Variations of apparent resistivity before the 2022 MS6.9 Menyuan earthquake in Qinghai Province revealed by the virtual fault dislocation model
-
摘要:
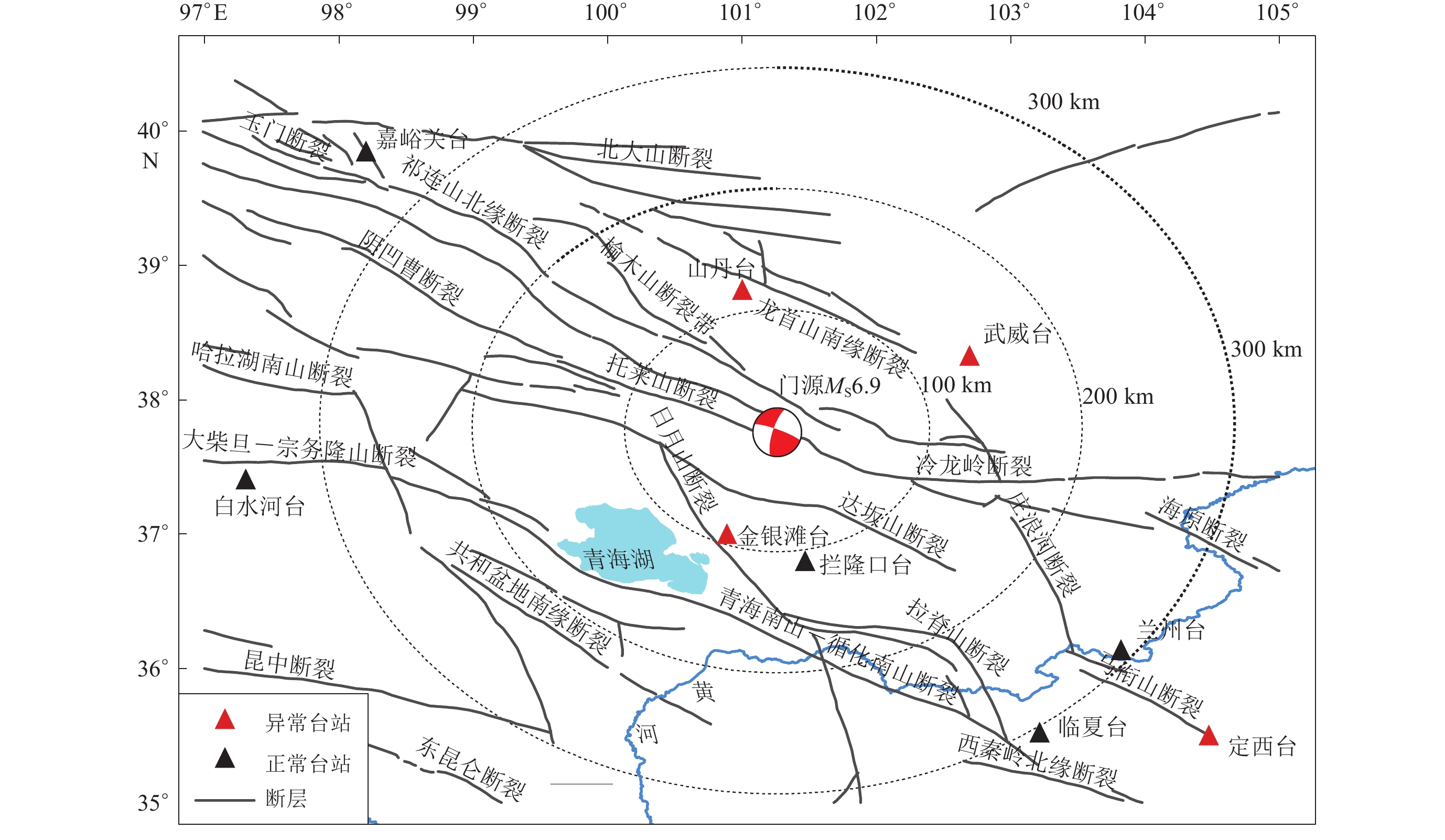
选取2022年1月8日青海门源MS6.9地震震中400 km范围内四个地电阻率观测台站的观测精度高、具有稳态年变、震前无显著干扰的地电阻率$ {\rho }_{{\mathrm{s}}} $观测数据,结合ERA5同化数据集中的多层土壤温度和土壤水分含量,在利用多项式拟合获取各台站(或测道)地电阻率正常年动态的基础上,分析了门源地震前地电阻率的异常变化。结果显示:金银滩台EW测道、武威台NS测道和山丹台EW测道、N45°W测道震前存在超阈值的异常变化,并呈现各向异性特征。基于断层虚位错模式分析了地电阻率异常变化与孕震过程之间的联系,结果表明:金银滩台震前处于压缩区并受到NNE方向的挤压,与主压应变近似正交的EW测道于震前10个月出现负异常;同样位于压缩区的武威台,受到了ENE向的挤压,NS测道的地电阻率在孕震早期(震前13个月)以负异常为主,孕震中晚期(震前3个月)出现了正异常;山丹台,位于膨胀区,受到近似NS向的拉张,与主张应变平行的NS测道未发现异常,但EW测道震前一年地电阻率出现正异常,N45°W测道的地电阻率也在震前半年左右出现超阈值并呈正异常。此外,金银滩台、山丹台和武威台距离门源地震震中的距离分别为92 km,113 km和139 km,相应的地电阻率异常最大变化幅值分别为−3.0σ,2.2σ和−2.1σ。此外,门源地震前地电阻率异常变化的时空特征与岩石实验结果及理论模型一致,也符合震源区应力应变积累程度较高、向外围方向逐渐衰减的分布特征。由此推断,2022年门源MS6.9地震前地电阻率的时空变化可能与区域介质变形及应力变化有关。
Abstract:An earthquake with MS6.9 struck the Menyuan County, Qinghai Province, northwestern China on 8 January 2022. There were four apparent resistivity observation stations with anomalies in an area within 400 km from the epicenter. Using the observed data with high quality and stable annual variation as well as the soil temperature and soil water provided by ERA5 assimilation datasets, a polynomial fitting was performed so as to subtract the normal annual dynamics and to detect the anomalies of the apparent resistivity prior to the earthquake. The results indicate that the above-threshold changes and anisotropic characteristics appeared before the earthquake in the EW channel at the Jinyintan station, NS channel at the Wuwei station, and the EW and N45°W channels at the Shandan station. A virtual fault dislocation model was used to examine the relationship between apparent resistivity changes and seismogenic process of the Menyuan earthquake. In the areas with compression along NNE direction, the decrease changes in the EW channel, which is approximately orthogonal to the direction of the principal compressive strain, has been observed at the Jinyintan station since ten months before the earthquake, the negative anomaly in the NS channel in the early stages of the earthquake preparation (13 months before the main shock) appeared at the Wuwei station, while it turned to an increase change three months before the earthquake. At the Shandan station, which is located in the relative extensional area, no anomalies were detected in the NS channel parallel to the principle tensile strain. However, an increase change was observed in the EW channel one year prior to the earthquake, and an increase change was also recorded in the N45°W channel of Shandan station half-year before the earthquake. Furthermore, at the Jinyintan station, Shandan station, and Wuwei station with epicentral distance of 92 km, 113 km, and 139 km, the corresponding maximum variation of anomalies are −3.0σ, 2.2σ and −2.1σ respectively. In addition, Variations of apparent resistivity before the 2022 MS6.9 Menyuan earthquake were consistent with the results from rock experiment and theoretical models. Moreover, the spatio-temporal characteristics of the variation of apparent resistivity before the MS6.9 Menyuan earthquake are likely consistent with the stress accumulation in the source region, as well as with the characteristics of stress accumulation by a high degree in the epicenter and gradual attenuation towards the periphery. Therefore, it can be deduced that the spatio-temporal variation of apparent resistivity before the MS6.9 Menyuan earthquake may be related to regional medium deformation and stress change.
-
-
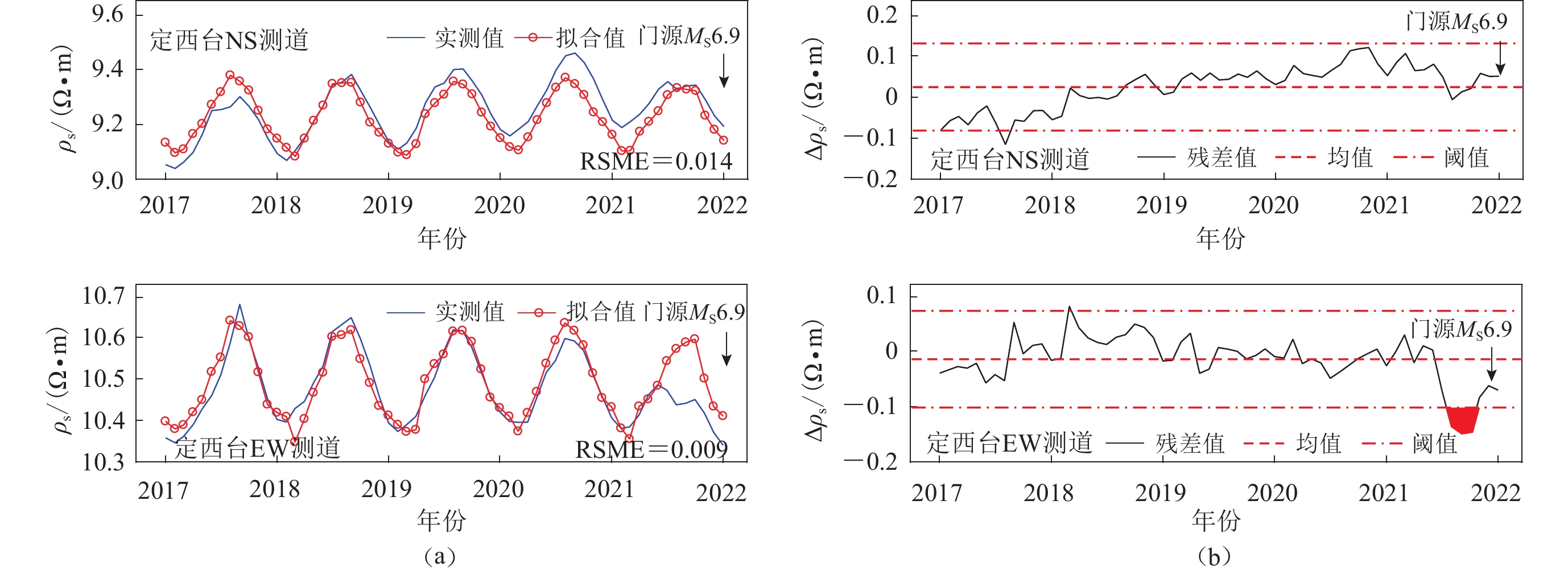
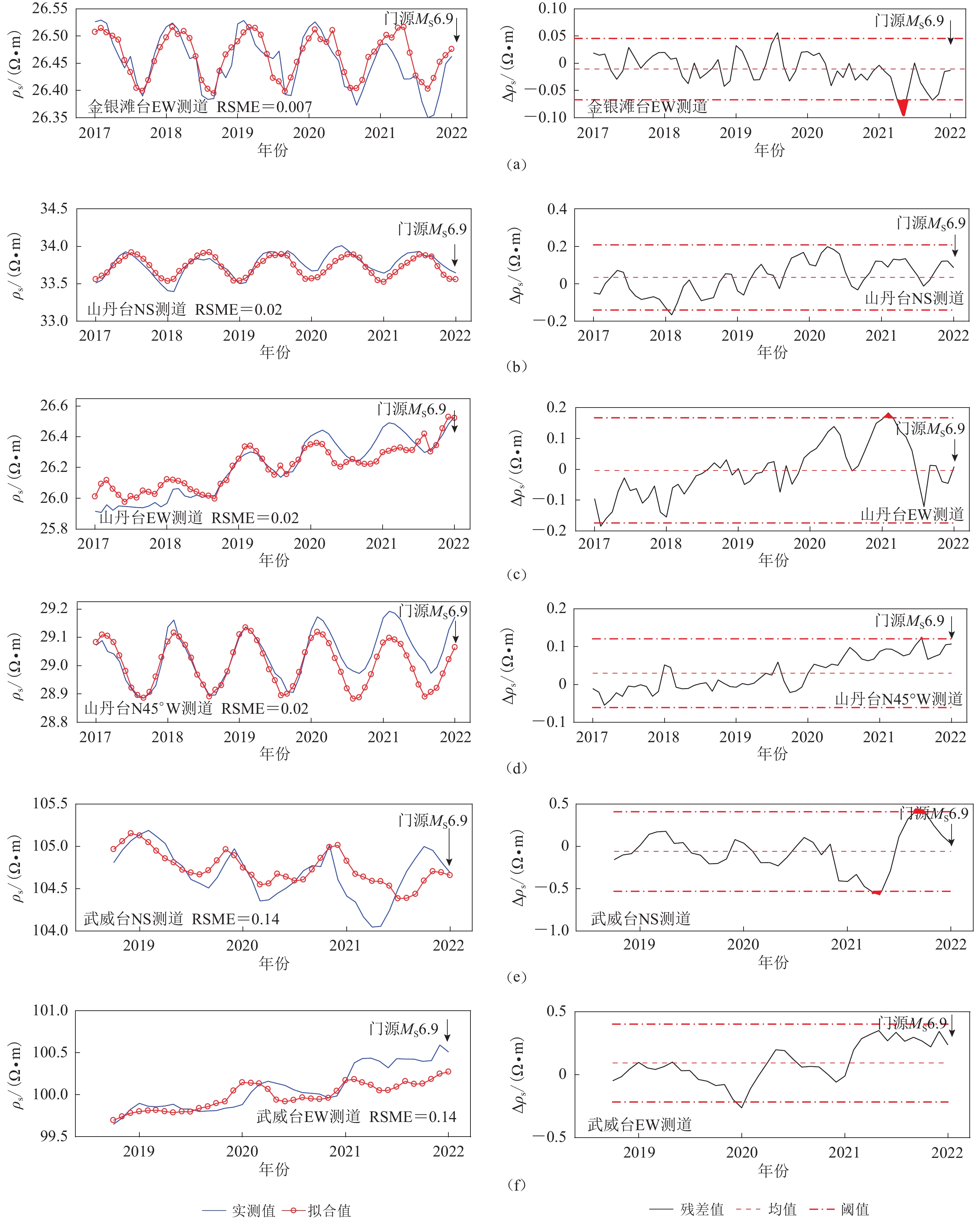
图 4 山丹台、金银滩台和武威台土壤水分含量和土壤温度拟合获取的地电阻率时间序列(左)及残差(右)
(a) 金银滩台EW测道;(b) 山丹台NS测道;(c) 山丹台EW测道;(d) 山丹台N45°W测道;(e) 武威台NS测道;(f) 武威台EW测道
Figure 4. Time series curves of apparent resistivity (left panels) and residual variance curves (right panels) at Shandan,Jinyintan and Wuwei stations obtained by a polynomial fitting of soil water content and soil temperature
(a) The EW channel of Jinyintan station;(b) The NS channel of Shandan station;(c) The EW channel of Shandan station;(d) The N45°W channel of Shandan station;(e) The NS channel of Wuwei station;(f) The EW channel of Wuwei station
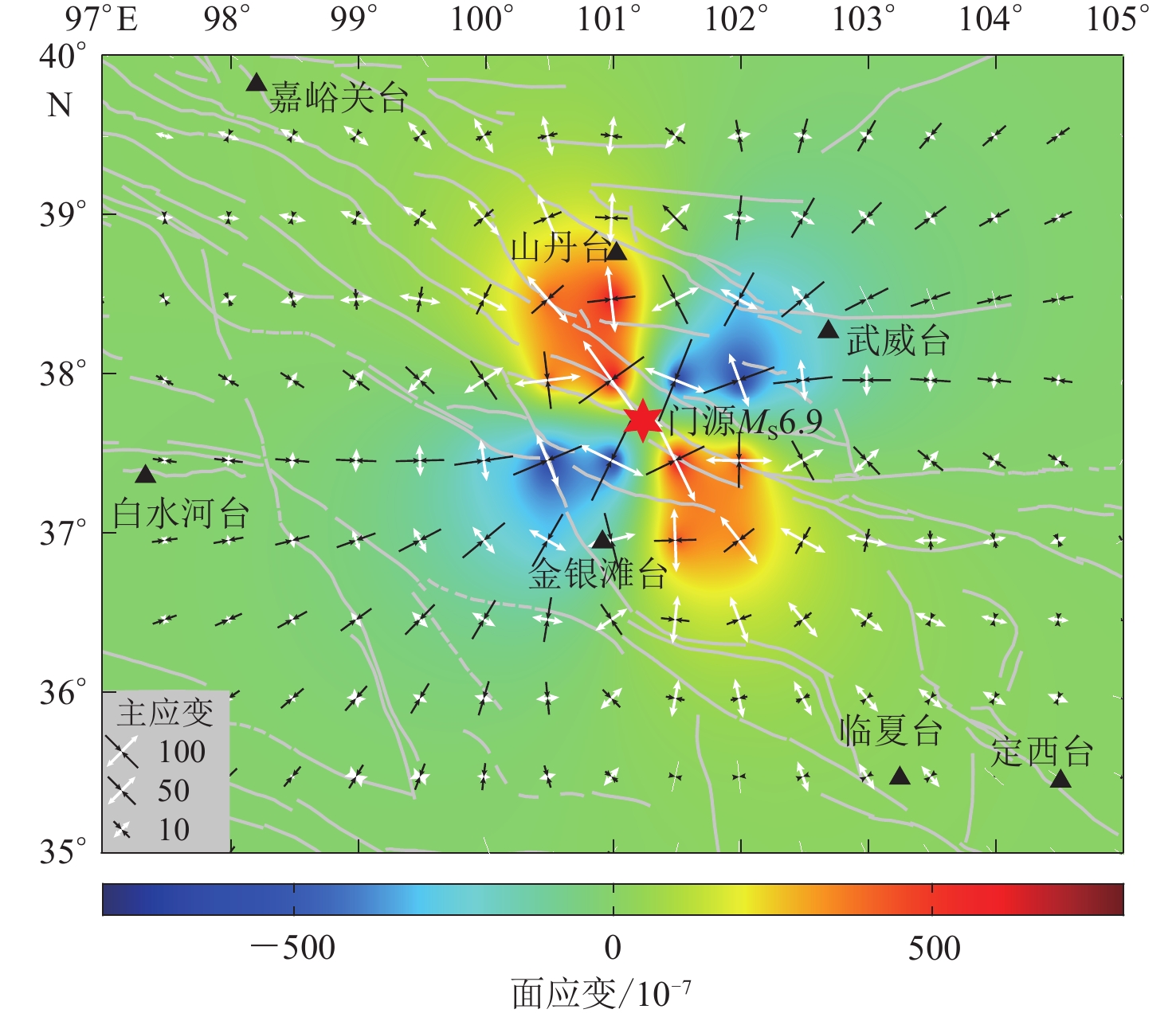
图 5 基于断层虚位错模式计算的门源MS6.9地震前震中区域的面应变及主应变
图中红色为面应变膨胀区,蓝色为面应变压缩区,白色箭头为主张应变,黑色箭头为主压应变
Figure 5. Distribution of surface strain and principal strain calculated using the virtual fault dislocation model in the epicenter before the Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake
The region in red color is the relative expansion area of surfacestrain,and the blue is the compression area of surface strain.The white arrows are the principal tensile strain,andthe black arrows are the principal compressive strain
表 1 2022年门源MS6.9地震周边400 km范围内地电阻率台站的基础信息
Table 1 Basic information of the apparent resistivity stations within 400 km to the epicenter of the 2022 Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake
台站 测道 震中距/km 数据质量 历史数据干扰因素 观测仪器 年变动态 备注 嘉峪关 N50°E 347 差 降雨、线路漏电、公路 ZD8M 无规律 2021年8—9月漏电干扰 N45°W 中 降雨、线路漏电、公路 夏高冬低 山丹 NS 113 优 线路漏电 ZD8B 夏高冬低 EW 优 线路漏电 夏低冬高 N45°W 优 线路漏电 夏低冬高 白水河 NS 345 优 大风 ZD8M 夏低冬高 2021年8月—2022年1月电极故障 EW 差 大风 夏高冬低 金银滩 NS 92 差 大风 ZD8M 无规律 EW 优 大风 夏低冬高 拦隆口 NS 114 差 大风、灌溉 ZD8M 夏低冬高 EW 差 大风、灌溉 夏高冬低 兰州 NS 296 差 地铁、塑料大棚 ZD8M 无规律 EW 差 地铁、塑料大棚 无规律 武威 NS 139 优 仪器故障 ZD8MI 夏低冬高 EW 优 仪器故障 夏高冬低 临夏 NS 310 中 漏电、塑料大棚、金属网 ZD8M 夏低冬高 2020—2021年测区存在施工建设 EW 差 漏电、塑料大棚、金属网 夏低冬高 定西 NS 388 优 漏电、灌溉 ZD8M 夏高冬低 EW 优 漏电、灌溉 夏高冬低 注:蓝色字为最终参与地电阻率异常分析的台站及测道。 表 2 地电阻率与土壤水分含量和土壤温度的相关系数
Table 2 Correlative coefficient between apparent resistivity and soil water content and soil temperature
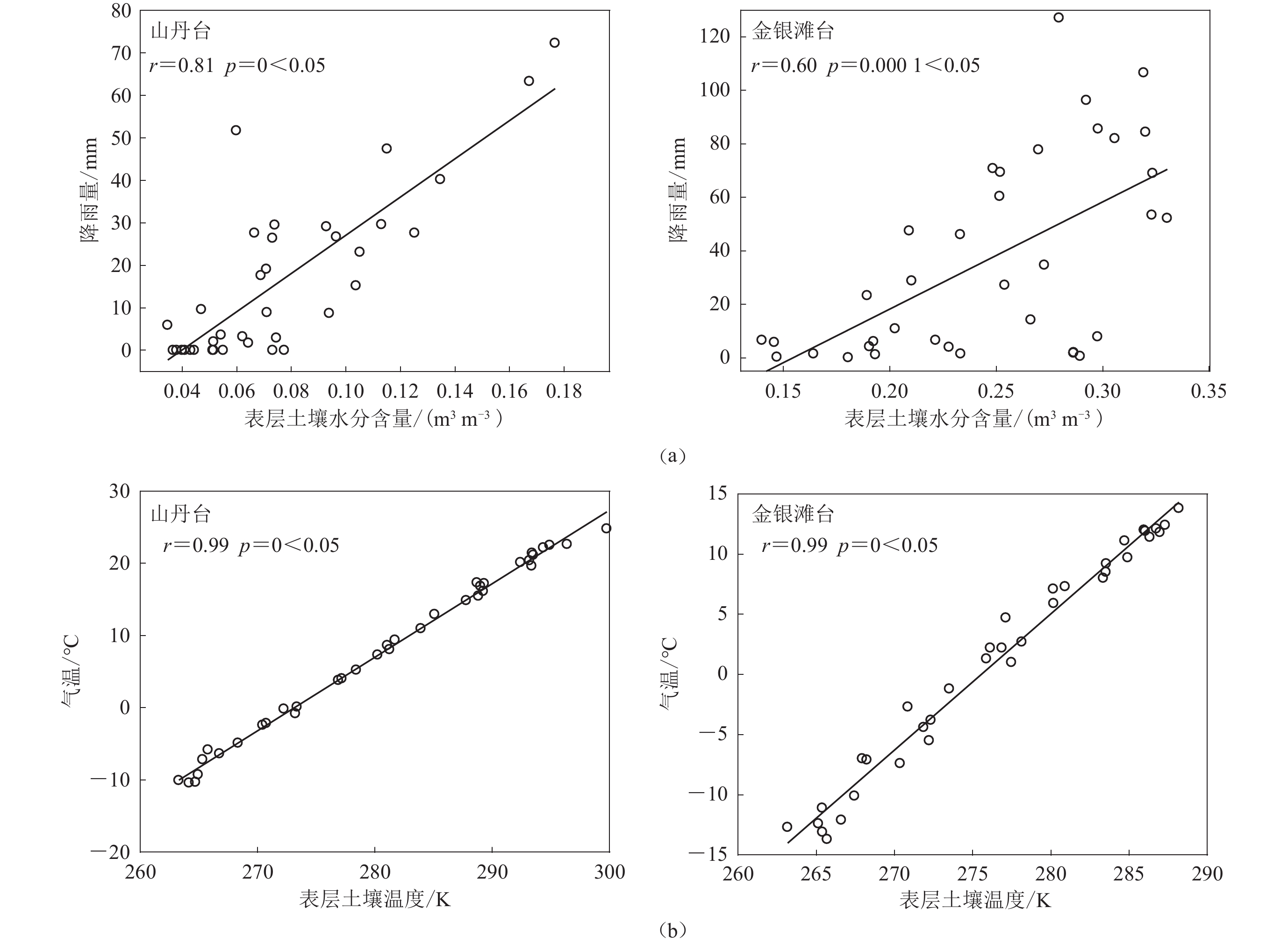
台站 测道 不同深度土壤水分含量与地电阻率的相关系数 不同深度土壤温度与地电阻率的相关系数 0—7 cm 7—28 cm 28—100 cm 100—289 cm 0—7 cm 0—28 cm 28—100 cm 100—289 cm 金银滩 EW −0.32 −0.39 0.08 −0.16 −0.63 −0.68 −0.78 −0.75 定西 NS 0.47 0.42 0.09 −0.25 0.62 0.67 0.77 0.80 EW 0.51 0.43 −0.02 −0.45 0.61 0.65 0.76 0.82 武威 NS 0.12 0.54 −0.33 0.29 −0.35 −0.30 −0.16 0.19 EW −0.03 −0.36 0.75 −0.79 0.01 0.00 −0.05 −0.12 山丹 NS 0.43 0.10 −0.27 −0.30 0.82 0.82 0.75 0.37 EW −0.32 −0.41 −0.34 −0.82 −0.21 −0.24 −0.27 −0.24 N45°W −0.65 −0.70 0.04 −0.22 −0.56 −0.66 −0.80 −0.87 注:蓝色数字为与地电阻率相关系数较高并参与拟合的土壤水分含量和土壤温度。 表 3 2022年门源MS6.9地震的震源参数(引自潘家伟等,2022)
Table 3 The source parameters of the Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake in 2022 (after Pan et al,2022)
断层中心位置 长度/km 宽度/km 中心深度/km 滑动量/cm 节面Ⅰ 东经/° 北纬/° 滑动角/° 走向/° 倾角/° 101.26 37.77 31 16 4 300 21 284 82 -
邓起东,张培震,冉勇康,杨晓平,闵伟,楚全芝. 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑),32(12):1020–1030. Deng Q D,Zhang P Z,Ran Y K,Yang X P,Min W,Chu Q Z. 2003. Basic characteristics of active tectonics of China[J]. Science in China:Series D,46(4):356–372. doi: 10.1360/03yd9032
杜学彬,李宁,叶青,马占虎,闫睿. 2007. 强地震附近视电阻率各向异性变化的原因[J]. 地球物理学报,50(6):1802–1810. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.06.021 Du X B,Li N,Ye Q,Ma Z H,Yan R. 2007. A possible reason for the anisotropic changes in apparent resistivity near the focal region of strong earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,50(6):1802–1810 (in Chinese).
杜学彬. 2010. 在地震预报中的两类视电阻率变化[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),40(10):1321–1330. Du X B. 2010. Two types of changes in apparent resistivity in earthquake prediction[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,54(1):145–156.
杜学彬,孙君嵩,陈军营. 2017. 地震预测中的地电阻率数据处理方法[J]. 地震学报,39(4):531–548. doi: 10.11939/jass.2017.04.008 Du X B,Sun J S,Chen J Y. 2017. Processing methods for the observation data of apparent resistivity in earthquake prediction[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,39(4):531–548 (in Chinese).
冯万鹏,何骁慧,张逸鹏,房立华,Sergey S,张培震. 2023. 2022年青海门源MW6.6地震的发震断层及孕震构造模式[J]. 科学通报,68(2/3):254–270. Feng W P,He X H,Zhang Y P,Fang L H,Sergey S,Zhang P Z. 2023. Seismic faults of the 2022 MW6.6 Menyuan,Qinghai earthquake and their implication for the regional seismogenic structures[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,68(2/3):254–270 (in Chinese).
高曙德,汤吉,杜学彬,刘小凤,苏永刚,陈彦平,狄国荣,梅东林,詹艳,王立凤. 2010. 汶川8.0级地震前后电磁场的变化特征[J]. 地球物理学报,53(3):512–525. Gao S D,Tang J,Du X B,Liu X F,Su Y G,Chen Y P,Di G R,Mei D L,Zhan Y,Wang L F. 2010. The change characteristics of electromagnetic field before to after Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,53(3):512–525 (in Chinese).
桂燮泰,关华平,戴经安. 1989. 唐山、松潘地震前视电阻率短临异常图象重现性[J]. 西北地震学报,11(4):71–75. Gui X T,Guan H P,Dai J A. 1989. The short-term and immediate anomalous pattern recurrences of the apparent resistivity before the Tangshan and Songpan earthquakes of 1976[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,11(4):71–75 (in Chinese).
李新,黄春林. 2004. 数据同化:一种集成多源地理空间数据的新思路[J]. 科学导报,22(2):13–16. Li X,Huang C L. 2004. Date assimilation:A new means for multi-source geospatial data integration[J]. Science &Technology Review,22(12):13–16 (in Chinese).
李新艳,曾宪伟,卢军,马禾青,崔瑾,卫定军. 2022. 基于断层虚位错模式分析2015年内蒙古阿左旗MS5.8地震前地电阻率变化[J]. 地震,42(2):89–99. doi: 10.12196/j.issn.1000-3274.2022.02.007 Li X Y,Zeng X W,Lu J,Ma H Q,Cui J,Wei D J. 2022. Anomalies of apparent resistivity before the 2015 Alxa Zuoqi MS5.8 earthquake in Inner Mongolia of China based on fault virtual dislocation model[J]. Earthquake,42(2):89–99 (in Chinese).
潘家伟,李海兵,Chevalier M L,刘栋梁,李超,刘富财,吴琼,卢海建,焦利青. 2022. 2022年青海门源MS6.9地震地表破裂带及发震构造研究[J]. 地质学报,96(1):215–231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.01.018 Pan J W,Li H B,Chevalier M L,Liu D L,Li C,Liu F C,Wu Q,Lu H J,Jiao L Q. 2022. Coseismic surface rupture and seismogenic structure of the 2022 MS6.9 Menyuan earthquake,Qinghai Province,China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,96(1):215–231 (in Chinese).
钱复业,赵玉林. 1980. 地震前地电阻率变化十例[J]. 地震学报,2(2):186–197. Qian F Y,Zhao Y L. 1980. Ten examples of changes in earth-resistivity prior to strong earthquakes[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,2(2):186–197 (in Chinese).
钱复业,赵玉林,于谋明,王志贤,刘小伟,常思敏. 1982. 地震前地电阻率的异常变化[J]. 中国科学(B辑),12(9):831–839. Qian F Y,Zhao Y L,Yu M M,Wang Z X,Liu X W,Chang S M. 1982. The anomalous changes of apparent resistivity before earthquakes[J]. Science in China:Series B,12(9):831–839 (in Chinese).
钱复业,赵玉林,许同春. 1987. 地电阻率季节干扰变化分析[J]. 地震学报,9(3):289–302. Qian F Y,Zhao Y L,Xu T C. 1987. Analyses of the seasonal variation of disturbance in apparent resistivity[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,9(3):289–302 (in Chinese).
钱家栋,陈有发,金安忠. 1985. 地电阻率法在地震预报中的应用[M]. 北京:地震出版社:196−205. Qian J D,Chen Y F,Jin A Z. 1985. Application of Earth-Resistivity Method in Earthquake Prediction[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press:196−205 (in Chinese).
石富强,张国强,方炜,邵辉成,张国苓. 2014. 陕西周至地电台地电阻率年变特征分析[J]. 地震学报,36(6):1113–1123. Shi F Q,Zhang G Q,Fang W,Shao H C,Zhang G L. 2014. Annual variation characteristics of apparent resistivity at Zhouzhi geoelectric station,Shaanxi Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,36(6):1113–1123 (in Chinese).
解滔,卢军. 2016. 地表固定干扰源影响下地电阻率观测随时间变化特征分析[J]. 地震地质,38(4):922–936. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.04.010 Xie T,Lu J. 2016. Apparent resistivity temporal variation characteristics affected by the fixed disturbance source on surface of measuring area[J]. Seismology and Geology,38(4):922–936 (in Chinese).
解滔,于晨,王亚丽,李美,卢军. 2020. 基于断层虚位错模式讨论2008年汶川MS8.0地震前视电阻率变化[J]. 中国地震,36(3):492–501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2020.03.012 Xie T,Yu C,Wang Y L,Li M,Lu J. 2020. Apparent resistivity variations before 2008 Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake based on fault virtual dislocation model[J]. Earthquake Research in China,36(3):492–501 (in Chinese).
解滔,薛艳,卢军. 2022a. 中国MS≥7.0地震前视电阻率变化及其可能原因[J]. 地球物理学报,65(8):3064–3077. Xie T,Xue Y,Lu J. 2022a. Changes in apparent resistivity and its possible reasons before earthquakes of MS≥7.0 in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,65(8):3064–3077 (in Chinese).
解滔,卢军,杜学彬. 2022b. 自适应变化幅度方法提取直流视电阻率中短期异常[J]. 中国地震,38(1):52–60. Xie T,Lu J,Du X B. 2022b. An adaptive variation amplitude method for extracting medium- and short-term anomalies of apparent resistivity[J]. Earthquake Research in China,38(1):52–60 (in Chinese).
解滔,于晨,王亚丽,李美,王中平,姚丽,卢军. 2022c. 2013年岷县-漳县MS6.6地震前通渭台的视电阻率变化[J]. 地震地质,44(3):701–717. Xie T,Yu C,Wang Y L,Li M,Wang Z P,Yao L,Lu J. 2022c. Apparent resistivity variation of Tongwei seismic station before the Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 earthquake in 2013[J]. Seismology and Geology,44(3):701–717 (in Chinese).
汪志亮,郑大林,余素荣. 2002. 地震地电阻率前兆异常现象[M]. 北京:地震出版社:45−49. Wang Z L,Zheng D L,Yu S R. 2002. Geoelectric Resistivity Precursor Anomalies of Earthquake[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press:45−49 (in Chinese).
许英才,郭祥云,冯丽丽. 2022. 2022年1月8日青海门源MS6.9地震序列重定位和震源机制解研究[J]. 地震学报,44(2):195–210. doi: 10.11939/jass.20220008 Xu Y C,Guo X Y,Feng L L. 2022. Relocation and focal mechanism solutions of the MS6.9 Menyuan earthquake sequence on January 8,2022 in Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,44(2):195–210 (in Chinese).
杨龙翔,刘学谦,孙召华. 2020. 金属大棚对周口台地电阻率干扰定量分析[J]. 地震工程学报,42(2):447–452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.02.447 Yang L X,Liu X Q,Sun Z H. 2020. Quantitative analysis of the disturbance to earth resistivity caused by a metal greenhouse at Zhoukou station[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,42(2):447–452 (in Chinese).
姚赛赛,高曙德,陈雪梅,张晓阳,杨超,醴武权. 2023. 2022年青海门源MS6.9地震前地电阻率变化分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,43(2):141–147. Yao S S,Gao S D,Chen X M,Zhang X Y,Yang C,Li W Q. 2023. Analysis of earth resistivity changes before the 2022 Qinghai Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,43(2):141–147 (in Chinese).
张国苓,王庆林,乔子云,贾立峰,张素欣. 2017. 地表点电流对地电阻率观测的影响[J]. 中国地震,33(1):122–128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2017.01.012 Zhang G L,Wang Q L,Qaio Z Y,Jia L F,Zhang S X. 2017. Influence from the surface disturbance current on geoelectrical resistivity observation[J]. Earthquake Research in China,33(1):122–128 (in Chinese).
张金铸,陆阳泉. 1983. 不同三轴应力条件下岩石电阻率变化的试验研究[J]. 地震学报,5(4):440–445. Zhang J Z,Lu Y Q. 1983. An experimental study on the variation of rock resistivity under triaxially different stresses[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,5(4):440–445 (in Chinese).
张学民,李美,关华平. 2009. 汶川8.0级地震前的地电阻率异常分析[J]. 地震,29(1):108–115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2009.01.014 Zhang X M,Li M,Guan H P. 2009. Anomaly analysis of earth resistivity observations before the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earthquake,29(1):108–115 (in Chinese).
赵和云,张文孝. 1985. 银川台地电阻率趋势变化及年变的分析[J]. 地震,(1):32–38. Zhao H Y,Zhang W X. 1985. Analysis of potential and annual variations of earth resistivity at Yinchuan station[J]. Earthquake,(1):32–38 (in Chinese).
赵玉林,钱复业,杨体成,刘建毅. 1983. 原地电阻率变化的实验[J]. 地震学报,5(2):217–225. Zhao Y L,Qian F Y,Yang T C,Liu J Y. 1983. Experiments in situ of electrical resistivity changes[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,5(2):217–225 (in Chinese).
赵玉林,卢军,李正南,钱复业,张洪魁. 1996. 唐山地震应变-电阻率前兆及虚错动模式[J]. 地震学报,18(1):78–82. Zhao Y L,Lu J,Li Z N,Qian F Y,Zhang H K. 1996. The precursors of strain-resistivity and virtual-dislocation model before Tangshan earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,18(1):78–82 (in Chinese).
Brace W F,Orange A S,Madden T R. 1965. The effect of pressure on the electrical resistivity of water-saturated crystalline rocks[J]. J Geophys Res,70(22):5669–5678. doi: 10.1029/JZ070i022p05669
Dobrovolsky I P,Zubkov S I,Miachkin V I. 1979. Estimation of the size of earthquake preparation zones[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,117(5):1025–1044. doi: 10.1007/BF00876083
Hillel D. 1998. Environmental Soil Physics[M]. San Diego:Academic Press:771.
Lin J,Stein R S. 2004. Stress triggering in thrust and subduction earthquakes and stress interaction between the southern San Andreas and nearby thrust and strike-slip faults[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,109(B2):B02303.
Lu J,Qian F Y,Zhao Y L. 1999. Sensitivity analysis of the Schlumberger monitoring array:Application to changes of resistivity prior to the 1976 earthquake in Tangshan,China[J]. Tectonophysics,307(3/4):397–405.
Lu J,Xue S Z,Qian F Y,Zhao Y L,Guan H P,Mao X J,Ruan A G,Yu S R,Xiao W J. 2004. Unexpected changes in resistivity monitoring for earthquakes of the Longmen Shan in Sichuan,China,with a fixed Schlumberger sounding array[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,145(1/2/3/4):87–97.
Lu J,Xie T,Li M,Wang Y L,Ren Y X,Gao S D,Wang L W,Zhao J L. 2016. Monitoring shallow resistivity changes prior to the 12 May 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake on the Longmen Shan tectonic zone,China[J]. Tectonophysics,675:244–257. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.03.006
Oki T,Kanae S. 2006. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources[J]. Science,313(5790):1068–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.1128845
Thomas J F, Christopher H S. 1971. Mechanism of underthrusting in southwest Japan: A model of convergent plate interactions[J]. J Geophys Res, 76(29): 7260–7292. Thomas J F,Christopher H S. 1971. Mechanism of underthrusting in southwest Japan:A model of convergent plate interactions[J]. J Geophys Res,76(29):7260–7292.
Wan Y G,Shen Z K,Bürgmann R,Sun J B,Wang M. 2017. Fault geometry and slip distribution of the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan,China earthquake,inferred from GPS and InSAR measurements[J]. Geophys J Int,208(2):748–766. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw421
Zhu Q,Nie X F,Zhou X B,Liao K H,Li H P. 2014. Soil moisture response to rainfall at different topographic positions along a mixed land-use hillslope[J]. Catena,119:61–70. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2014.03.010




 下载:
下载: