Changes of shear-wave splitting parameters in Jinping hydro-power station, Sichuan
-
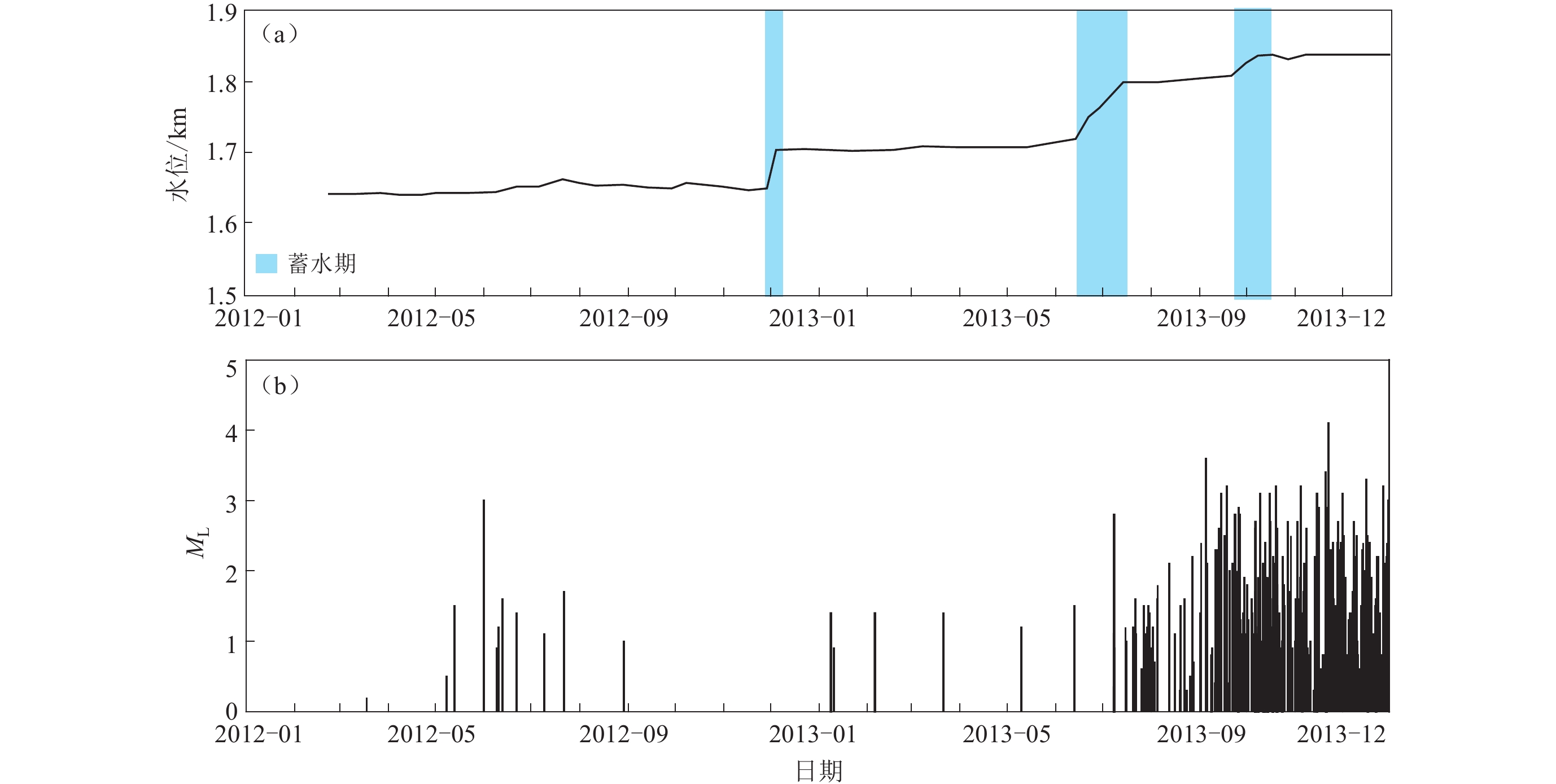
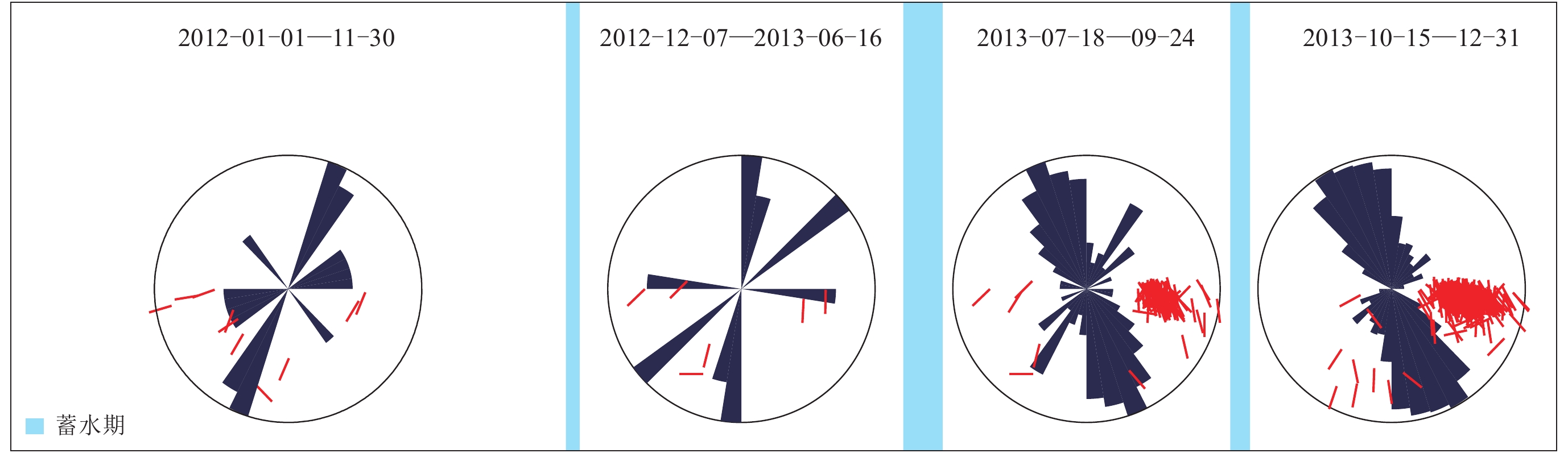
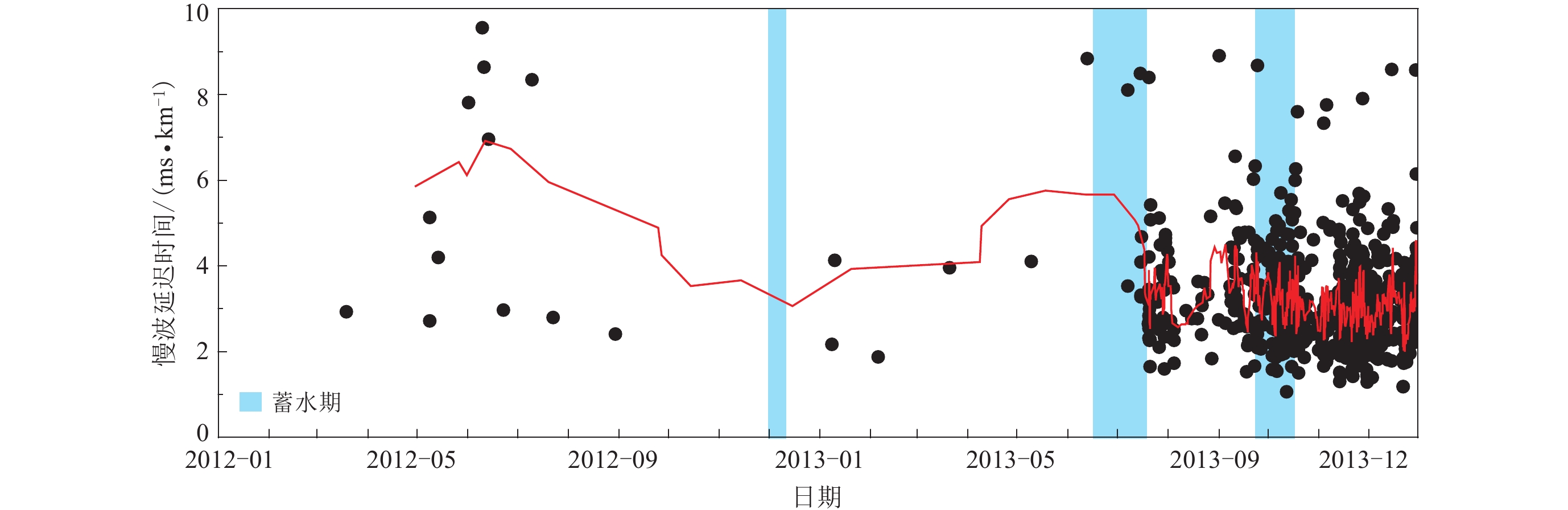
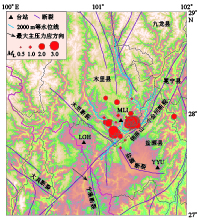
摘要: 通过分析四川锦屏水电站地区2012年1月至2013年12月库区的地震活动性和木里台的剪切波分裂参数变化,研究了水电站3次大规模蓄水对该地区地震活动性和地壳应力的影响. 结果显示:经3次蓄水,该地区的地震活动呈持续增强趋势,最终保持在较高水平,尤其是第二次蓄水之后,地震活动增强最为明显;木里台的快剪切波偏振方向在锦屏水电站3次蓄水前后表现出明显的变化. 锦屏水电站在蓄水之前,木里台快剪切波偏振方向的优势取向为北东向,与锦屏山—小金河断裂走向一致;第一次蓄水之后,快剪切波偏振方向则变得较为分散,无明显的优势取向;第二次蓄水之后,快剪切波偏振方向偏转为南东向;第三次蓄水之后,快剪切波偏振方向表现为一致的南东向;慢剪切波延迟时间在第二次蓄水前后明显变短. 这些显著的变化说明了锦屏水电站第二次蓄水之后原地小范围内的地壳应力方向迅速改变,地壳应力也随着地震活动的增强而释放.Abstract: This paper focused on the influences on the seismic activity and the crustal stress caused by three water storages in Jinping hydro-power station, according to the seismic activity in Jinping hydro-power station and the change of shear-wave splitting parameters of the station MLI from January 2012 to December 2013 . The results show that, after three water storages, the seismic activity in this region continued to increase, especially after the second water storage, and finally remained at a high level. Moreover, the polarization direction of fast shear-wave at the seismic station MLI also showed significant changes before and after three water storages of the hydro-power station. Before the water storage of Jinping hydro-power station, the predominant polarization direction at MLI seismic station was northeast, which was in agreement with the strike of Jinpingshan-Xiaojinhe fault. After the first storage, the polarization directions are distributed scatteredly. After the second water storage, the predominant polarization direction changed to southeast. And the polarization directions showed the southeast consistently after the third water storage. As for the station MLI, the delay time of slow shear-wave has changed before and after the three storages of Jinping hydro-power station, especially after the second storage the delay time of slow shear-wave decreased obviously. Thus, the seismic activity, the polarization directions of fast shear-wave and the delay time of slow shear-wave changed significantly after the second water storage of Jinping hydro-power station, suggesting that the direction of crustal stress changed quickly in a small region after the second water storage, and the crustal stress also released with the enhanced seismic activity.
-
-
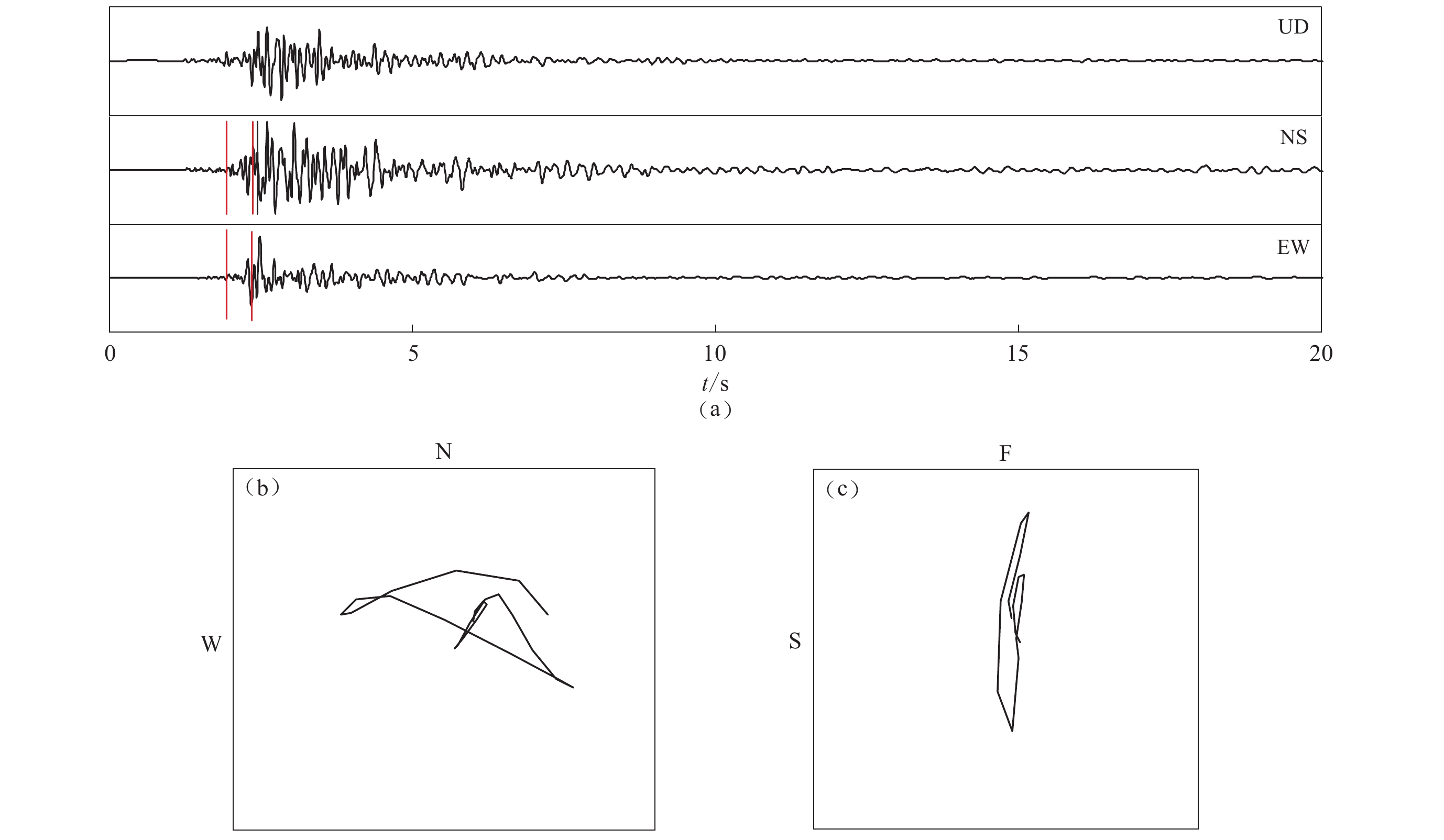
图 3 木里台剪切波分裂分析示意图
(a) 地震波三分向记录,两条红色竖线是图(b)和(c)中截取的剪切波数据段;(b) 水平向剪切波质点偏振图;(c) 快(F)、慢(S)剪切波的质点偏振图
Figure 3. The shear-wave splitting analysis of the seismic data recorded by station MLI
(a) Three-component waveform,where two red vertical lines mark the cut shear-wave section in Figs. (b) and (c);(b) Trail of particle of the shear-wave; (c) Trails of particle of the fast and slow waves
-
陈翰林, 赵翠萍, 修济刚, 陈章立. 2009. 龙滩库区水库地震震源机制及应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 31(4): 686-698. Chen H L, Zhao C P, Xiu J G, Chen Z L. 2009. Study on the characteristics of focal mechanisms of reservoir induced earthquakes and stress field in the Longtan reservoir area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 31(4): 686-698 (in Chinese).
杜方, 吴江. 2008. 四川盐源—云南宁蒗间5.8级地震发震特征[J]. 四川地震, (3): 11-19. Du F, Wu J. 2008. Character of Yuanyan M5.8 earthquake on 24 May 2001[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, (3): 11-19(in Chinese).
高原, 郑斯华, 周惠兰. 1999. 唐山地区快剪切波偏振图像及其变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 42(2): 228-232. Gao Y, Zheng S H, Zhou H L. 1999. Polarization patterns of fast shear wave in Tangshan region and their variations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 42(2): 228-232 (in Chinese).
赖院根, 刘启元, 陈九辉, 刘洁, 李顺成, 郭飙, 黄志斌. 2006. 首都圈地区横波分裂与地壳应力场特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(1): 189-196. Lai Y G, Liu Q Y, Chen J H, Liu J, Li S C, Guo B, Huang Z B. 2006. Shear wave splitting and the features of the crustal stress field in the capital circle[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(1): 189-196 (in Chinese).
刘莎, 吴朋, 杨建思, 苏金蓉. 2014. 吉林省前郭地区地震各向异性的初步探讨[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(7): 2088-2098. Liu S, Wu P, Yang J S, Su J R. 2014. Preliminary study of seismic anisotropy in Qianguo area, Jilin Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(7): 2088-2098 (in Chinese).
刘莎, 吴朋. 2015. 紫坪铺水库水位变化对剪切波分裂参数的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(11): 4106-4114. Liu S, Wu P. 2015. The effect of water level changes in Zipingpu reservoir on the parameters of shear wave splitting[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11): 4106-4114 (in Chinese).
刘莎, 吴朋, 杨建思, 苏金蓉. 2015. 2012年6月24日宁蒗-盐源MS5.7地震的剪切波分裂探讨[J]. 地震学报, 37(5): 787-795. Liu S, Wu P, Yang J S, Su J R. 2015. Discussion on shear-wave splitting of the June 24, 2012 Ninglang-Yanyuan MS5.7 earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 37(5): 787-795 (in Chinese).
秦嘉政, 刘丽芳, 钱晓东. 2009. 水库诱发地震活动特征及其预测方法研究[J]. 地震研究, 32(2): 105-113. Qin J Z, Liu L F, Qian X D. 2009. Research on characteristics and prediction of reservoir induced seismicity[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 32(2): 105-113 (in Chinese).
唐荣昌, 韩渭宾. 1993. 四川活动断裂与地震[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 368. Tang R C, Han W B. 1993. Active Faults and Earthquakes in Sichuan Province[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 368 (in Chinese).
陶玮, Masterlark T, 沈正康, Ronchin E, 张永. 2014. 紫坪铺水库造成孔隙弹性耦合变化及其对2008年汶川地震触发作用[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(10): 3318-3331. Tao W, Masterlark T, Shen Z K, Ronchin E, Zhang Y. 2014. Triggering effect of the Zipingpu reservoir on the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan, China, earthquake due to poroelastic coupling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(10): 3318-3331 (in Chinese).
向宏发, 徐锡伟, 虢顺民, 张晚霞, 李洪武, 于贵华. 2002. 丽江—小金河断裂第四纪以来的左旋逆推运动及其构造地质意义: 陆内活动地块横向构造的屏蔽作用[J]. 地震地质, 24(2): 188-198. Xiang H F, Xu X W, Guo S M, Zhang W X, Li H W, Yu G H. 2002. Sinistral thrusting along the Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault since Quaternary and its geologic-tectonic significance: Shielding effect of transverse structure of intracontinental active block[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(2): 188-198(in Chinese).
张永久, 高原, 石玉涛, 太龄雪. 2010. 四川紫坪铺水库库区地震剪切波分裂研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(9): 2091-2101. Zhang Y J, Gao Y, Shi Y T, Tai L X. 2010. The shear-wave splitting study of Sichuan Zipingpu reservoir region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(9): 2091-2101 (in Chinese).
钟羽云, 周昕, 张帆.2013.水库水位变化与地震活动关系研究[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 32(2): 35-40. Zhong Y Y, Zhou X, Zhang F. 2013. On relation between reservoir water level changes and seismic activity[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 32(2): 35-40(in Chinese).
Crampin S, Zatsepin S V. 1997. Modelling the compliance of crustal rock: II. Response to temporal changes before earthquakes[J]. Geophys. J. Int, 129(3): 495-506.
Crampin S, Volti T, Chastin S, Gudmundsson A, Stefánsson R. 2002. Indication of high pore-fluid pressures in a seismically-active fault zone[J]. Geophys J Int, 151(2): F1-F5.
Gao Y, Crampin S. 2004. Observations of stress relaxation before Earthquakes[J]. Geophys J Int, 157(2): 578-582.
Gao Y, Crampin S. 2008. Shear-wave splitting and Earthquake forecasting[J]. Terra Nova, 20(6): 440-448.
Gao Y, Wu J, Fukao Y, Shi Y T, Zhu A L. 2011. Shear wave splitting in the crust in North China: stress, faults and tectonic implications[J]. Geophys. J. Int., 187(2): 642-654.
Gao Y, Wang P D, Zheng S H, Wang M, Chen Y T, Zhou H L. 1998. Temporal changes in shear-wave splitting at an isolated swarm of small earthquakes in 1992 near Dongfang, Hainan Island, southern China[J]. Geophys J Int, 135(1): 102-112.
Gerst A, Savage M K. 2004. Seismic anisotropy beneath Ruapehu volcano: A possible eruption forecasting tool[J]. Science, 306(5701): 1543-1547.
Liu S, Crampin S, Luckett R, Yang J S. 2014. Changes in shear wave splitting before the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption in Iceland[J]. Geophys J Int, 199(1): 102-112.
Miller V, Savage M. 2001. Changes in seismic anisotropy after volcanic eruptions: Evidence from mount Ruapehu[J]. Science, 293(5538): 2231-2233.
Talwani P. 1997. On the nature of reservoir-induced seismicity[J]. Pure Appl. Geophys., 150(3/4): 473-492. doi: 10.1007/s000240050089.
Tang C H, Rial J A, Lees J M. 2005. Shear-wave splitting: A diagnostic tool to monitor fluid pressure in geothermal fields[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 32(21): L21317.




 下载:
下载: