensional large-scale hill topography simulated by a fast parallel IBEM. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration. 2020(04): 855-873 .  必应学术
必应学术
7. 郝明辉,张郁山. 基于DEM数据的地形效应经验预测模型研究. 土木工程学报. 2019(02): 86-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李英民,王肖巍,宋维举. 动态子结构法在凸起地形地震动响应中的应用. 哈尔滨工业大学学报. 2019(06): 156-161+170 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王良,卢育霞,马林伟,孔德政. 黄土河谷场地地形放大效应的研究. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2018(02): 167-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 郝明辉,张郁山. SV波斜入射下凸起地形对地震动特性的影响分析. 震灾防御技术. 2018(03): 552-561 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 黄栋,乔建平,张小刚,陈宇龙. 堆积层斜坡地震动地形效应试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2017(03): 587-598 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张季,梁建文,巴振宁. SH波入射时凸起场地的地形和土层放大效应. 地震工程与工程振动. 2016(02): 56-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. Hao Minghui,Zhang Yushan. Analysis of the Adjacent Terrain Effect on the Properties of Ground Motion. Earthquake Research in China. 2016(01): 74-87 .  必应学术
必应学术
14. 郝明辉,张郁山. 相邻地形对地震动特性的影响分析. 中国地震. 2015(04): 656-667 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)




 下载:
下载: