Experimental research on the effects of explosion depth on the air-gun source excitation wave signals
-
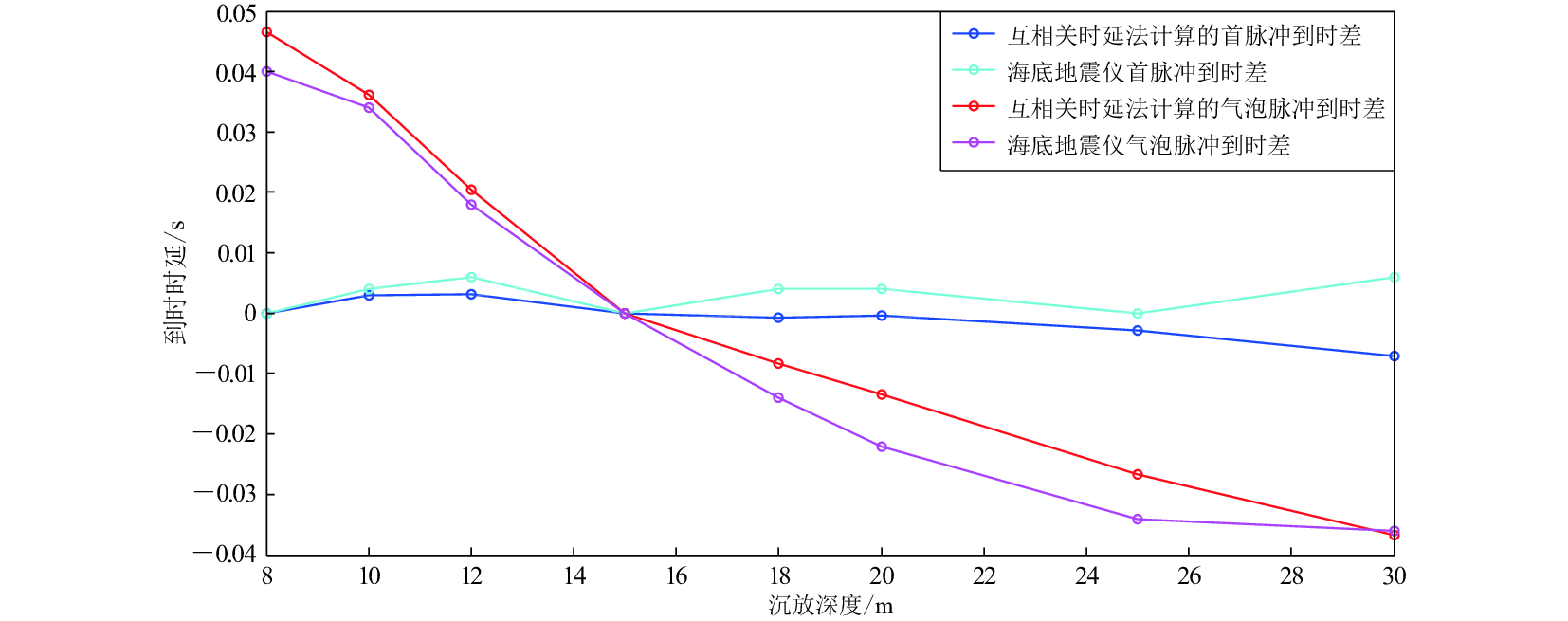
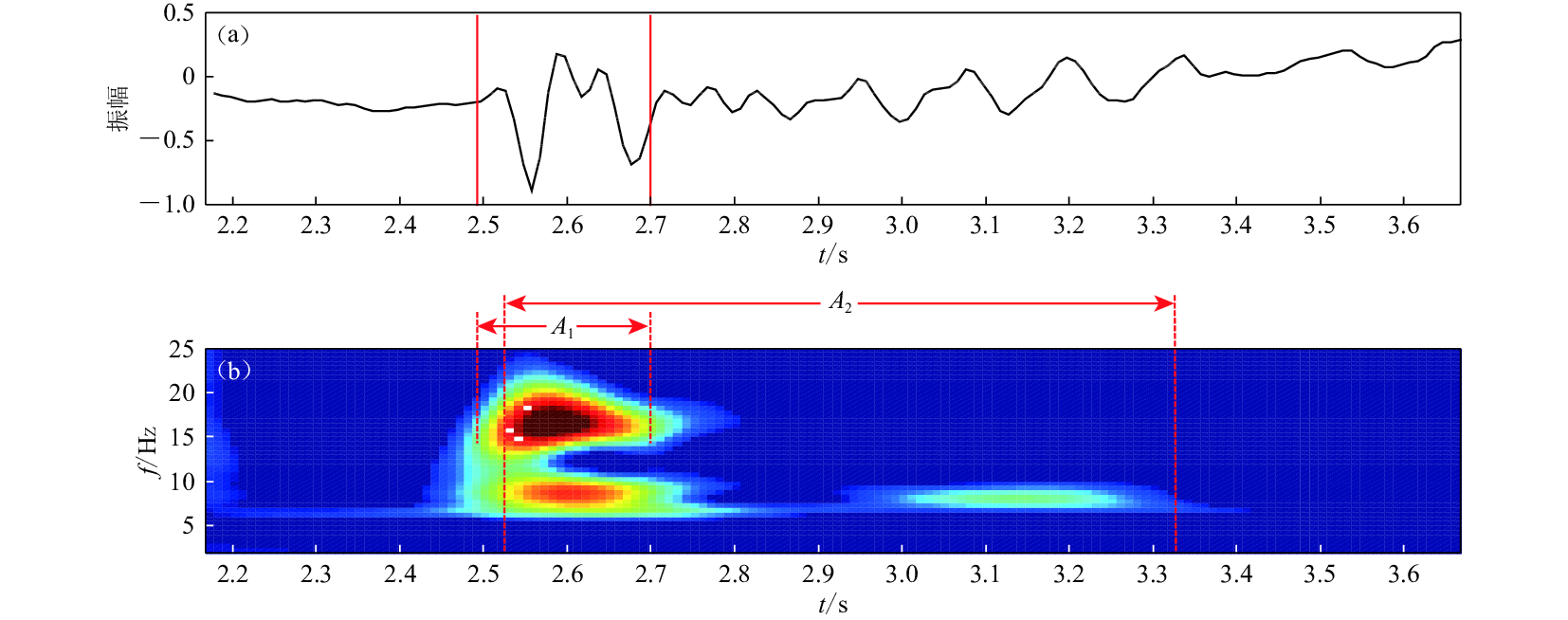
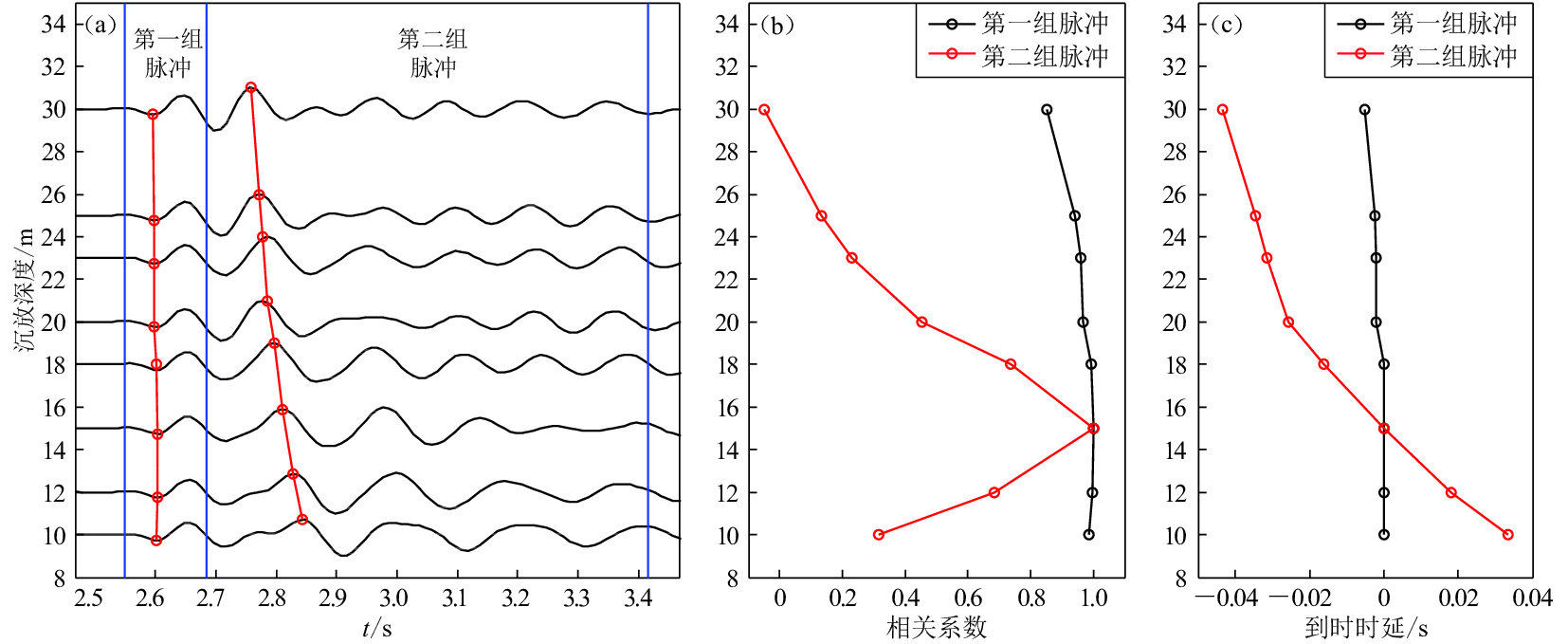
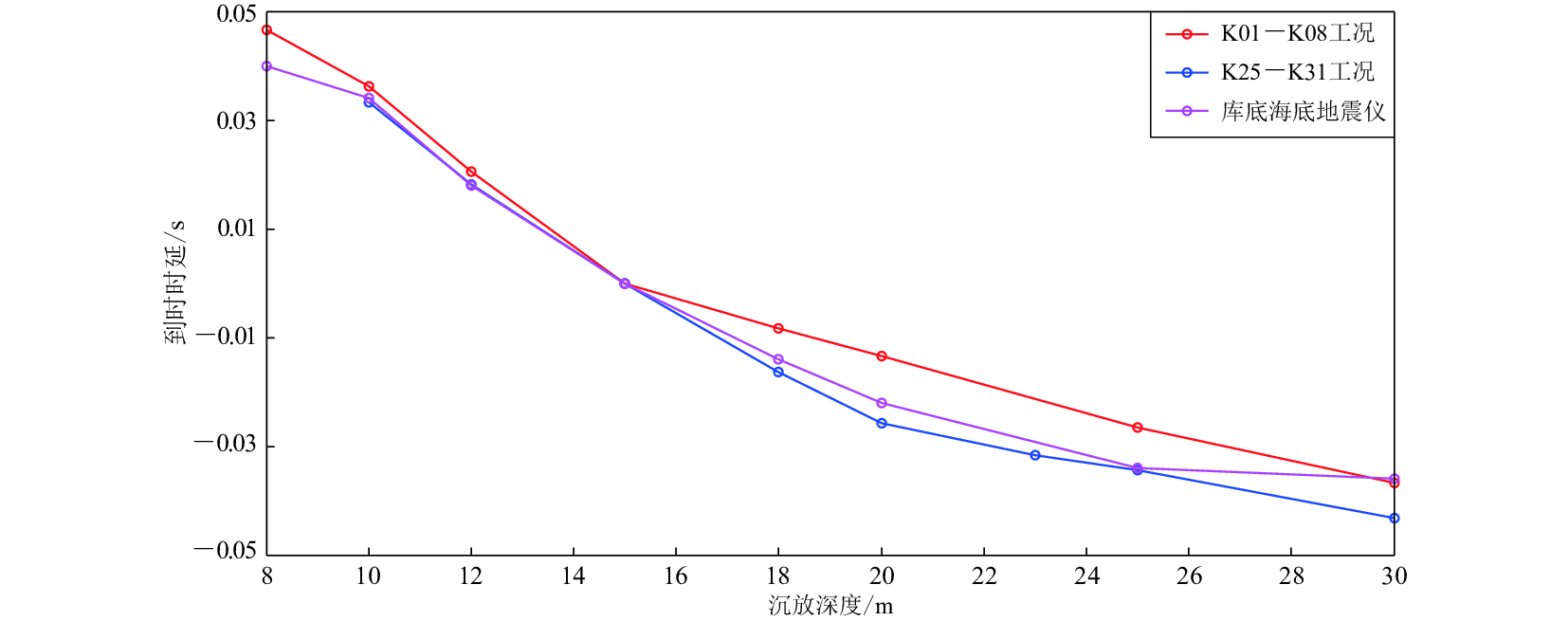
摘要: 以2014年11月福建街面水库气枪震源激发试验观测数据为研究对象,利用基于互相关的时延估计法对不同沉放深度及不同水深的气枪激发展开研究,分析沉放深度及激发环境水深对气枪震源激发信号到时的影响。结果显示:激发位置不变,气枪沉放深度在8—30 m范围内变化时,震中距为13 km的测震台站记录到的气枪信号的首脉冲到时差异很小,而气泡脉冲到时则有明显差异,且随着沉放深度的增加,气泡脉冲信号到时提前,8 m沉放深度与30 m沉放深度气泡脉冲的到时差近80 ms,这种变化与布设在库底的海底地震仪记录到的信号变化相一致,分析认为这种变化与气枪沉放深度增加引起的气枪激发信号的周期减小有关;在不同水位开展的相同沉放深度的激发信号差异不大。因此,应用气枪震源监测地壳介质变化时需注意气枪震源沉放深度变化所带来的影响。Abstract: This paper investigates the effects of explosion depth and water-level on the time delay based on the experiments carried out at Jiemian reservoir in Sanming of Fujian by Fujian Earthquake Agency in November of 2014. Analyses on the data from the station YXBM show that under the same water level, pressure pulses are affected by air-gun explosion depth so little that the correlation coefficient is high and the time delay is low, while those of the bubble pulses are significantly different. They arrive faster as the explosion depth increases. The arrival time of bubble pulses advances nearly 80 ms when the explosion depth changes from 8 m to 30 m, which is quite consistent with the records of the ocean bottom seismometer. The time delay is related to the decreasing of the period of signals resulted from the explosion depth increasing. Both of the pressure pulses and bubble pulses are similar while stimulated at the same explosion depth of air-gun under different water levels. So the explosion depth should be considered in the future study of exploring and monitoring the subsurface structure and its temporal variations using air-gun active source.
-
-
表 1 不同沉放深度的气枪源激发试验工况详表
Table 1 The experimental conditions of air-gun source excitation under different explosion depths
试验编号 水深/m 沉放深度/m 距离库底高度/m 激发枪 试验编号 水深/m 沉放深度/m 距离库底高度/m 激发枪 K01 46 8 A枪 K25 46 10 36 A,B,
C,D
4杆枪K02 10 K26 12 34 K03 12 K27 15 31 K04 15 K28 18 28 K05 18 K29 20 26 K06 20 K24 23 23 K07 25 K30 25 21 K08 30 K31 30 16 表 2 不同水位激发的试验工况详表
Table 2 The experimental condition of air-gun excitation under different water levels
试验编号 水深/m 沉放深度/m 距离库底高度/m 试验编号 水深/m 沉放深度/m 距离库底高度/m K40 55 20 35 K51 25 10 15 K41 23 32 K53 12 13 K42 25 30 K55 15 10 K43 27 28 K57 20 8 12 K44 30 25 K58 10 10 K45 35 15 20 K59 12 8 K46 18 17 K47 20 15 K48 23 12 -
陈海潮, 葛洪魁, 王宝善, 宋丽莉, 王伟涛. 2012. 利用主动震源监测地下介质衰减特性变化[J]. 地震学报, 34(6): 804-817. Chen H C, Ge H K, Wang B S, Song L L, Wang W T. 2012. Monitoring temporal variation of subsurface wave attenuation using active source[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 34(6): 804-817 (in Chinese).
林建民, 王宝善, 葛洪魁, 徐平, 陈颙. 2010. 大容量气枪震源子波激发特性分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(2): 342-349. Lin J M, Wang B S, Ge H K, Xu P, Chen Y. 2010. Characters of large volume air-gun source excitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(2): 342-349(in Chinese).
刘自凤, 苏有锦, 王宝善, 王彬, 杨军, 李孝宾. 2015. 宾川主动源地震波走时变化分析方法研究[J]. 地震研究, 38(4): 591-597. Liu Z F, Su Y J, Wang B S, Wang B, Yang J, Li X B. 2015. Study on analysis method of travel time variations of seismic wave of active source in Binchuan[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 38(4): 591-597 (in Chinese).
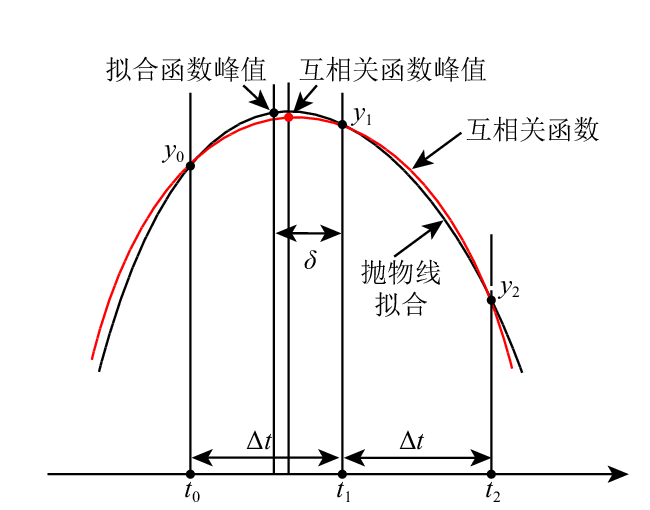
孙洋, 徐慨, 杨海亮. 2013. 基于广义互相关时延估计算法的性能分析[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 41(1): 33-34, 144. Sun Y, Xu K, Yang H L. 2013. Performance analysis of time-delay estimation based on generalized cross-correlation algorithm[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 41(1): 33-34, 144 (in Chinese).
王宝善, 王伟涛, 葛洪魁, 徐平, 王彬. 2011. 人工震源地下介质变化动态监测[J]. 地球科学进展, 26(3): 249-256. Wang B S, Wang W T, Ge H K, Xu P, Wang B. 2011. Monitoring subsurface changes with active sources[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 26(3): 249-256(in Chinese).
王宝善, 葛洪魁, 王彬, 王海涛, 张元生, 蔡辉腾, 陈颙. 2016. 利用人工重复震源进行地下介质结构及其变化研究的探索和进展[J]. 中国地震, 32(2): 168-179. Wang B S, Ge H K, Wang B, Wang H T, Zhang Y S, Cai H T, Chen Y. 2016. Practices and advances in exploring the subsurface structure and its temporal evolution with repeatable artificial sources[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 32(2): 168-179(in Chinese).
夏季, 金星, 蔡辉腾, 徐嘉隽. 2016. 大容量气枪震源子波时频特性及其影响因素[J]. 中国地震, 32(2): 249-260. Xia J, Jin X, Cai H T, Xu J J. 2016. The time-frequency characteristic of large volume air-gun source wavelet and its influencing factors[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 32(2): 249-260(in Chinese).
杨微, 葛洪魁, 王宝善, 袁松勇, 宋丽莉, 贾玉华, 李宜晋. 2010. 由精密控制人工震源观测到的绵竹5.6级地震前后波速变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(5): 1149-1157. Yang W, Ge H K, Wang B S, Yuan S Y, Song L L, Jia Y H, Li Y J. 2010. Velocity changes observed by the precisely controlled active source for the Mianzhu MS5.6 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(5): 1149-1157(in Chinese).
Aggarwal Y P, Sykes L R, Simpson D W, Richards P G. 1975. Spatial and temporal variations in tS/tP and in P wave residuals at Blue Mountain Lake, New York: Application to earthquake prediction[J]. J Geophys Res, 80(5): 718-732.
Brenguier F, Shapiro N M, Campillo M, Ferrazzini V, Duputel Z, Coutant O, Nercessian A. 2008. Towards forecasting volcanic eruptions using seismic noise[J]. Nat Geosci, 1(2): 126-130.
Céspedes I, Huang Y, Ophir J, Spratt S. 1995. Methods for estimation of subsample time delays of digitized echo signals[J]. Ultrason Imaging, 17(2): 142-171.
Lumley D E. 2004. Business and technology challenges for 4D seismic reservoir monitoring[J]. Lead Edge, 23(11): 1166-1168.
Poli P, Campillo M, Pedersen H, LAPNET Working Group. 2012. Body-wave imaging of Earth’s mantle discontinuities from ambient seismic noise[J]. Science, 338(6110): 1063-1065.
Savarensky E F. 1968. On the prediction of earthquakes[J]. Tectonophysics, 6(1): 17-27.
Schaff D P, Beroza G C. 2004. Coseismic and postseismic velocity changes measured by repeating earthquakes[J]. J Geophys Res, 109(B10): B10302.
Silver P G, Daley T M, Niu F L, Majer E L. 2007. Active source monitoring of cross-well seismic travel time for stress-induced changes[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 97(1B): 281-293.
Wang B S, Zhu P, Chen Y, Niu F L, Wang B. 2008. Continuous subsurface velocity measurement with coda wave interferometry[J]. J Geophys Res, 113(B12): B12313.
Zhan Z W, Tsai V C, Clayton R W. 2013. Spurious velocity changes caused by temporal variations in ambient noise frequency content[J]. Geophys J Int, 194(3): 1574-1581.





 下载:
下载: