Estimation of time error for a single station based on Green’s function by ambient noise cross-correlation
-
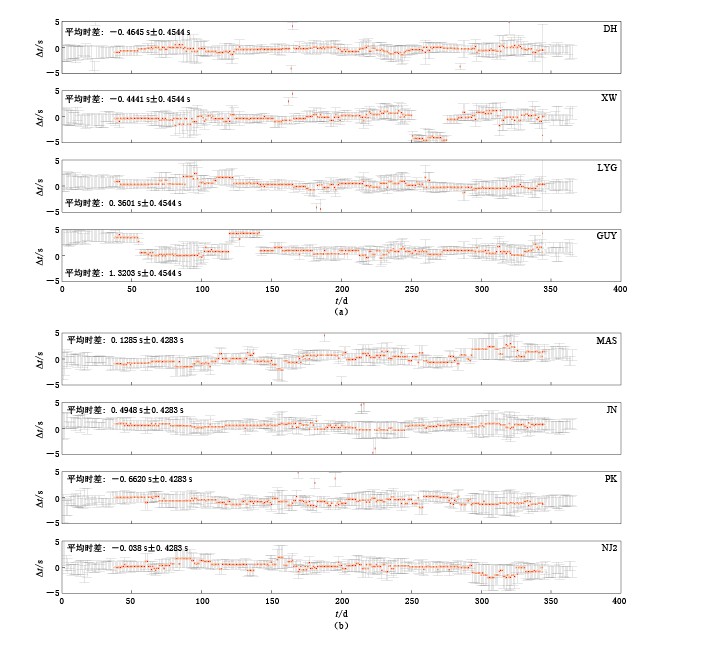
摘要: 从江苏省数字地震台网2011年的宽频带记录数据中, 选取了不同背景噪声区域下的两组不同台间距的台站(A, B每组4个台站), 两组台站的平均台间距分别为44.6和30.5 km. 首先, 运用滑动窗互相关技术, 测量出各台站对间背景噪声互相关格林函数随时间的偏移量ΔDSi-Sj, 然后通过奇异值分解来求解由ΔDSi-Sj与系数矩阵构成的超定方程, 从而计算出单个台站的时钟误差ΔSi;并引入协方差矩阵来估计不同置信水平下计算结果的误差范围. 计算结果表明, 除去明显的钟差误差(>3 s)外, 8个台站的时间误差平均均方根为0.4215 s, A与B两组台站在置信水平为95%时的时间误差范围分别为±0.4544 s和±0.4283 s; 而采用HYPOSAT定位方法对2010—2011年江苏地区的地震进行定位, 得到的平均走时残差约为0.386 s. 两者的计算精度基本相当, 表明基于背景噪声互相关格林函数计算出的单台时间误差是可信的.Abstract: From the broadband data recorded by the digital seismic network of Jiangsu Province in 2011, this paper selected two station groups A and B (each has four stations). The two groups were under different ambient noise area and the average station distances were 44.6 km and 30.5 km, respectively. Firstly, by the sliding window cross-correlation technique, the offsets of the Green’s function were measured by ambient noise cross correlation between station-pairs in the year 2011. Then, the singular value decomposition was applied to solve the over-determined equation of ΔDSi-Sj and the coefficient matrices, so as to calculate clock error ΔSi for a single station. And the covariance matrix was introduced to estimate the error range of calculation results under different confidence level. The results showed that ignoring the obvious clock error ( >3 s), the average RMS of time errors for eight stations was about 0.4215 s, and on the 95% confidence level, the errors ranges for the two groups of stations were ±0.454 4s and ±0.4283, respectively. The average travel time residual was about 0.386 s by adopting HYPOSAT to locate actual earthquakes in Jiangsu region during the period of 2010—2011. Therefore, both residuals are consistent in accuracy, suggesting it is reliable to estimate the time error for a single station based on Green’s function by noise cross-correlation.
-
-
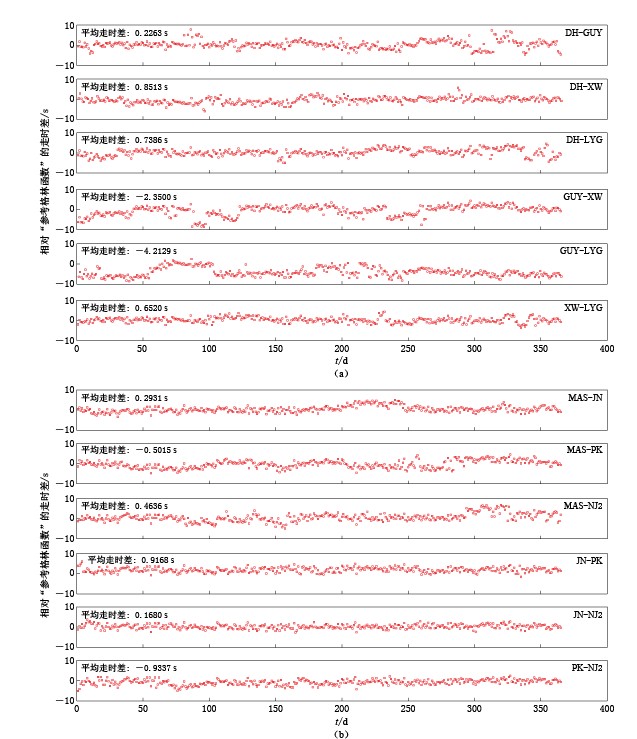
图 2 2011-03-10台站对PX-DHS和MCH-WX的背景噪声互相关格林函数(a)和2011-01-10 XW台人为加入30 s钟差前(上图)后(下图)的背景噪声互相关格林函数(b)
Figure 2. The cross-correlation Green’s function of the ambient noise for station pairs PX-DHS and MCH-WX on March 10, 2011 (a) and that for station pair LYG-XW before (upper) and after (lower) artificially adding the 30 s clock error on original data of the station XW on January 10, 2011 (b)
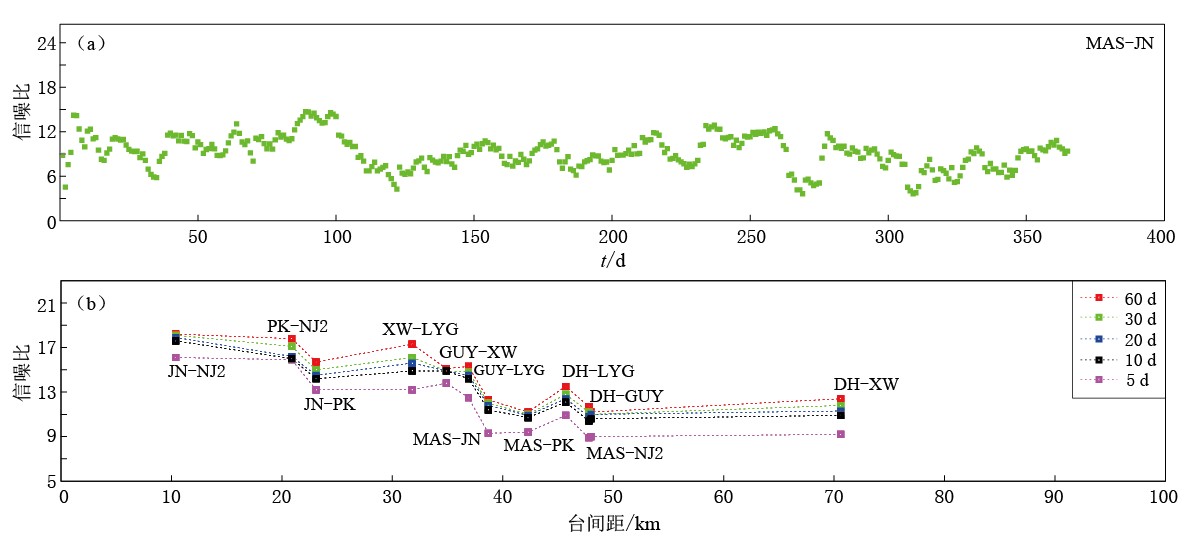
图 3 2011年台站对MAS-JN背景噪声互相关格林函数的信噪比(a)和各台站对 采用不同窗长(分别为10, 20, 30, 60天)叠加得到的信噪比结果(b)
Figure 3. The signal-to-noise ratio of the cross-correlation Green’s function of ambient noise for station pair MAS-JN in 2011 (a) and the superimposed signal-to-noise ratio results of all station pairs with different window length (10, 20, 30, 60 days) (b)
表 1 不同置信水平下计算结果的均方根和误差范围
Table 1 The RMS results and error ranges of calculation results under different confidence level
系数矩阵 G 中的随机误差 置信水平 标度因子 均方根时差/s 误差范围/s A组 B组 A组 B组 0.00 90.00% 1.644 9 0.750 1 0.450 4 ±0.381 3 ±0.359 4 95.00% 1.960 0 0.750 1 0.450 2 ±0.454 4 ±0.428 3 99.00% 2.575 8 0.750 1 0.450 4 ±0.597 1 ±0.562 8 0.10 90.00% 1.644 9 0.710 5 0.474 6 ±0.374 2 ±0.367 5 95.00% 1.960 0 0.783 0 0.473 7 ±0.492 6 ±0.420 2 99.00% 2.575 8 0.760 3 0.430 5 ±0.618 0 ±0.610 2 0.15 90.00% 1.644 9 0.842 0 0.474 0 ±0.394 6 ±0.378 6 95.00% 1.960 0 0.762 9 0.446 9 ±0.412 3 ±0.443 1 99.00% 2.575 8 0.721 0 0.428 2 ±0.531 5 ±0.510 7 0.20 90.00% 1.644 9 0.666 6 0.469 6 ±0.339 8 ±0.307 4 95.00% 1.960 0 0.672 6 0.434 1 ±0.388 8 ±0.381 6 99.00% 2.575 8 0.802 3 0.424 2 ±0.624 6 ±0.481 7 0.25 90.00% 1.644 9 0.857 8 0.506 3 ±0.526 5 ±0.509 5 95.00% 1.960 0 0.786 2 0.565 6 ±0.509 3 ±0.689 9 99.00% 2.575 8 0.708 3 0.501 6 ±0.527 7 ±0.665 1 0.30 90.00% 1.644 9 0.786 9 0.383 7 ±0.345 6 ±0.376 5 95.00% 1.960 0 0.837 4 0.495 2 ±0.573 3 ±0.588 2 99.00% 2.575 8 0.732 2 0.521 4 ±0.558 5 ±0.688 2 -
刘志坤, 黄金莉. 2010. 利用背景噪声互相关研究汶川地震震源区地震波速度变化[J].地球物理学报, 53 (4): 853-863. 王俊, 徐戈, 孙业君. 2009. 江苏省区域地表背景噪声特性的分析[J].地震研究, 32 (2): 155-161. 王伟涛, 倪四道, 王宝善. 2011. 地球背景噪声干涉应用研究的新进展[J].中国地震, 27 (1): 1-13. 夏英杰, 倪四道, 曾祥方. 2011. 汶川地震前地脉动信号的单台法研究[J].地球物理学报, 54 (10): 2590-2596. 张雁滨, 蒋骏, 李胜乐, 陈德璁, 杨辉, 李畅. 2010. 热带气旋引起的震颤波[J].地球物理学报, 53 (2): 335-341. 张志涌等(编著). 2011. 精通MATLAB R2011a[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社: 125-133. 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 2004. 地震台站观测环境技术要求 (GB/T19531.4-2004)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-12. Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Barmin M P, Levshin A L, Lin F, Moschetti M P, Shapiro N M, Yang Y. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J].Geophys J Int, 169 (3): 1239-1260.
Bormann P. 2012. New Manual of Seismological Observatory Practice[M/OL]. Potsdam: GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences: 16-20, doi:10.2312/GFZ.NMSOP-2_ch8. [2012-03-20].http://bib.telegrafenberg.de/publizieren/vertrieb/nmsop/.
Brenguier F, Shapiro N M, Campillo M, Ferrazzini V, Duputel Z, Coutant O, Nercessian A. 2008. Towards forecasting volcanic eruptions using seismic noise[J].Nature Geoscience, 1 : 126-130.
Campillo M, Paul A. 2003. Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda[J].Science, 299 (5606): 547-549.
Clarke D, Zaccarelli L N, Shaprio M, Brenguier F. 2011. Assessment of resolution and accuracy of moving window cross spectral technique for monitoring crustal temporal variations using ambient seismic noise[J].Geophys J Int, 186 (2): 867-882.
Dennis M L. 2008. The proof of the position is in the testing[C]//42nd Annual Alaska Surveying and Mapping Conference. Alaska: Urban and Regional Information Systems Association: 1-4.
Klein F W. 2002. User's Guide to HYPOINVERSE-2000, a Fortran Program to Solve for Earthquake Locations and Magnitudes[R]. US Geological Survey Open File Report 02-171: 116-120.
Larose E, Margerin L, Derode A, Fink M. 2006. Correlation of random wave fields: an interdisciplinary review[J].Geophysics, 71 (4): 111-121.
Lobkis O, Weaver R. 2001. On the emergence of the Green's function in the correlations of a diffuse field [J].J Acoust Soc Amer, 110 (6): 3011-3017.
Longuet H M S. 1950. A theory of the origin of microseisms[J].Philos T R Soc A, 243 (857): 1-35.
McNamara D E, Boaz R I. 2005. Seismic Noise Analysis System Using Power Spectral Density Probability Density Functions: A Stand-Alone So ftware Package[R]. US Geological Survey Open-File Report: 11-20.
Menke W. 1984. Geophysical Data Analysis: Discrete Inverse Theory[M] . Orlando, Florida: Academic Press: 89-114.
Nakahara H. 2006. A systematic study of theoretical relations between spatial correlation and Green's function in one-, two- and three-dimensional random scalar wavefields[J].Geophys J Int, 167 (3): 1097-1105.
Sabra K G, Gerstoft P, Roux P, Kuperman W A, Fehler M C. 2005. Extracting time-domain Green's function estimates from ambient seismic noise[J].Geophys Res Lett, 32 (3): L03310, doi:10.1029/2004GL02/1862.
S′anchez S F, Campillo M. 2006. Retrieval of the Green's function from cross correlation: the canonical elastic problem[J].Bull Seism Soc Amer, 96 (3): 1182-1191.
Schönfelder C S. 2008. Synchronizing seismic networks with ambient noise[J].Geophys J Int, 174 (3): 966-970.
Schönfelder C S, Wegler U. 2006. Passive image interferometry and seasonal variations of seismic velocities at Merapi Volcano, Indonesia[J].Geophys Res Lett, 33 (21): L21302, doi:10.1029/2006GL027797.
Schweitzer J. 2001. HYPOSAT: An enhanced routine to locate seismic events[J].Pure Appl Geophys, 158 (1/2): 277-289.
Shapiro N M, Campillo M. 2004. Emergence of broadband Rayleigh waves from correlations of the ambient seismic noise[J].Geophys Res Lett, 31 (7), doi:10.1029/2004GL019491.
Shapiro N M, Campillo M, Stehly L, Ritzwoller M H. 2005. High resolution surface wave tomography from ambient seismic noise[J].Science, 307 (5715): 1615-1618.
Stehly L, Campillo M, Shapiro N M. 2006. A study of the seismic noise from its long range correlation properties[J].J Geophys Res, 111 (B10): B10306.
Stehly L, Campillo M, Shapiro N M. 2007. Traveltime measurements from noise correlation: Stability and detection of instrumental time-shifts[J].Geophys J Int, 171 (1): 223-230.
Wegler U, Schönfelder C S. 2007. Fault zone monitoring with passive image interferometry[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 168 (3): 1029-1033.
Yao H J, van der Hilst R D, de Hoop M V. 2006. Surface wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: Ⅱ . Crustal and upper-mantle structure[J]. Geophys J Int, 173 (1): 205-219.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 包雪,叶放,张晗,金春伟. 宽频带地震仪性能现场检测方法进展研究. 地球物理学进展. 2023(04): 1739-1756 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 田原,王伟涛,李丽,于常青,张海明. 基于背景噪声互相关函数的地震观测密集台阵时钟偏差分析方法. 北京大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(04): 638-648 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 胡梦迪,金星,李军. 利用噪声互相关技术计算福建台网台站绝对钟差. 防灾减灾学报. 2020(03): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 寇华东,王伟君,彭菲,闫坤. 利用地震背景噪声互相关检测流动地震台波形时钟漂移. 地震. 2020(04): 103-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 詹小艳,王恒知,王俊,缪发军,薛莹莹,朱升初. 基于波谱包络特征的地震事件检测. 地震研究. 2018(02): 258-263 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王俊,郑定昌,郑江蓉,詹小艳,江昊琳,李正楷,张金川. 利用背景噪声自相关研究芦山M7.0地震震源区地壳相对波速的时空变化特征. 地震地质. 2016(01): 152-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: