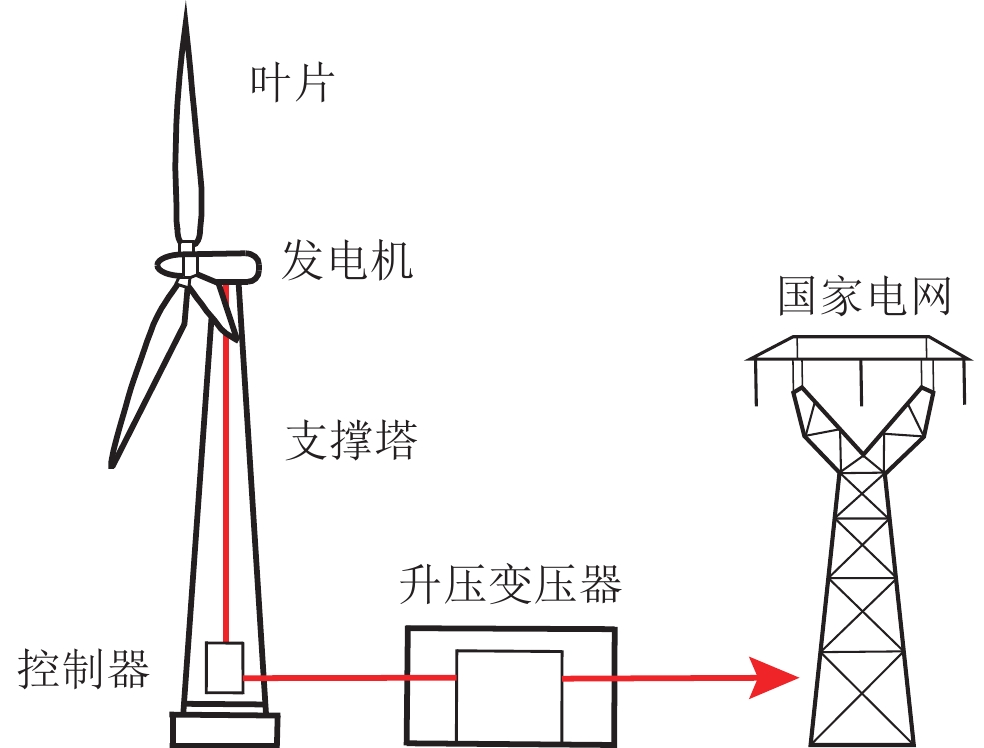
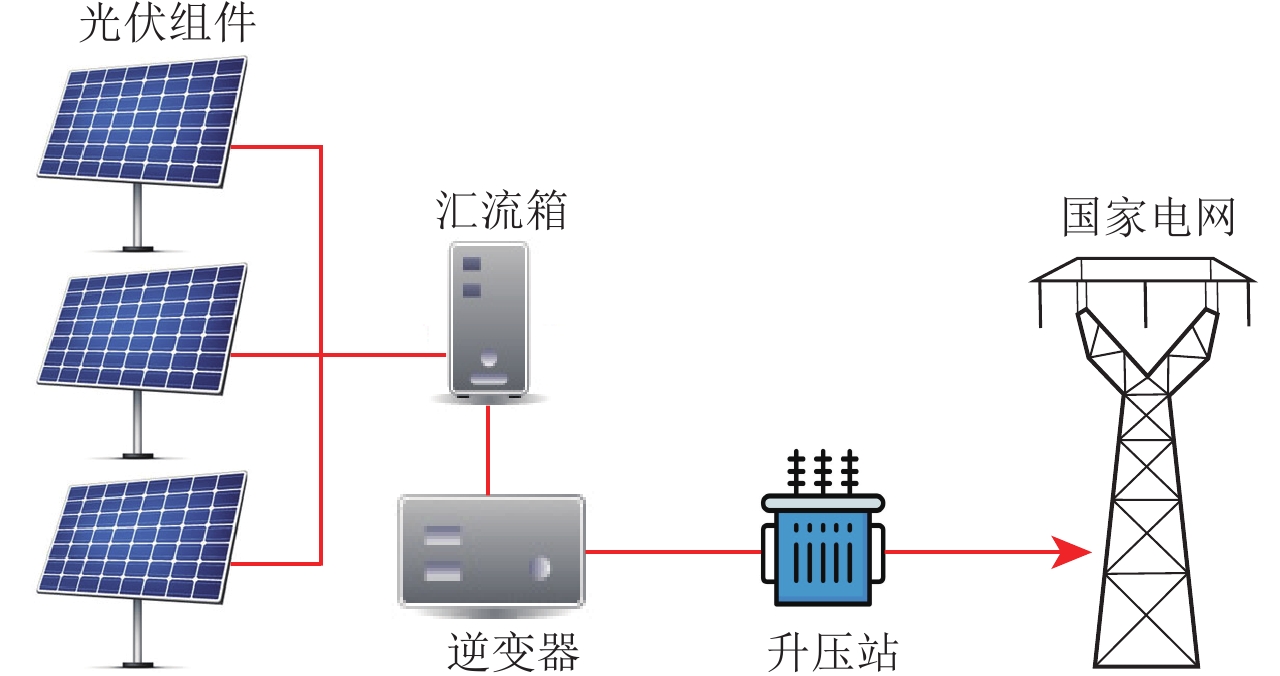
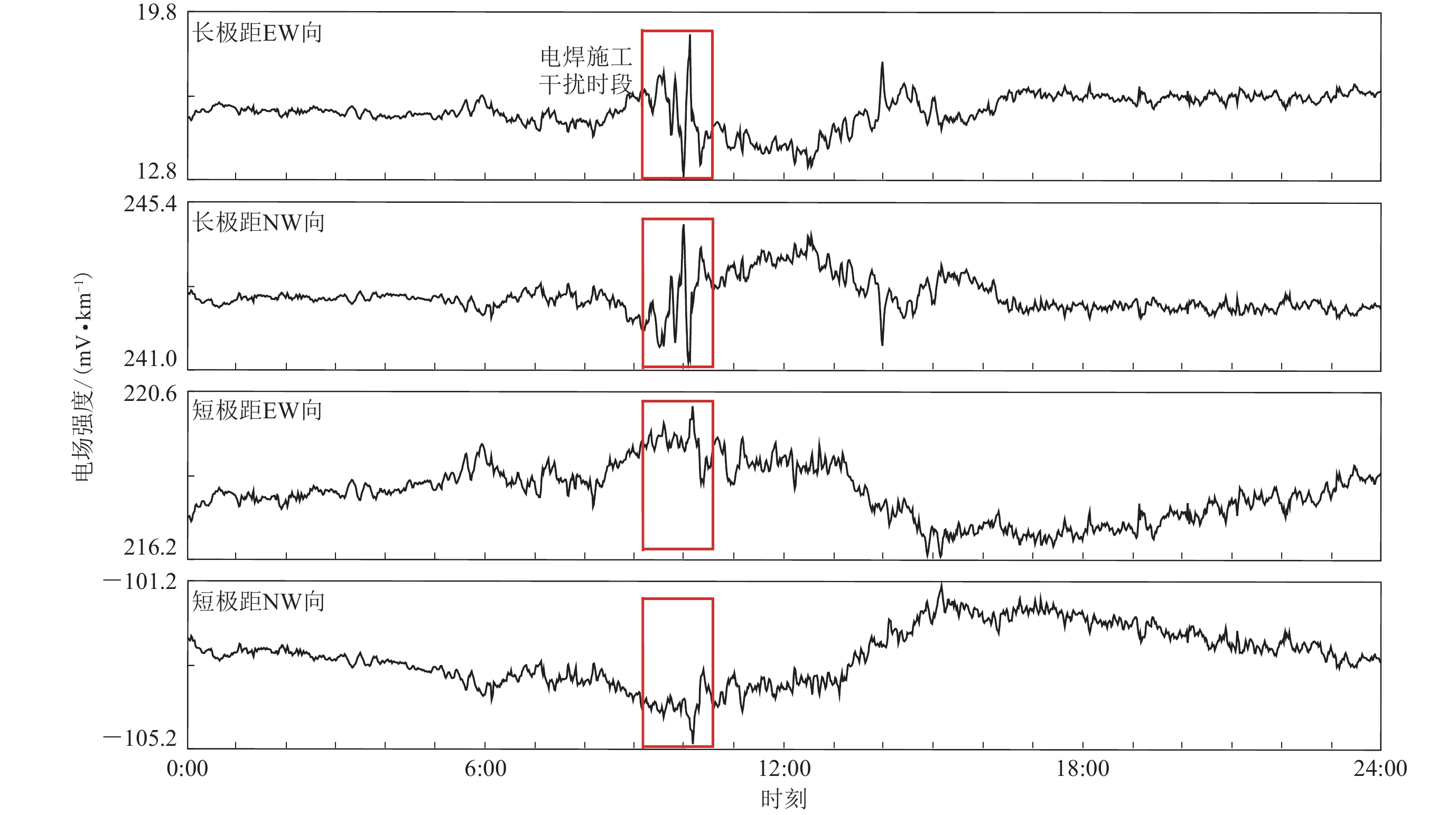
Interference characteristics of new energy power generation on electromagnetic observation environment:Taking the electromagnetic observation of Xuzhuangzi station of Tianjin as an example
-
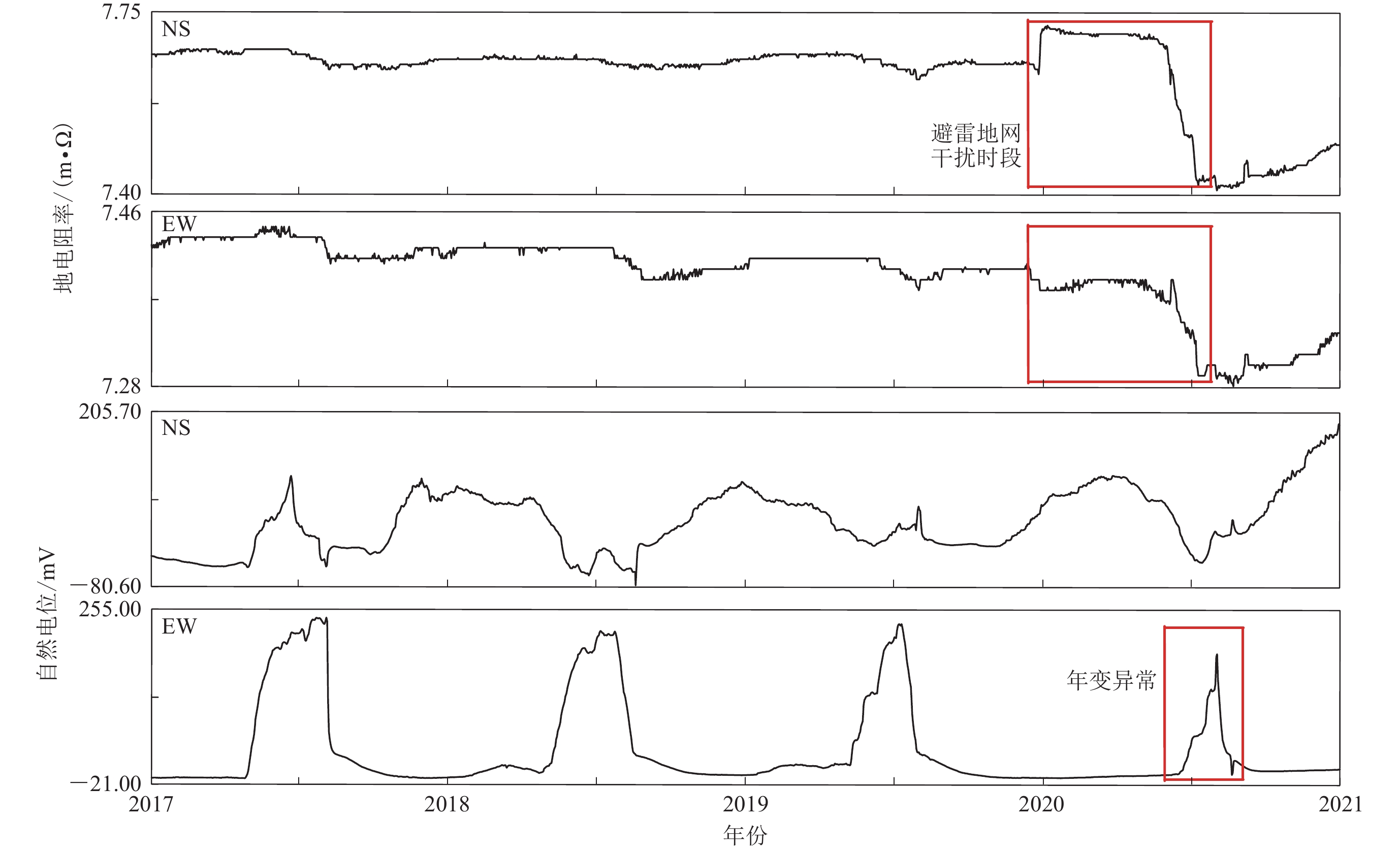
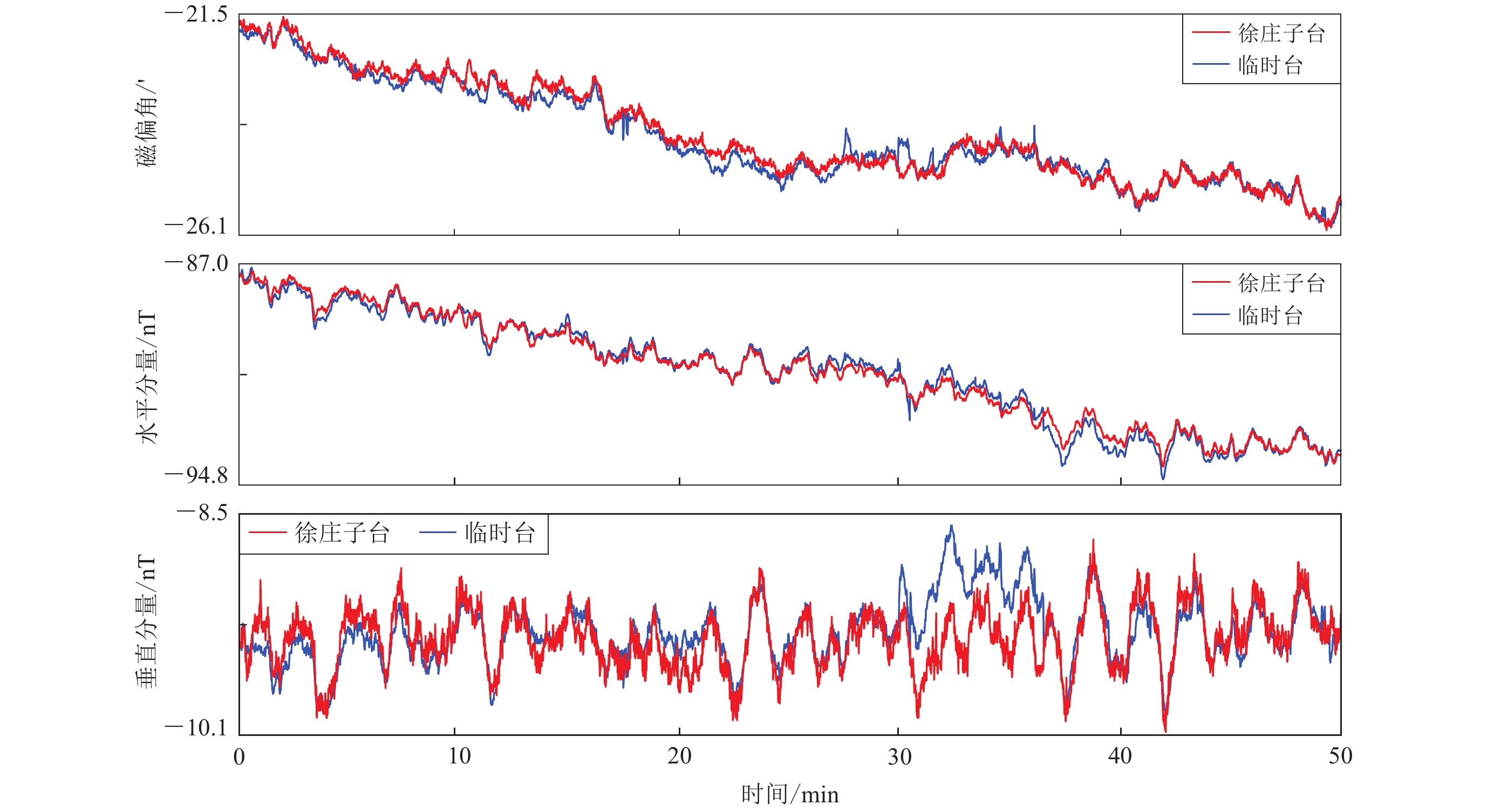
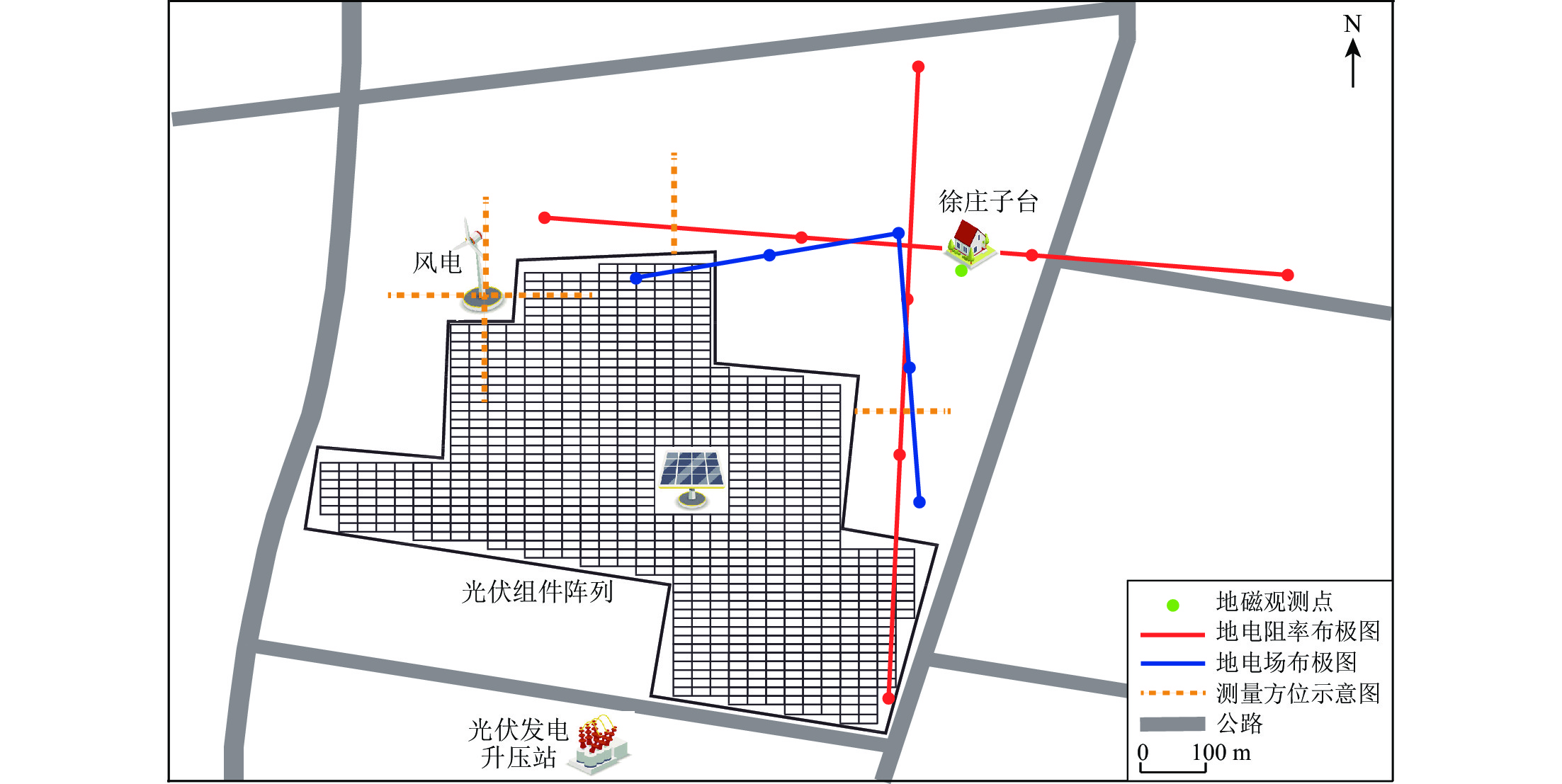
摘要: 利用天津市徐庄子地震台的电磁观测数据,针对台站周边观测区域内近年来出现的风电和光伏发电设施,通过野外试验测量,从多个角度深入剖析了不同观测环境中电磁观测数据在时间和空间上的变化形态,分别总结了风力发电、光伏发电的建设和运行状态对电磁观测环境干扰的影响特征。结果显示:风力发电机组对电磁观测环境的影响明显小于光伏发电设备,可视为一个干扰点,需规范其与观测设施的距离;若要确保光伏发电设备不影响电磁观测,需要将每个系统视为一个整体,并使二者保持足够大的距离。Abstract: New energy power generation is an important measure taken by the countries to replace non-renewable energy sources so as to achieve sustainable utilization of power resources under the sustainable development strategy. Wind power and photovoltaic power generation are clearly defined as the key development fields of renewable energy. These big power generation facilities will have a great impact on the original seismic observation environment. Based on the electromagnetic observation project of the Xuzhuangzi station of Tianjin, aiming at the wind power and photovoltaic power generation facilities in the observation area around the station in recent years we analyzed the temporal and spatial changes of electromagnetic observation data in different observation environments by the field experimental measurement, and summarized the influence characteristics of the construction and operation of wind power generation and photovoltaic power generation on electromagnetic observation environment interference. The results show that the impact of wind turbine is significantly less than that of photovoltaic power system on the electromagnetic observation environment, which can be regarded as an interference point to regulate the distance between wind turbine and observation facilities. In order to ensure that the photovoltaic power system does not affect the electromagnetic observation, it is necessary to treat each system as a whole and maintain a sufficiently large separation distance between them. This paper can provide a reference for the protection and evaluation of electromagnetic observation environment by building similar new energy power generation equipment in the seismic field, which is of important practical significance for protecting the observation environment of seismic stations.
-
-
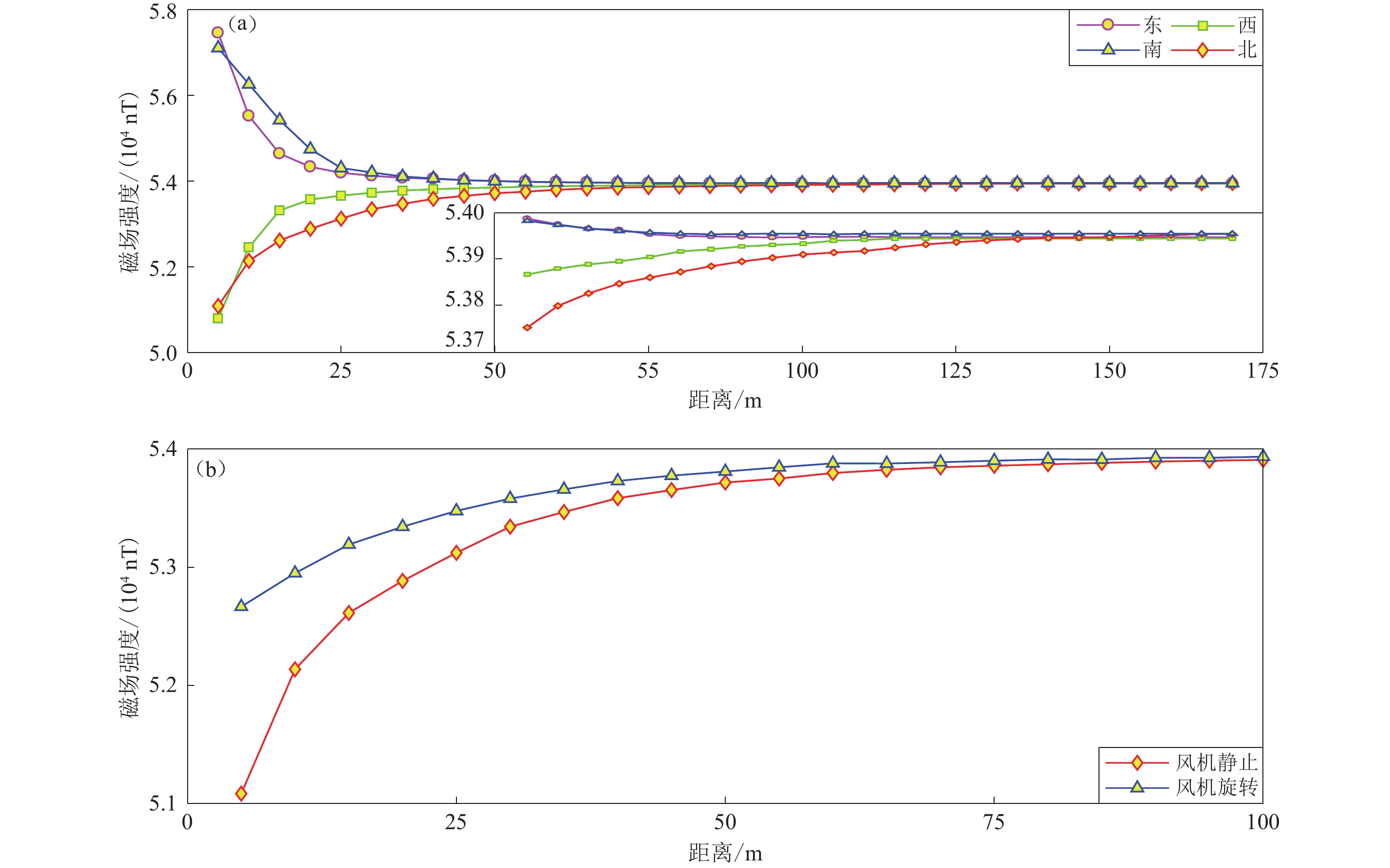
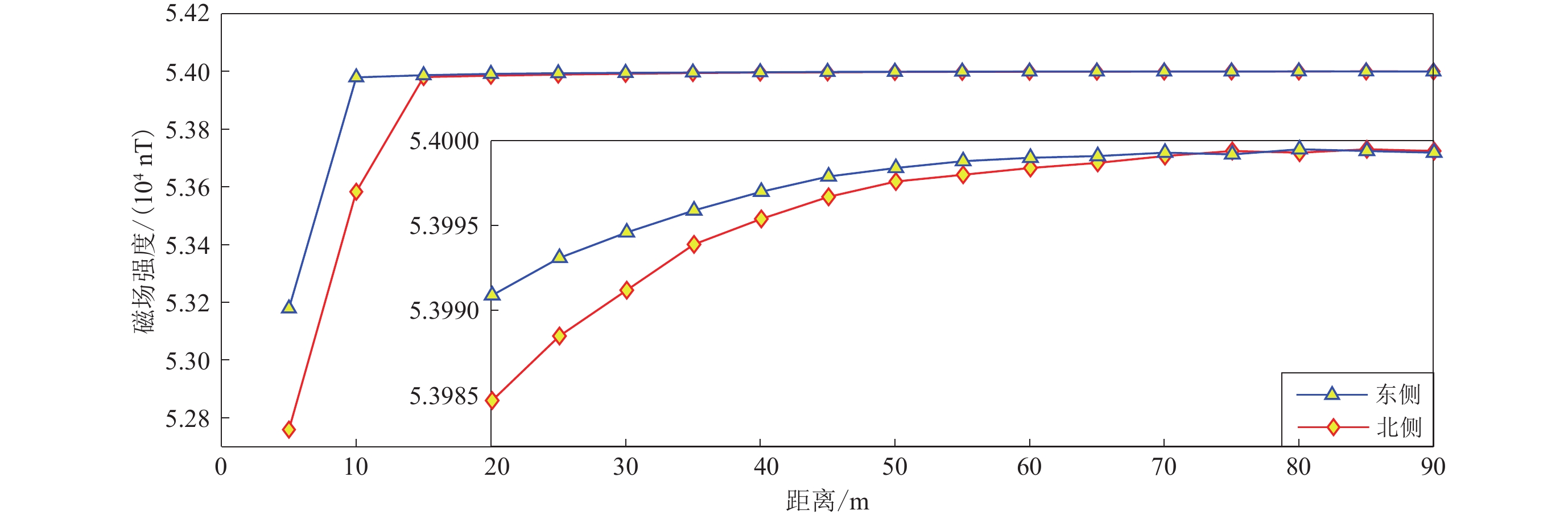
图 3 风力发电设备周围磁场变化曲线
(a) 风机静止时不同方向的磁场变化;(b) 风机静止和旋转发电状态下南侧的磁场变化
Figure 3. Magnetic field variation curve around the wind power equipment
(a) The magnetic field variation in different directions when the fan is stationary;(b) The magnetic field variation on the south side when the wind turbine is stationary and rotating,respectively
-
鲍海英,蒋延林,樊晓春,毕雪梅,卜玉菲,张秀霞. 2020. 高压直流输电对地电场观测的影响探讨[J]. 中国地震,36(3):607–619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2020.03.022 Bao H Y,Jiang Y L,Fan X C,Bi X M,Bu Y F,Zhang X X. 2020. Study on the impact of high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission interference on geotechnical stations in Jiangsu Province[J]. Earthquake Research in China,36(3):607–619 (in Chinese).
毕金孟,马永,马朝晖. 2020. 徐庄子地震台地磁观测干扰因素剖析[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,41(2):130–137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2020.02.015 Bi J M,Ma Y,Ma Z H. 2020. An analysis of the disturbance factors of geomagnetic observation at Xuzhuangzi seismic station[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,41(2):130–137 (in Chinese).
陈志刚,徐学恭,马永,康健,张明东. 2019. 京沪高铁干扰地电场观测的实验研究[J]. 国际地震动态,(12):36–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2019.12.006 Chen Z G,Xu X G,Ma Y,Kang J,Zhang M D. 2019. Experimental study on interference of Beijing-Shanghai high-speed railway in geoelectric field observation[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology,(12):36–42 (in Chinese).
冯志生,王建宇,蒋延林,吴晶,梅卫萍. 2001. 地磁垂直分量日变幅逐日比及其与地震关系的探讨[J]. 华南地震,21(2):20–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2001.02.004 Feng Z S,Wang J Y,Jiang Y L,Wu J,Mei W P. 2001. Ratio of daily variation amplitude of geomagnetic vertical component and its relation with earthquake[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,21(2):20–27 (in Chinese).
冯志生,梅卫萍,张秀霞,庄明龙,张晓勇. 2004. 中强震前地磁谐波振幅比的趋势性变化特征初步研究[J]. 西北地震学报,26(1):50–56. Feng Z S,Mei W P,Zhang X X,Zhuang M L,Zhang X Y. 2004. Preliminary study on the characteristics of long and medium term variation for the amplitude ratio of geomagnetic humorous wave before moderate-strong earthquakes[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,26(1):50–56 (in Chinese).
蒋延林,张秀霞,杨冬梅,陈俊,赵卫红,张骞,王福才. 2014. 高压直流输电对地磁观测影响的特征分析[J]. 地震,34(3):132–139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2014.03.013 Jiang Y L,Zhang X X,Yang D M,Chen J,Zhao W H,Zhang Q,Wang F C. 2014. Influence characteristics of high voltage direct current transmission on geomagnetic observation[J]. Earthquake,34(3):132–139 (in Chinese).
雷晴,颜龙,史勇军. 2020. 基于数据跟踪分析的新疆区域电磁仪器环境干扰特征分析[J]. 地震工程学报,42(6):1507–1516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.06.1507 Lei Q,Yan L,Shi Y J. 2020. Environmental interference characteristics of electromagnetic instruments in Xinjiang area based on data tracking analysis[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,42(6):1507–1516 (in Chinese).
马钦忠. 2018. 与2008 年汶川MS8.0 地震有关的成都台地电场异常信号[J]. 地震学报,40(3):351–363. Ma Q Z. 2018. Abnormal signals of geoelectric field related to Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake recorded at the Chengdu station[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,40(3):351–363 (in Chinese).
马永,陈志刚. 2017. 地电场观测中常见干扰的对比分析[J]. 大科技,(20):299–300. Ma Y,Chen Z G. 2017. Comparative analysis of common interferences in geoelectric field observation[J]. Super Science,(20):299–300 (in Chinese).
牛微,李珊珊. 2005. 我国新能源发电技术应用现状及发展[J]. 沈阳工程学院学报(自然科学版),1(4):28–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1603.2005.04.008 Niu W,Li S S. 2005. Application situation and prospect of generating electricity technology by new energy in our country[J]. Journal of Shenyang Institute of Engineering (Natural Science)
,1(4):28–30 (in Chinese). 彭玉柱,张世民,李建章. 2015. 中强地震前周至台地电阻率的异常变化[J]. 震灾防御技术,10(2):455–463. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150227 Peng Y Z,Zhang S M,Li J Z. 2015. Precursory anomalies of geo-resistance before moderate-strong earthquake based on observed data at Zhouzhi seismic station[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention,10(2):455–463 (in Chinese).
王立凤,赵国泽,陈小斌,汤吉,蔡军涛,詹艳,韩冰,程远志,赵凌强,肖骑彬. 2017. 芦山MS7.0地震余震期间大地电磁视电阻率变化[J]. 地震学报,39(1):64–77. Wang L F,Zhao G Z,Chen X B,Tang J,Cai J T,Zhan Y,Han B,Cheng Y Z,Zhao L Q,Xiao Q B. 2017. Variation of magnetotelluric apparent resistivity during the major aftershock period of Lushan earthquake in epicentral area[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,39(1):64–77 (in Chinese).
中国地震局. 2019. 地震标准汇编[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 958–975. China Earthquake Administration. 2019. Seismic Standards Collection[M]. Beijing: China Standard Press: 958–975 (in Chinese).
中国地震局监测预报司. 2002. 地震电磁数字观测技术[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 120–126. Department of Monitoring and Forecasting, China Earthquake Administration. 2002. Earthquake Observation of Electromagnetic Technology[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 120–126 (in Chinese).
钟李彬,林建,李雪浩,胡俊明,李国超,颜晓晔. 2017. 成灌高铁运行对成都地磁台观测数据干扰测试[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,38(5):81–85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2017.05.015 Zhong L B,Lin J,Li X H,Hu J M,Li G C,Yan X Y. 2017. Testing and analysis of observation data to Chengdu geomagnetic observation on Chengguan high-speed rail[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,38(5):81–85 (in Chinese).




 下载:
下载: