Correlation analysis on co-seismic response between well water level and temperature caused by the Nepal MS8.1 earthquake
-
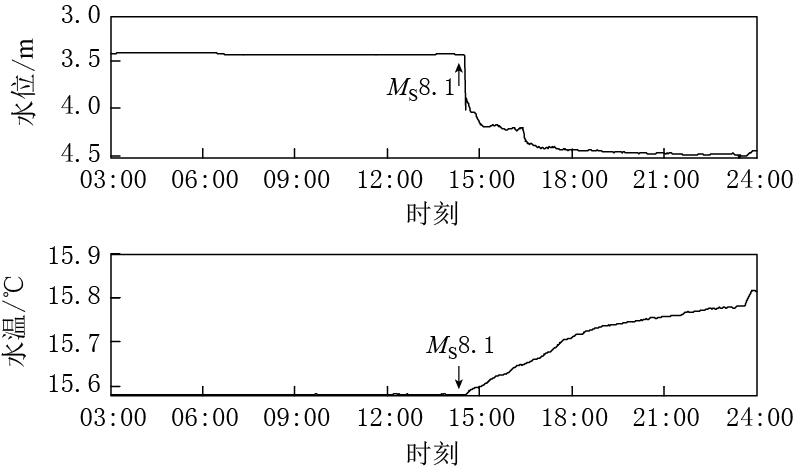
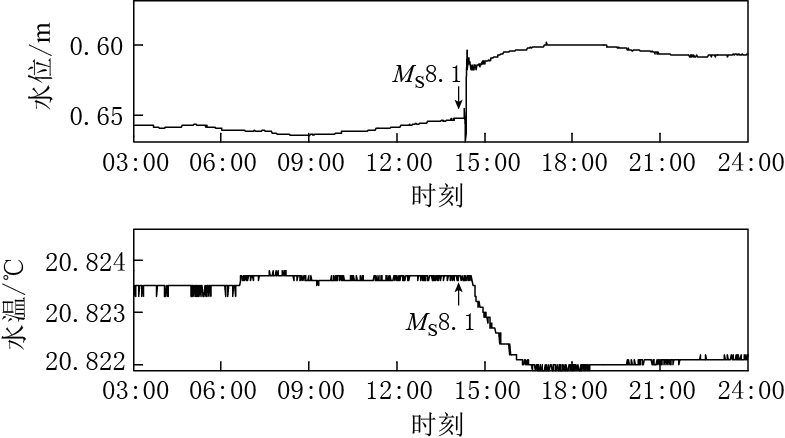
摘要: 尼泊尔MS8.1地震引起中国大陆大量地震观测井水位和水温的同震响应. 从宏观结果看, 在54个同时存在水位和水温同震效应的观测井中, 有51口观测井的变化类型为水位上升-水温上升、 水位下降-水温下降、 水位振荡-水温上升或下降(以下降为主), 井水位与井水温同震效应表现出良好的相关性, 这可能与地下水动力学作用有关; 有3口观测井的水位变化与水温变化方向相反, 且水温变化均为震后效应. 另外, 有1口观测井水位无变化而水温同震效应明显. 这些不同类型的同震变化与井孔条件、 水温梯度、 传感器位置及水位埋深等多种因素有关. 从微观结果看, 井水位同震效应出现的时间及变化幅度与井水温同震效应出现的时间及变化幅度之间的关联性比较复杂, 这与井孔条件和温度梯度等因素有关.
-
关键词:
- 尼泊尔MS8.1地震 /
- 同震效应 /
- 地下水动力学 /
- 机理
Abstract: It were recorded that a large number of co-seismic responses of well water level and temperature in Chinese mainland caused by the Nepal MS8.1 earthquake. There is good correlation between well water level and water temperature for 51 observation wells, which appears as water level rise to water temperature rise, water level drop to water temperature drop or water level oscillation to water temperature rise/drop (most of the co-seismic water tempe-ratures drop). The good correlation is resulted from the groundwater dynamics. As for three observation wells, the change in water level is in the opposite direction to the change in water temperature, which is the post-seismic effect. Meanwhile, one observation well has only water temperature co-seismic change but no water level change, which may have great relation to the borehole condition, water temperature gradient, sensor position and water level depth. The results also show that there is complex relationship between the initial time and amplitude of groundwater level change and those of groundwater temperature change, which is affected by borehole condition and temperature gradient.-
Keywords:
- Nepal MS8.1 earthquake /
- co-seismic response /
- groundwater dyna-mics /
- mechanism
-
-
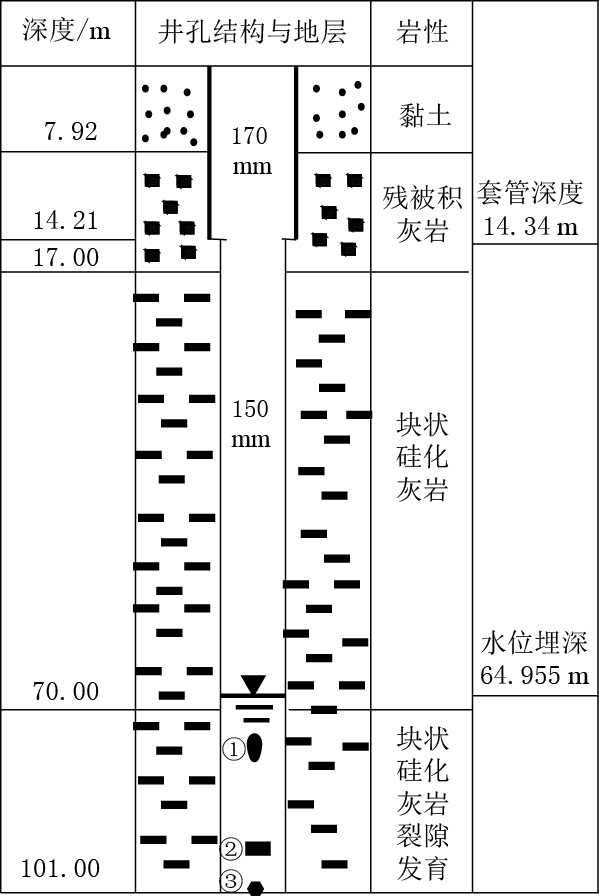
图 3 昌平地震台西1井井孔地层柱状图及水温仪探头位置
① SZW-1水温仪探头(浅);② ZKGD3000地下水数据监测系统;③ SZW-1水温仪探头(深,放置底部,现已深埋泥中)
Figure 3. Borehole stratigraphic column and water temperature analyzer probe position of the west 1 well at the seismic station Changping
①SZW-1 water temperature probes (shallow); ② ZKGD3000 groundwater data monitoring system; ③ SZW-1 water temperature probes(deep,buried in the bottom mud now)
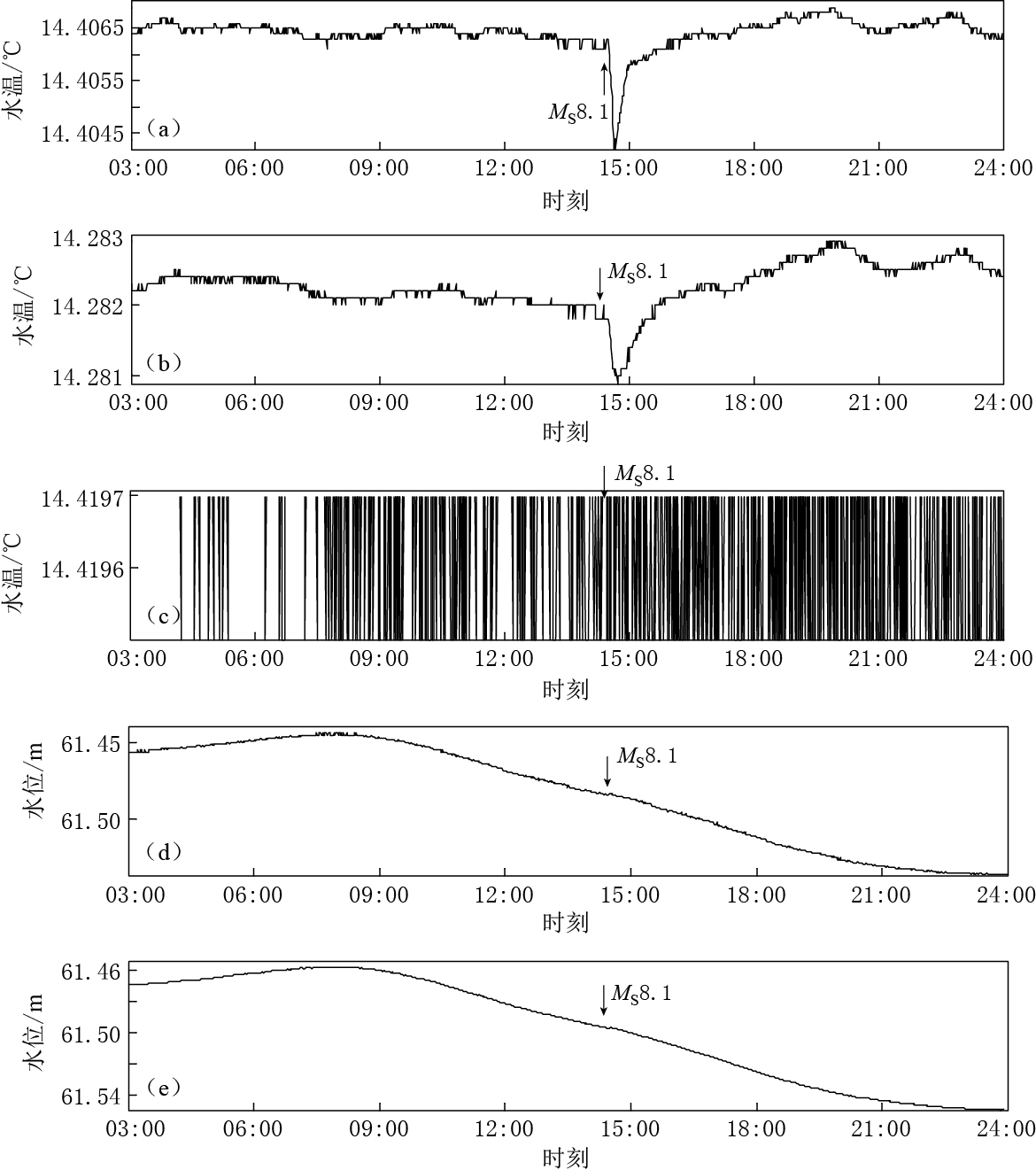
图 4 2015年4月25日昌平地震台西1井井水温和井水位记录曲线图
(a) SZW-1水温曲线(浅); (b) ZKGD3000地下水数据监测系统水温曲线; (c) SZW-1水温曲线(深);(d)SWY-Ⅱ水位曲线;(e)ZKGD3000地下水数据监测系统水位曲线
Figure 4. The curves of water temperature and water level in the west 1 well at the seismic station Changping on 25 April 2015
(a) The curve of SZW-1 water temperature (shallow); (b) The water temperature curve of ZKGD3000 groundwater data monitoring system; (c) The curve of SZW-1 water temperature (deep); (d) The curve of SWY-Ⅱ water level; (e) The water level curve of ZKGD3000 groundwater data monitoring system
表 1 尼泊尔MS8.1地震引起的中国大陆井水位和井水温同震效应统计表
Table 1 Statistics of simultaneous co-seismic step change of well water level and temperature in Chinese mainland caused by the Nepal MS8.1 earthquake
所在地区 台站名 水位 水温 变化形态 变化幅度/m 变化形态 变化幅度/℃ 北京 五里营 上升 0.041 上升 0.014 安徽 巢湖台 下降 0.085 下降 0.003 北京 左家庄 上升 0.019 上升 0.002 福建 福清江兜 上升 0.001 上升 0.002 甘肃 平凉柳湖 下降 0.107 下降 0.005 广西 桂平 上升 0.150 上升 - 海南 文昌 上升 0.010 上升 0.004 河南 焦作 上升 0.009 上升 0.001 黑龙江 黑河 上升 0.007 上升 0.011 湖北 黄梅独山 下降 0.014 下降 0.025 湖南 长沙 上升 0.017 上升 0.028 辽宁 瓦房店 上升 0.250 上升 0.006 辽宁 丹东变电 上升 0.047 上升 0.008 辽宁 沈家台 上升 0.016 上升 0.0005 山东 聊城 上升 0.115 上升 - 山东 蒙阴 下降 0.010 上升 - 山西 祁县 上升 0.180 上升 0.020 山西 沁县漫水 下降 0.058 下降 0.003 山西 孝义 下降 0.033 下降 0.010 四川 南溪 上升 0.072 上升 0.005 四川 邛崃 上升 0.010 上升 0.003 四川 泸沽湖 下降 0.136 下降 0.002 四川 西昌川32井 下降 0.022 下降 0.092 四川 德阳 下降 0.005 下降 0.002 天津 宝坻新台 下降 0.192 上升 0.020 西藏 拉萨地磁台 下降 0.0244 下降 0.005 北京 沙河 下降 0.131 下降 0.017 云南 弥勒局 上升 0.624 上升 0.012 云南 普洱大寨 上升 0.140 上升 0.010 云南 丽江局 下降 0.008 下降 0.009 云南 元谋 下降 0.004 下降 0.001 重庆 北碚柳荫 上升 0.037 下降 - 重庆 荣昌华江 上升 0.074 上升 0.003 注:"-"代表震后效应. -
刘耀炜. 2009. 动力加载作用与地下水物理动态过程研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京): 68-73. Liu Y W. 2009. Dynamic Loading and Physical Dynamics Process of Groundwater[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing): 68-73 (in Chinese).
杨竹转. 2011. 地震波引起的井水位水温同震变化及其机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所: 70-73. Yang Z Z. 2011. Variations of Well Water Level and Temperature Caused by Earthquakes and Their Generation Mechanism[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration: 70-73 (in Chinese).
尹宝军. 2010. 唐山井地下水动态特征的研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所: 145-150. Yin B J. 2010. Study on the Fluctuant Characteristic of Underground Water at Tangshan Well[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: 145-150 (in Chinese).
Wang C Y, Manga M. 2014. Earthquake and water[G]//Encyclopedia of Complexity and System Science.New York: Springer: 1-18.





 下载:
下载: