Recognition of small magnitude seismic events type based on time-frequency features and machine learning
-
摘要:
本研究聚焦于华北地区小震级(ML≤3.0)地震事件,利用K-近邻算法(KNN)、自适应提升算法(AdaBoost)和轻量级梯度提升机算法(LGBM)对天然地震、人工爆炸以及矿震塌陷事件进行类型识别,得到了较好的效果。对地震事件波形记录和时频谱进行分析,提取了时间、P/S幅值比、频率、过零率、峰值振幅、峰值地面加速度、能量、信号、角度及其它比值10个类别的62个特征,将这些特征作为分类的基础。采用三种分类算法分别对二分类任务和三分类任务进行模型训练,最后对测试数据的类型进行识别,所有分类模型的识别准确率均达90.0%以上,其中LGBM的综合性能最强,AdaBoost次之;不同分类任务中天然地震与矿震分类模型的表现最佳。
Abstract:The identification and classification of seismic events hold significant importance in seismic monitoring and earthquake disaster mitigation. This research primarily focuses on
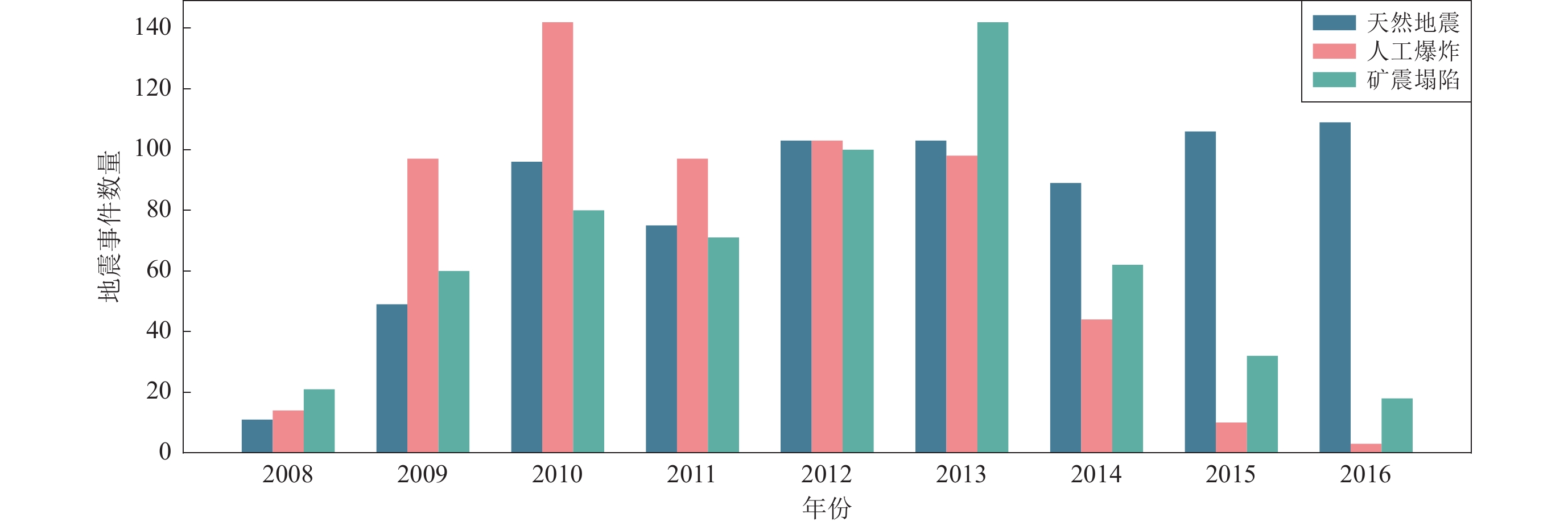
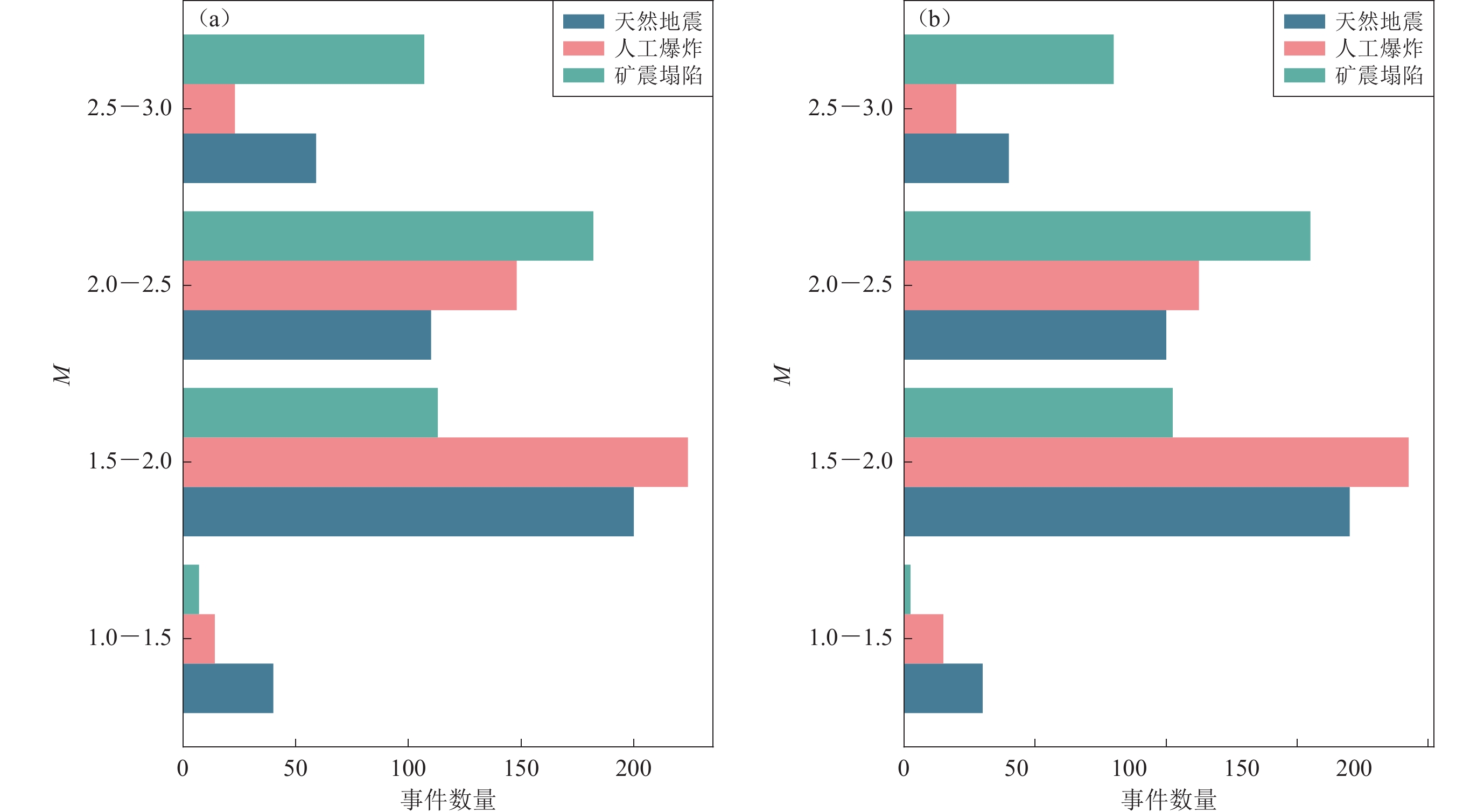
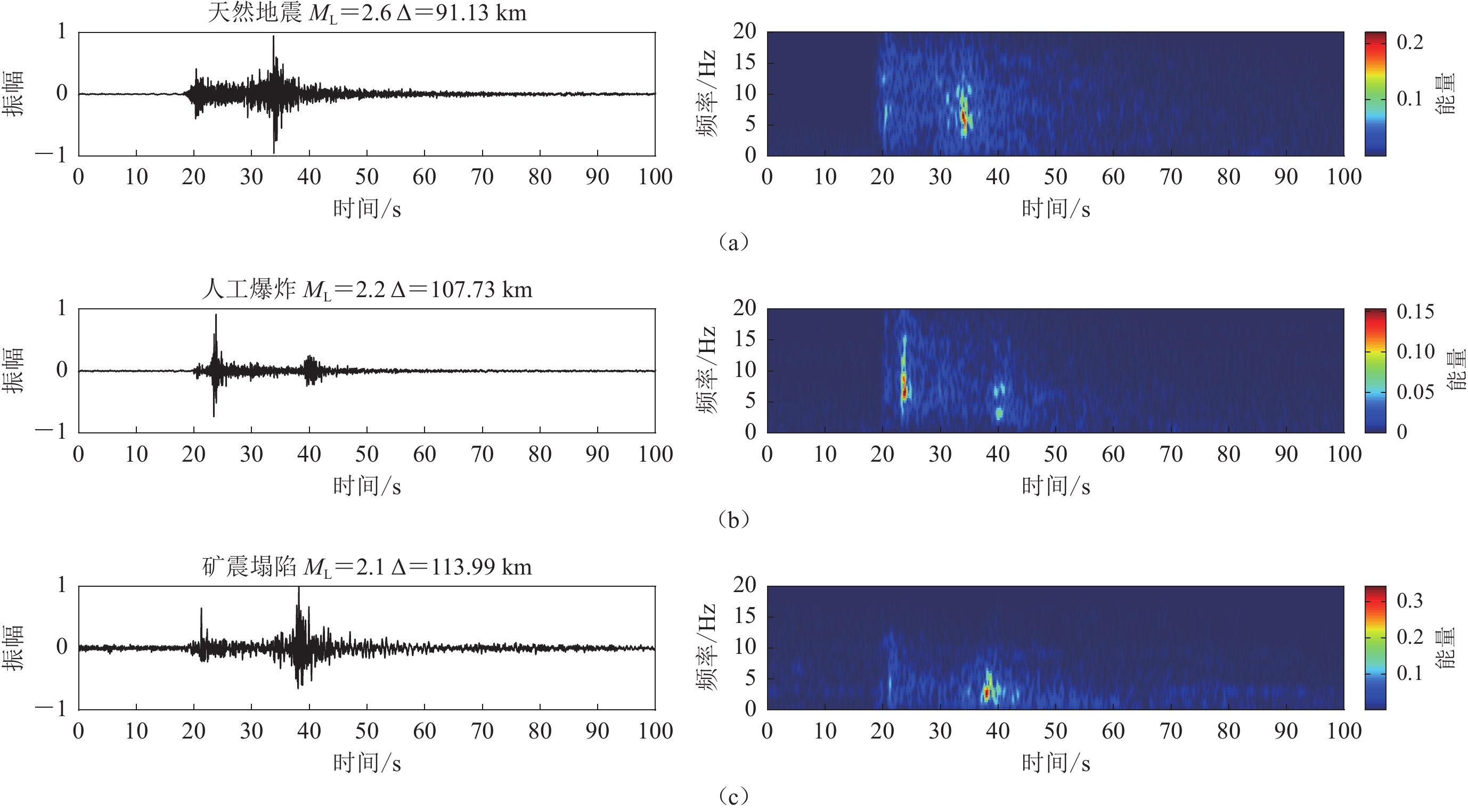
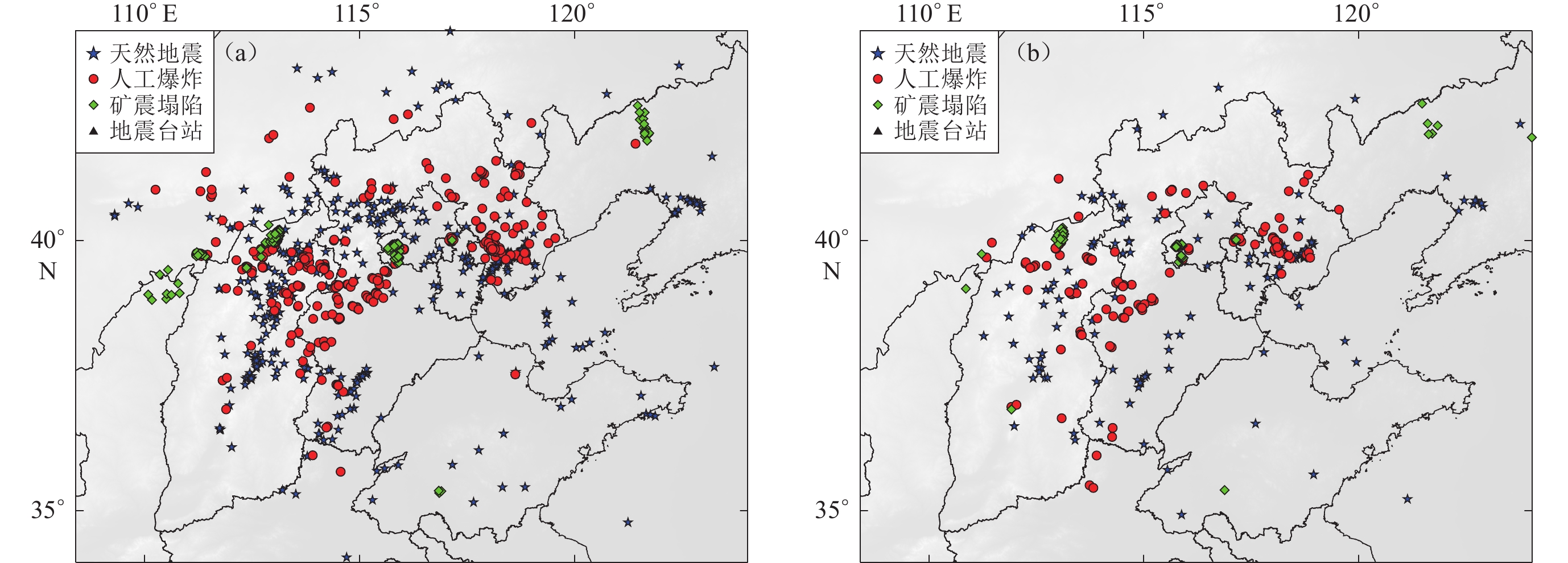
1935 seismic event data with low magnitude (ML≤3.0) in the North China region, encompassing three distinct types of events: natural earthquakes, artificial explosions, and mining collapses. Preliminary analysis involved the geographical distribution examination, annual trends, and magnitude distribution of these events. Preprocessing of raw seismic data included amplitude normalization, detrending, mean removal, and band-pass filtering (0.5—20 Hz). Additionally, short-time Fourier transform analysis was utilized to visualize waveform and spectrogram characteristics, facilitating the observation and analysis of both time and frequency domain features. Based on the analysis results, 62 features across 10 categories, including time, P/S amplitude ratio, frequency, zero-crossing rate, peak amplitude, peak ground acceleration, energy, signal characteristics, angle, and other ratios, were extracted as the foundation for classification.This research employed K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost), and Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM) algorithms to train models using the extracted 62 features for binary and ternary classification tasks of natural earthquakes, artificial explosions, and mining collapses. The basic principles of KNN, AdaBoost, and LGBM algorithms were initially introduced, followed by a description of the training process for the classification models. To ensure balanced sample distribution for each event type, data were selected based on uniform distribution of time and geographical location. Ultimately, 545 events for each event type, totaling
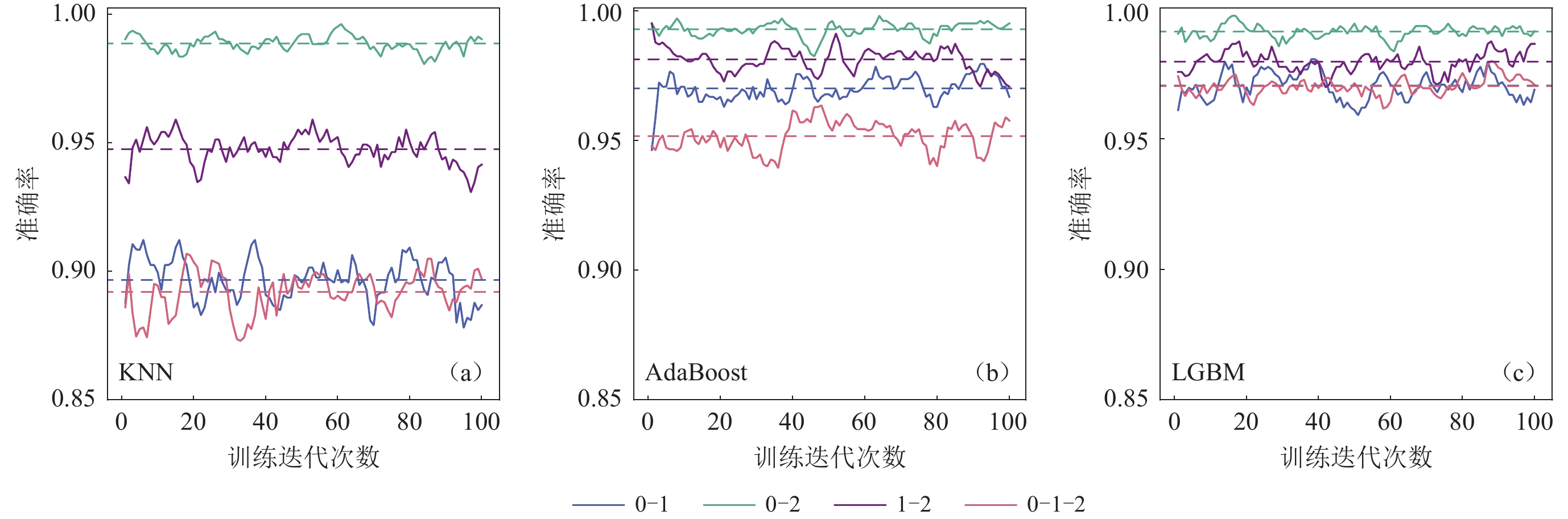
1635 seismic events, were chosen as the sample data for building the classification models. The dataset was divided into training and testing sets using a holdout method, with 75% of the data used for model construction and validation, and 25% for evaluating model performance. The training data covered the main geographical range of the North China region (109.3°—123.5°E, 34.1°—43.7°N), ensuring the models could capture the region’s diversity and complexity. The testing data covered a slightly different geographical range (110.8°—124.1°E, 34.9°—42.7°N).The 62 features were used to train classification models by KNN, AdaBoost, and LGBM algorithms. Models were trained with number 0 representing natural earthquakes, number 1 representing artificial explosions, and number 2 representing mining collapses. Various classification models were evaluated using KNN, AdaBoost, and LGBM, with each model trained and tested 100 times for 0−1, 0−2, 1−2, and 0−1−2 classification tasks. AdaBoost and LGBM demonstrated superior performance compared to KNN across all classification tasks, especially in 0−1 and 0−1−2 classification task. LGBM consistently exhibited the best overall performance, maintaining an accuracy of over 95% and showing high stability. In different classification tasks, 0−2 classification yielded the most outstanding results, followed by 1−2 classification.
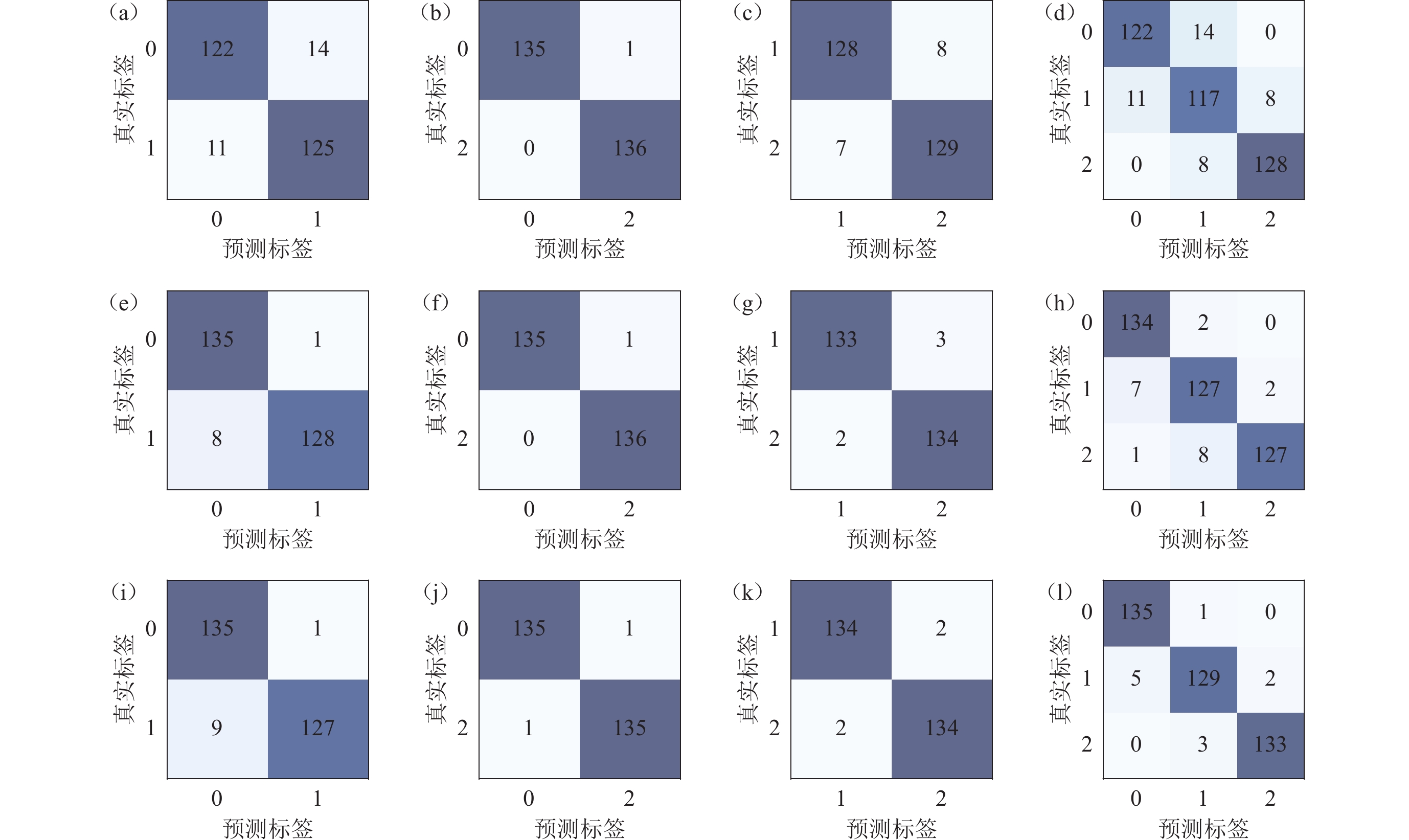
Following the training of classification models, the focus shifted to comprehensive evaluation of these models using testing data. Each model was used to identify the event types in the testing data, yielding performance results for each model across different classification tasks. Confusion matrices were generated based on identification results, demonstrating excellent performance for each classification task, particularly in the 0−2 classification using three different classification algorithms.
Based on confusion matrices, performance evaluation metrics, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score, were calculated. In the 0−1 classification task, AdaBoost performed the best, achieving an accuracy of 96.69%. In the 0−2 classification task, all three algorithms performed well, with metrics exceeding 99.26%. In the 1−2 and 0−1−2 classifications, LGBM exhibited the best performance. Overall, each classification model demonstrated excellent performance, with accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score all exceeding 89.71%.
LGBM exhibited superior overall performance, maintaining an accuracy of over 95.90% and demonstrating high stability. KNN still has significant room for improvement, possibly due to its sensitivity to data, resulting in relatively weaker performance compared to AdaBoost and LGBM. AdaBoost’s overall performance lies between LGBM and KNN.
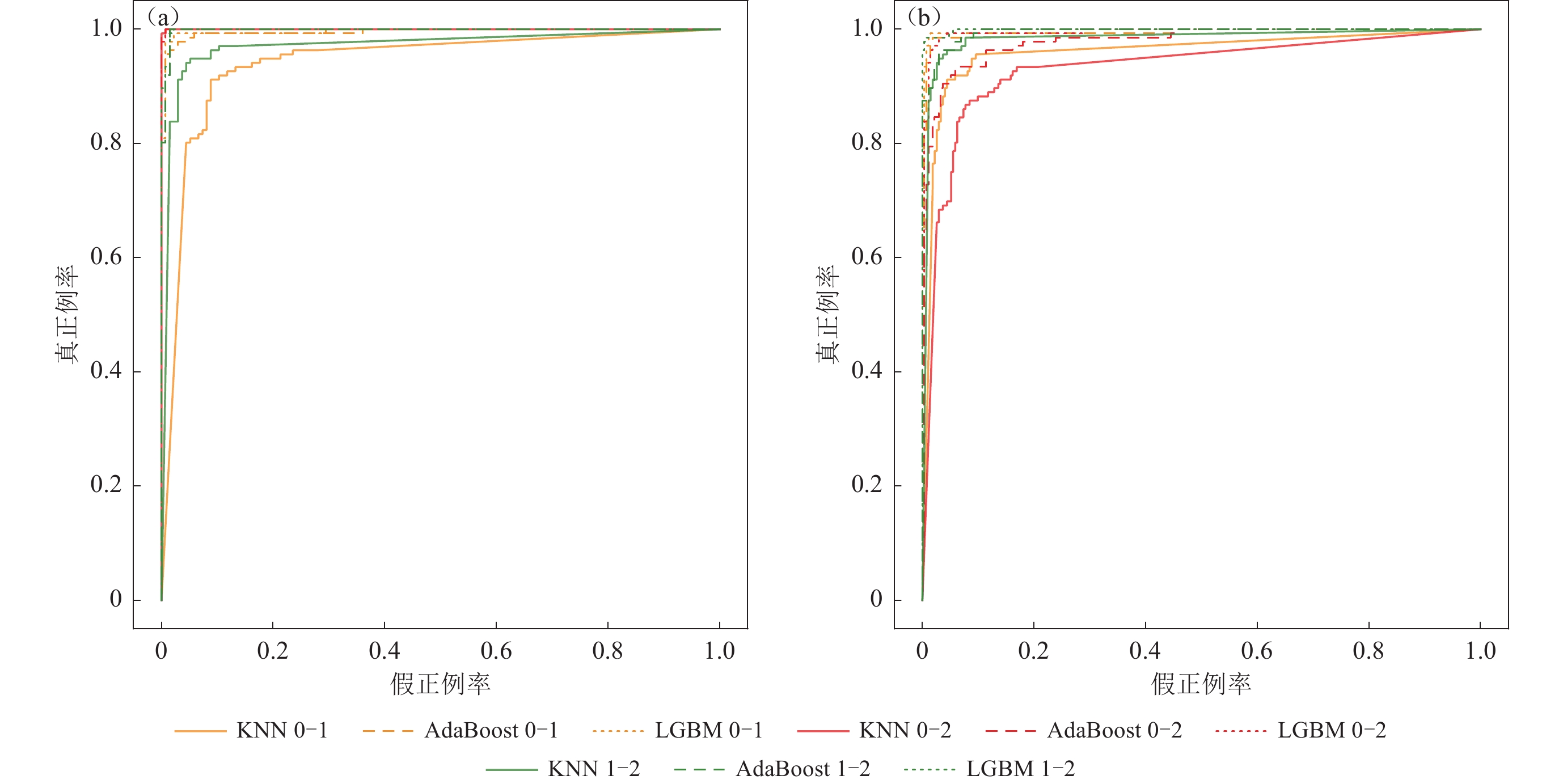
Finally, ROC curves were plotted to visualize the recognition of the testing dataset using three different classification algorithms (KNN, AdaBoost, LGBM). While KNN algorithm performance for 0−1 and 1−2 classifications requires optimization, all other models performed exceptionally well in the ternary classification scenario. Confusion matrices and evaluation metrics indicate that the constructed classification models perform well on testing data, with ROC curve analysis further confirming the excellent performance of the classification models in various tasks and revealing the applicability of different algorithms in their respective tasks, providing strong support for the practical application of the models.
-
-
图 5 特征分布图
(a) 阈值之上的平均下降频率特征分布;(b) 滤波波段为9.5—10.5 Hz的P/S振幅比特征分布;(c) 1—20 Hz频带的P/S振幅比特征分布
Figure 5. Distribution of features
(a) Distributions of features of the decay average frequency above the threshold;(b) The P/S amplitude ratio distribution at 9.5—10.5 Hz filter band;(c) The P/S amplitude ratio distribution at the frequency band from 1 to 20 Hz
表 1 所提取的特征表
Table 1 Table of extracted features
特征 物理意义 数量 时间 地震波形从起始点到达波峰所需的时间;从波峰到达结束点所需的时间;从起始点到结束点所经历的总时间;地震波形超过设定阈值的持续时间;地震波形在超过设定阈值后到达波峰所需的时间;地震波形在超过设定阈值后从波峰到结束点所需的时间;地震波形在超过设定阈值前波形的上升、下降时间;两个相邻的波峰或波谷之间的时间间隔,即两个相邻波峰或波谷之间的周期长度(Kim et al,2 021;薛思敏等,2 022)。 9 P/S幅值比 P波与S波峰值振幅之比(Yıldırım et al,2 011);对P波、S波进行傅里叶变换,滤波波段为1—20 Hz时振幅之比(Wang et al,2 021)。 21 频率 地震信号中波形每秒振动的次数,为周期的倒数(Levshin et al,1995);中心频率,地震信号在频率域中的中心位置;主频率,地震信号中振幅最大的频率;平均频率,地震信号频谱的加权平均频率;地震波形在上升或下降阶段的平均频率;波形上升、下降时,地震信号在超过设定阈值的情况下的平均频率;地震信号复倒频谱的实部(魏富胜,黎明,
2 003)。9 过零率 地震波形从正向值变为负向值,或从负向值变为正向值的次数;地震信号在超过设定阈值的情况下的过零率;峰值振幅前、后的过零率;地震信号在超过设定阈值的情况下的最大振幅前、后的过零率(Dargahi-Noubary,1998)。 6 峰值振幅 地震波形中振幅达到的最大值(Horasan et al,2009;Badawy et al,2019)。 1 峰值地面加速度 地震信号中垂直地面方向的最大加速度值(Goforth et al,2006)。 1 能量 地震信号总能量;峰值振幅前吸收能量、峰值振幅后衰减能量(刘莎等,2012)。 3 信号 地震信号强度;信号均方根(Laasri et al,2015;Saad et al,2019)。 2 其它比值 地震波形的上升时间、下降时间与峰值振幅之比(the ratio of rise time to amplitude,缩写为RA;the ratio of decay time to amplitude,缩写为DA);阈值之上的上升、下降时间和振幅的比值;RA,DA与地震波形的平均频率之比(ratio of RA to average frequency,缩写为RA/AF;ratio of DA to average frequency,缩写为DA/AF)(吴顺川等,2020)。 6 角度 地震波形的上升、下降角度,为RA,DA的反正切函数(Ma et al,2015);地震信号在超过设定阈值的情况下的上升、下降角度。 4 表 2 不同分类模型准确率平均值、最大值、最小值
Table 2 Average,maximum and minimum accuracy of different classification model
分类模型 0−1准确率 0−2准确率 1−2准确率 0−1−2准确率 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 KNN 89.66% 91.22% 87.80% 98.84% 99.61% 98.05% 94.73% 95.90% 93.07% 89.19% 90.68% 87.30% AdaBoost 96.99% 97.95% 94.63% 99.28% 99.80% 98.24% 98.12% 99.51% 97.07% 95.17% 96.35% 93.94% LGBM 97.03% 98.05% 95.90% 99.10% 99.71% 98.34% 97.95% 98.73% 96.98% 97.01% 97.98% 96.16% 表 3 不同分类模型对不同分类任务的评价指标
Table 3 Evaluation metrics of different classification models for different classification task
分类模型 评价指标 0−1 0−2 1−2 0−1−2 KNN 准确率 90.81% 99.63% 94.49% 91.75% 精度 91.73% 100.00% 94.81% 93.15% 召回率 89.71% 99.26% 94.12% 93.03% F1分数 90.71% 99.63% 94.47% 93.03% AdaBoost 准确率 96.69% 99.63% 98.16% 95.10% 精度 94.41% 100.00% 98.52% 96.11% 召回率 99.26% 99.26% 97.79% 98.99% F1分数 96.75% 99.63% 98.15% 97.52% LGBM 准确率 96.32% 99.26% 98.53% 97.30% 精度 93.75% 99.26% 98.53% 97.31% 召回率 99.26% 99.26% 98.53% 97.30% F1分数 96.44% 99.26% 98.53% 97.30% -
边银菊. 2005. Fisher方法在震级比mb/MS判据识别爆炸中的应用研究[J]. 地震学报,27(4):414–422. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2005.04.008 Bian Y J. 2005. Application of Fisher method to discriminating earthquakes and explosions using criterion mb/MS[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,27(4):414–422 (in Chinese).
蔡杏辉,廖诗荣,张燕明,陈惠芳,林彬华. 2021. 基于支持向量机的地震事件类型自动识别及应用[J]. 华南地震,41(2):27–35. Cai X H,Liao S R,Zhang Y M,Chen H F,Lin B H. 2021. Automatic identification of earthquake event types based on support vector machine and its application[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,41(2):27–35 (in Chinese).
陈润航,黄汉明,柴慧敏. 2018. 地震和爆破事件源波形信号的卷积神经网络分类研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,33(4):1331–1338. doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0326 Chen R H,Huang H M,Chai H M. 2018. Study on the discrimination of seismic waveform signals between earthquake and explosion events by convolutional neural network[J]. Progress in Geophysics,33(4):1331–1338 (in Chinese).
范晓易,曲均浩,刘方斌,周少辉. 2020. 使用支持向量机识别地震类型的影响因素分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,40(10):1034–1038. Fan X Y,Qu J H,Liu F B,Zhou S H. 2020. Analysis of influencing factors in use of support vector machine method to identify earthquake types[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,40(10):1034–1038 (in Chinese).
工业和信息化部. 2011. “十二五”民用爆炸物品行业发展规划[S]. 工业和信息化部. 2016. “十三五”民用爆炸物品行业发展规划[S]. 靳玉贞,林木金,范晓瑜,刘晓萍,何佳,杨世英,孟彩菊. 2015. 山西地区爆破、塌陷(矿震)特殊地震动特征识别[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,36(3):63–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2015.03.012 Jin Y Z,Lin M J,Fan X Y,Liu X P,He J,Yang S Y,Meng C J. 2015. Feature recognition of explosion,collapse (mine earthquake) to specific ground motion in Shanxi region[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,36(3):63–66 (in Chinese).
靳玉贞,刘炜,何佳,杨世英,孟彩菊,刘晓萍. 2019. 太原基准地震台核爆震相识别[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,40(4):59–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2019.04.009 Jin Y Z,Liu W,He J,Yang S Y,Meng C J,Liu X P. 2019. Identification of nuclear explosion waveform recorded by Taiyuan Fundamental Seismic Station[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,40(4):59–64 (in Chinese).
梁皓,孙丽,陈姝荞,支明. 2023. 基于支持向量机算法的地震事件分类研究:以东北地区为例[J]. 地球物理学报,66(12):5030–5040. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0829 Liang H,Sun L,Chen S Q,Zhi M. 2023. Research on seismic event classification based on SVM algorithm:An application in Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,66(12):5030–5040 (in Chinese).
刘莎,杨建思,田宝峰,郑钰,姜旭东,徐志强. 2012. 首都圈地区爆破、矿塌和天然地震的识别研究[J]. 地震学报,34(2):202–214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2012.02.007 Liu S,Yang J S,Tian B F,Zheng Y,Jiang X D,Xu Z Q. 2012. Discrimination between explosions,mine collapses and earthquakes in capital region of China[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,34(2):202–214 (in Chinese).
任涛,林梦楠,陈宏峰,王冉冉,李松威,刘晓雨,刘杰. 2019. 基于Bagging集成学习算法的地震事件性质识别分类[J]. 地球物理学报,62(1):383–392. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0380 Ren T,Lin M N,Chen H F,Wang R R,Li S W,Liu X Y,Liu J. 2019. Seismic event classification based on bagging ensemble learning algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,62(1):383–392 (in Chinese).
王婷婷,边银菊. 2011. 识别天然地震和人工爆破的判据选择[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,32(6):62–67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2011.06.012 Wang T T,Bian Y J. 2011. Criterion selection of earthquake and explosion recognition[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,32(6):62–67 (in Chinese).
魏富胜,黎明. 2003. 震源性质的倒谱分析[J]. 地震学报,25(1):47–54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2003.01.006 Wei F S,Li M. 2003. Cepstrum analysis of source character[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,25(1):47–54 (in Chinese).
隗永刚,杨千里,王婷婷,蒋长胜,边银菊. 2019. 基于深度学习残差网络模型的地震和爆破识别[J]. 地震学报,41(5):646–657. doi: 10.11939/jass.20190030 Wei Y G,Yang Q L,Wang T T,Jiang C S,Bian Y J. 2019. Earthquake and explosion identification based on Deep Learning residual network model[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,41(5):646–657 (in Chinese).
吴顺川,甘一雄,任义,郑立夫. 2020. 基于RA与AF值的声发射指标在隧道监测中的可行性[J]. 工程科学学报,42(6):723–730. Wu S C,Gan Y X,Ren Y,Zheng L F. 2020. Feasibility research of AE monitoring index in tunnel based on RA and AF[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering,42(6):723–730 (in Chinese).
吴涛,庞聪,江勇,丁炜,廖成旺. 2022. 基于随机子空间和AdaBoost集成学习的地震事件性质辨识研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,37(3):981–988. doi: 10.6038/pg2022FF0234 Wu T,Pang C,Jiang Y,Ding W,Liao C W. 2022. Identification and classification of earthquake types based on Cov-SSI and AdaBoost ensemble learning algorithm[J]. Progress in Geophysics,37(3):981–988 (in Chinese).
薛思敏,黄汉明,施佳鹏,袁雪梅,黎炳君. 2022. 基于EMD的IMF时域统计特征提取及其应用于震动事件源类型识别研究[J]. 地震工程学报,44(1):100–107. Xue S M,Huang H M,Shi J P,Yuan X M,Li B J. 2022. Extraction of IMF time-domain features based on EMD and its application to recognition of vibration event source type[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,44(1):100–107 (in Chinese).
杨千里,王婷婷,边银菊. 2020. 基于广义S变换的地震与爆炸识别[J]. 地震学报,42(5):613–628. Yang Q L,Wang T T,Bian Y J. 2020. Recognition of earthquakes and explosions based on generalized S transform[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,42(5):613–628 (in Chinese).
赵永,刘卫红,高艳玲. 1995. 北京地区地震、爆破和矿震的记录图识别[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,16(4):48–54. Zhao Y,Liu W H,Gao Y L. 1995. Distinguishing earthquake,explosion and mine earthquake in Beijing area[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,16(4):48–54 (in Chinese).
Badawy A,Gamal M,Farid W,Soliman M S. 2019. Decontamination of earthquake catalog from quarry blast events in northern Egypt[J]. J Seismol,23(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1007/s10950-019-09873-8
Barama L,Williams J,Newman A V,Peng Z G. 2023. Global nuclear explosion discrimination using a convolutional neural network[J]. Geophys Res Lett,50(17):e2022GL101528. doi: 10.1029/2022GL101528
Chiang A,Dreger D S,Ford S R,Walter W R. 2014. Source characterization of underground explosions from combined regional moment tensor and first-motion analysis[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,104(4):1587–1600. doi: 10.1785/0120130228
Chiang A,Ichinose G A,Dreger D S,Ford S R,Matzel E M,Myers S C,Walter W R. 2018. Moment tensor source-type analysis for the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea-declared nuclear explosions (2006−2017) and 3 September 2017 collapse event[J]. Seismol Res Lett,89(6):2152–2165.
Dargahi-Noubary G R. 1998. Statistical estimation of corner frequency and its application to seismic event-identification[J]. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng,17(5):297–309. doi: 10.1016/S0267-7261(98)00016-5
Freund Y,Schapire R E. 1997. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting[J]. J Comput Syst Sci,55(1):119–139. doi: 10.1006/jcss.1997.1504
Gaebler P,Ceranna L,Nooshiri N,Barth A,Cesca S,Frei M,Grünberg I,Hartmann G,Koch K,Pilger C,Ross J O,Dahm T. 2019. A multi-technology analysis of the 2017 North Korean nuclear test[J]. Solid Earth,10(1):59–78. doi: 10.5194/se-10-59-2019
Goforth T T,Hetzer C H,Stump B W. 2006. Characteristics of regional seismograms produced by delay-fired explosions at the Minntac iron mine,Minnesota[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,96(1):272–287. doi: 10.1785/0120050068
Horasan G,Güney A B,Küsmezer A,Bekler F,Öğütçü Z,Musaoğlu N. 2009. Contamination of seismicity catalogs by quarry blasts:An example from İstanbul and its vicinity,northwestern Turkey[J]. J Asian Earth Sci,34(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.03.012
Jia L Z,Chen H F,Xing K. 2022. Rapid classification of local seismic events using machine learning[J]. J Seismol,26(5):897–912. doi: 10.1007/s10950-022-10109-5
Kim G,Ku B,Ko H. 2021. Multifeature fusion-based earthquake event classification using transfer learning[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett,18(6):974–978. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2993302
Kong Q K,Wang R J,Walter W R,Pyle M,Koper K,Schmandt B. 2022. Combining deep learning with physics based features in explosion-earthquake discrimination[J]. Geophys Res Lett,49(13):e2022GL098645. doi: 10.1029/2022GL098645
Koper K D,Holt M M,Voyles J R,Burlacu R,Pyle M L,Wang R J,Schmandt B. 2021. Discrimination of small earthquakes and buried single-fired chemical explosions at local distances (<150 km) in the western United States from comparison of local magnitude (ML) and coda duration magnitude (MC)[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,111(1):558–570. doi: 10.1785/0120200188
Laasri E H A,Akhouayri E S,Agliz D,Zonta D,Atmani A. 2015. A fuzzy expert system for automatic seismic signal classification[J]. Expert Syst Appl,42(3):1013–1027. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.08.023
Levshin A L,Ritzwoller M H. 1995. Characteristics of surface waves generated by events on and near the Chinese nuclear test site[J]. Geophys J Int,123(1):131–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1995.tb06666.x
Lindenbaum O,Rabin N,Bregman Y,Averbuch A. 2020. Seismic event discrimination using deep CCA[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett,17(11):1856–1860. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2959554
Ma J,Zhao G Y,Dong L J,Chen G H,Zhang C X. 2015. A comparison of mine seismic discriminators based on features of source parameters to waveform characteristics[J]. Shock Vib,2015(1):919143.
Mousavi S M,Horton S P,Langston C A,Samei B. 2016. Seismic features and automatic discrimination of deep and shallow induced-microearthquakes using neural network and logistic regression[J]. Geophys J Int,207(1):29–46. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw258
Peng K,Tang Z,Dong L J,Sun D Y. 2021. Machine learning based identification of microseismic signals using characteristic parameters[J]. Sensors,21(21):6967. doi: 10.3390/s21216967
Pérez N,Venegas P,Benitez D,Grijalva F,Lara R,Ruiz M. 2022. Benchmarking seismic-based feature groups to classify the Cotopaxi volcanic activity[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett,19:7500505.
Pomeroy P W,Best W J,McEvilly T V. 1982. Test ban treaty verification with regional data-A review[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,72(6B):S89–S129. doi: 10.1785/BSSA07206B0089
Ren J Q,Zhou S H,Wang J Y,Yang S,Liu C. 2022. Research on identification of natural and unnatural earthquake events based on AlexNet convolutional neural network[J]. Wireless Commun Mobile Comput,2022(1):6782094.
Saad O M,Shalaby A,Sayed M S. 2019. Automatic discrimination of earthquakes and quarry blasts using wavelet filter bank and support vector machine[J]. J Seismol,23(2):357–371. doi: 10.1007/s10950-018-9810-5
Sanina I A,Nesterkina M A,Konstantinovskaya N L,Gabsatarova I P. 2021. Identification of the nature of seismic events that occurred in the East European platform as recorded by the Mikhnevo small-aperture seismic array at regional distances[J]. Seism Instr,57(1):38–54. doi: 10.3103/S0747923921010084
Selby N D,Bowers D,Douglas A,Heyburn R,Porter D. 2005. Seismic discrimination in southern Xinjiang:The 13 March 2003 Lop Nor earthquake[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,95(1):197–211. doi: 10.1785/0120040040
Shang X Y,Li X B,Morales-Esteban A,Chen G H. 2017. Improving microseismic event and quarry blast classification using Artificial Neural Networks based on Principal Component Analysis[J]. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng,99:142–149. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.05.008
Tan A,Horasan G,Kalafat D,Gülbağ A. 2021. Discrimination of earthquakes and quarries in the Edirne district (Turkey) and its vicinity by using a linear discriminate function method and artificial neural networks[J]. Acta Geophys,69(1):17–27. doi: 10.1007/s11600-020-00519-9
Taylor S R,Denny M D,Vergino E S,Glaser R E. 1989. Regional discrimination between NTS explosions and western U. S. earthquakes[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,79(4):1142–1176. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0790041142
Tibi R,Linville L,Young C,Brogan R. 2019. Classification of local seismic events in the Utah region:A comparison of amplitude ratio methods with a spectrogram-based machine learning approach[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,109(6):2532–2544. doi: 10.1785/0120190150
Voyles J R,Holt M M,Hale J M,Koper K D,Burlacu R,Chambers D J A. 2020. A new catalog of explosion source parameters in the Utah region with application to ML-MC-based depth discrimination at local distances[J]. Seismol Res Lett,91(1):222–236. doi: 10.1785/0220190185
Wang T T,Bian Y J,Yang Q L,Ren M Y. 2021. Correction of P/S Amplitude ratios for low-magnitude seismic events based on Bayesian Kriging method[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,111(5):2799–2813. doi: 10.1785/0120200293
Wang T T,Bian Y J,Zhang Y X,Hou X L. 2023. Using artificial intelligence methods to classify different seismic events[J]. Seismol Res Lett,94(1):1–16. doi: 10.1785/0220220055
Yıldırım E,Gülbağ A,Horasan G,Doğan E. 2011. Discrimination of quarry blasts and earthquakes in the vicinity of Istanbul using soft computing techniques[J]. Comput Geosci,37(9):1209–1217. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2010.09.005
Yue L,Qu J H,Zhou S H,Qu B A,Zhang Y W,Xu Q F. 2023. Seismic event classification based on a two-step convolutional neural network[J]. J Seismol,27(3):527–535. doi: 10.1007/s10950-023-10153-9
Zhang Y X,Wang T T,Bian Y J,Yang Q L. 2021. Features of different types of seismic events in China’s Capital Region[J]. Earthq Sci,34(6):489–506. doi: 10.29382/eqs-2021-0035




 下载:
下载: