Research on seismic characteristics and identification of artificial explosion in different areas and natural earthquake
-
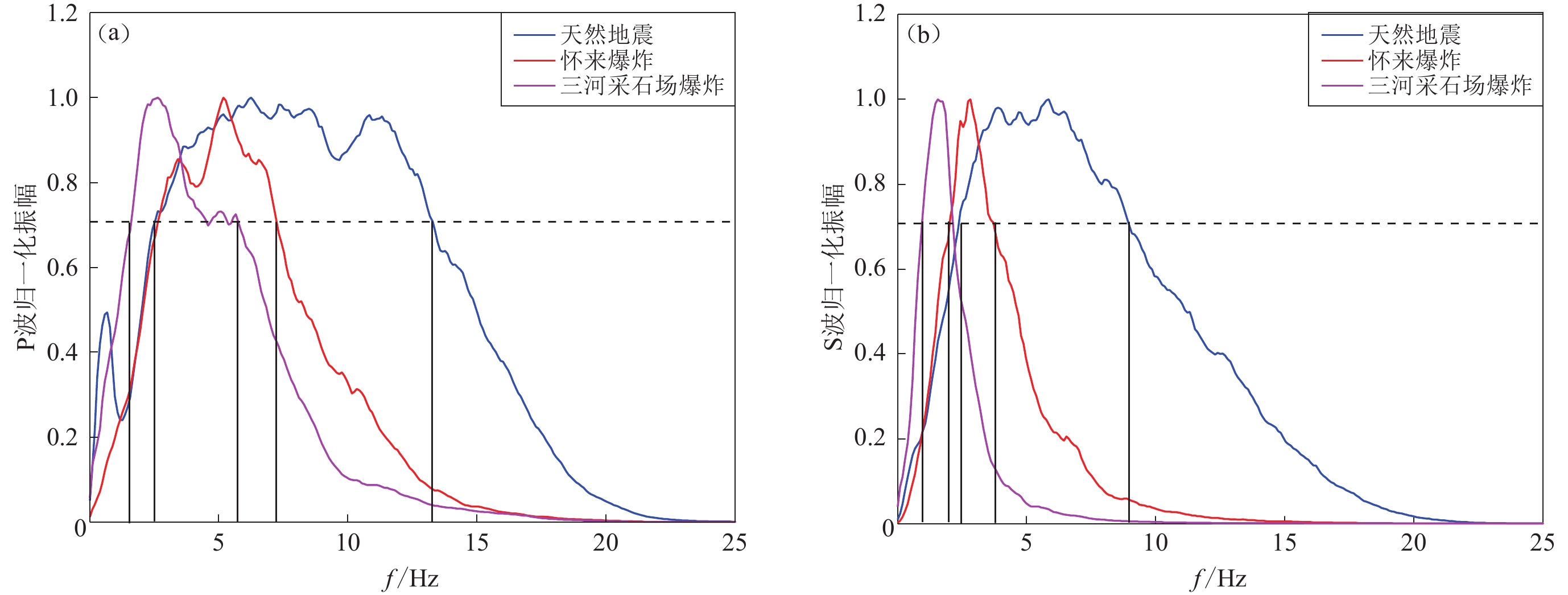
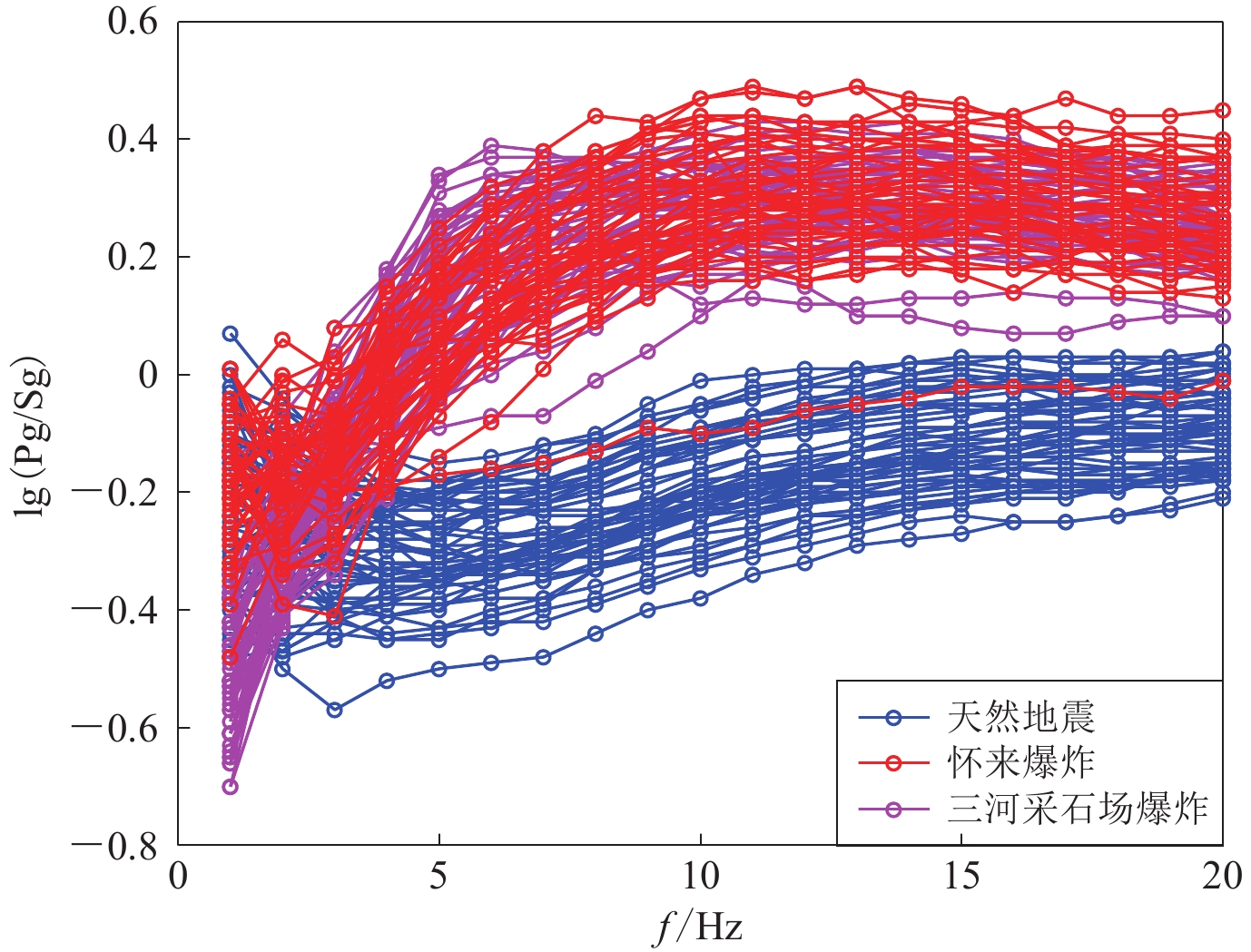
摘要: 本文分析了河北怀来多次爆炸、河北三河采石场多次爆炸和低震级天然地震事件的记录特征和时频差异。结果显示:河北怀来爆炸的P波能量强、衰减快、S波发育弱;河北三河采石场爆炸的P波、S波主频均低于怀来爆炸,S波与面波混淆,不同震中距的台站记录低频发育明显;而天然地震的有效频带更宽,频率成分更为复杂。将Pg/Sg谱比判据应用于小震级地震与爆炸的识别中,探索交叉频带谱比对不同地区爆炸的识别。结果表明:高频(>5 Hz)Pg/Sg谱比判据可将研究数据中的爆炸与小震级地震完全区分;与Sg低频(0—2 Hz)有关的交叉频带谱比可对两个不同地区的爆炸进行识别,交叉频带的谱比判据较传统的单一频带谱比判据能够更好地反映出不同类型事件的特征差异。Abstract: The differences of the seismic characteristics and frequency of the Huailai explosions, the Sanhe quarry explosions and the natural earthquakes with low magnitude are discussed. The results show that the two different area explosions have obviously different seismic characteristics and frequency distribution, Huailai explosion has stronger P wave energy than S wave and fast attenuation; The main frequencies of P wave and S wave in Sanhe quarry explosion are lower than that in Huailai explosion, S wave and surface wave are confused, and the low frequency developed obviously at different distances; While for natural earthquakes, the effective frequency band is wider and the frequency components are more complex than explosions. Pg/Sg spectral ratios in small-magnitude earthquakes and explosions were studied and cross-band spectral ratios were explored. Results obtained show that the high frequency (>5 Hz)Pg/Sg spectral ratio discriminants can completely distinguish explosions from low magnitude earthquakes; The spectral ratios of the cross-band related to low frequency (0−2 Hz) of Sg can effectively identify explosions in these two areas, Pg/Sg discriminants of the crossed frequency band can better reflect the difference characteristics of different types of events than that of the traditional single frequency band.
-
-
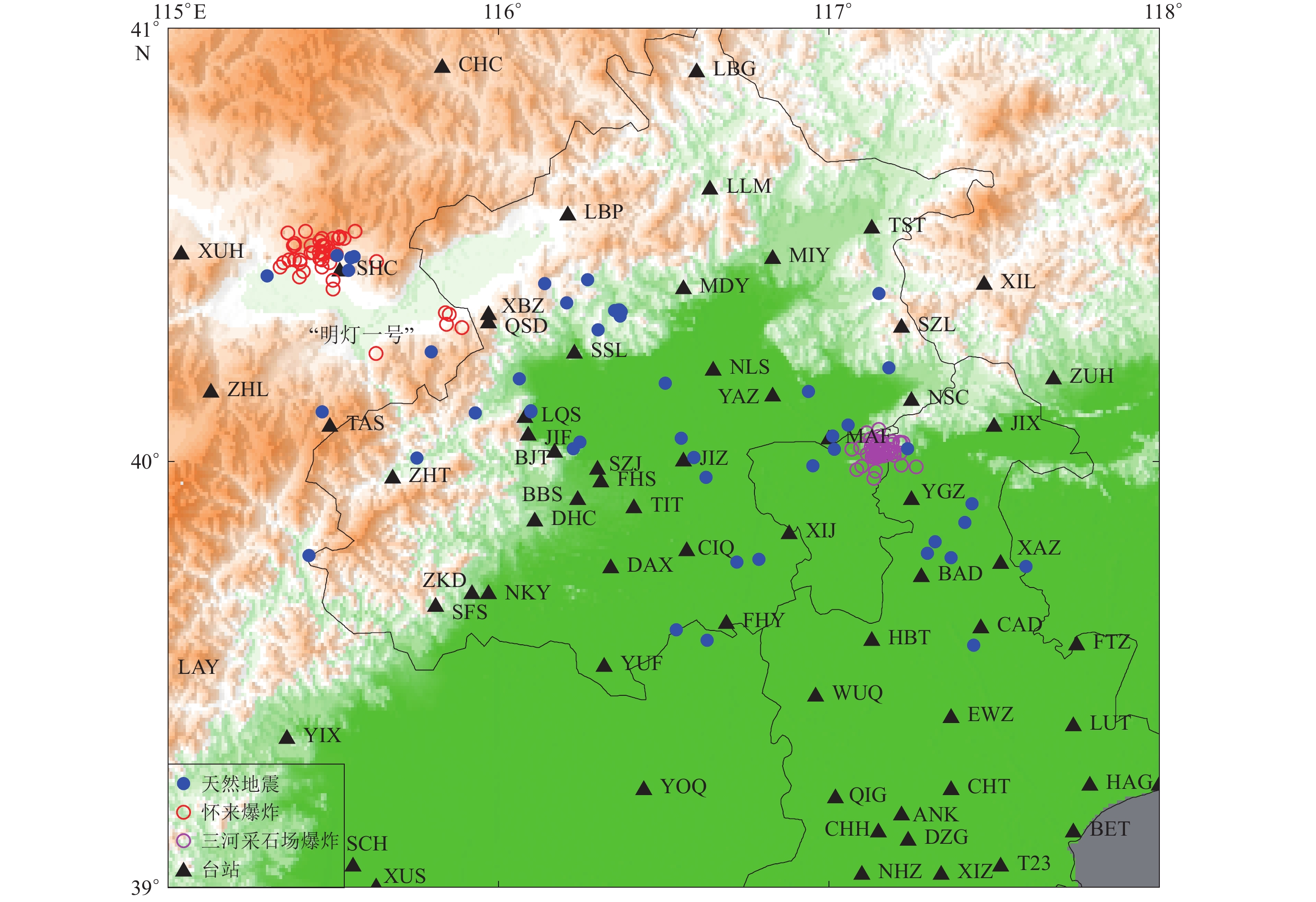
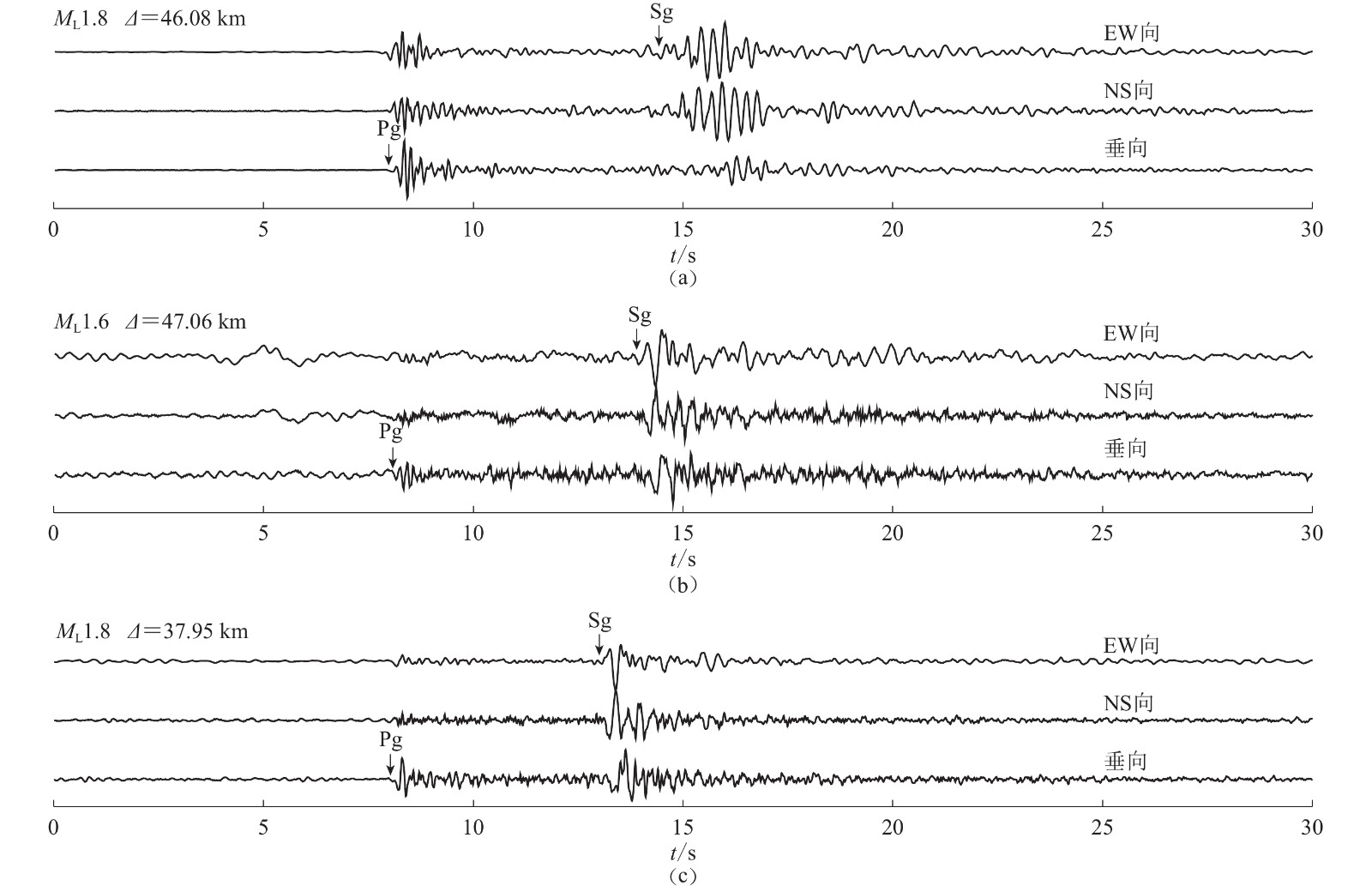
图 2 不同类型事件的地震记录波形
(a)“明灯一号”大当量爆炸;(b)三河采石场爆炸;(c)天然地震。波形上方为事件发生时间及震级,波形右上角为记录台网、台站和震中距,下同
Figure 2. Seismic waveforms for different types of events
(a) “Bright Lamp No.1” large yield explosion;(b) Quarry blast;(c) Earthquake. The time and the magnitude of the events are net on the top of traces,and the station and epicentral distance are on the top right corner of the waveforms,the same below
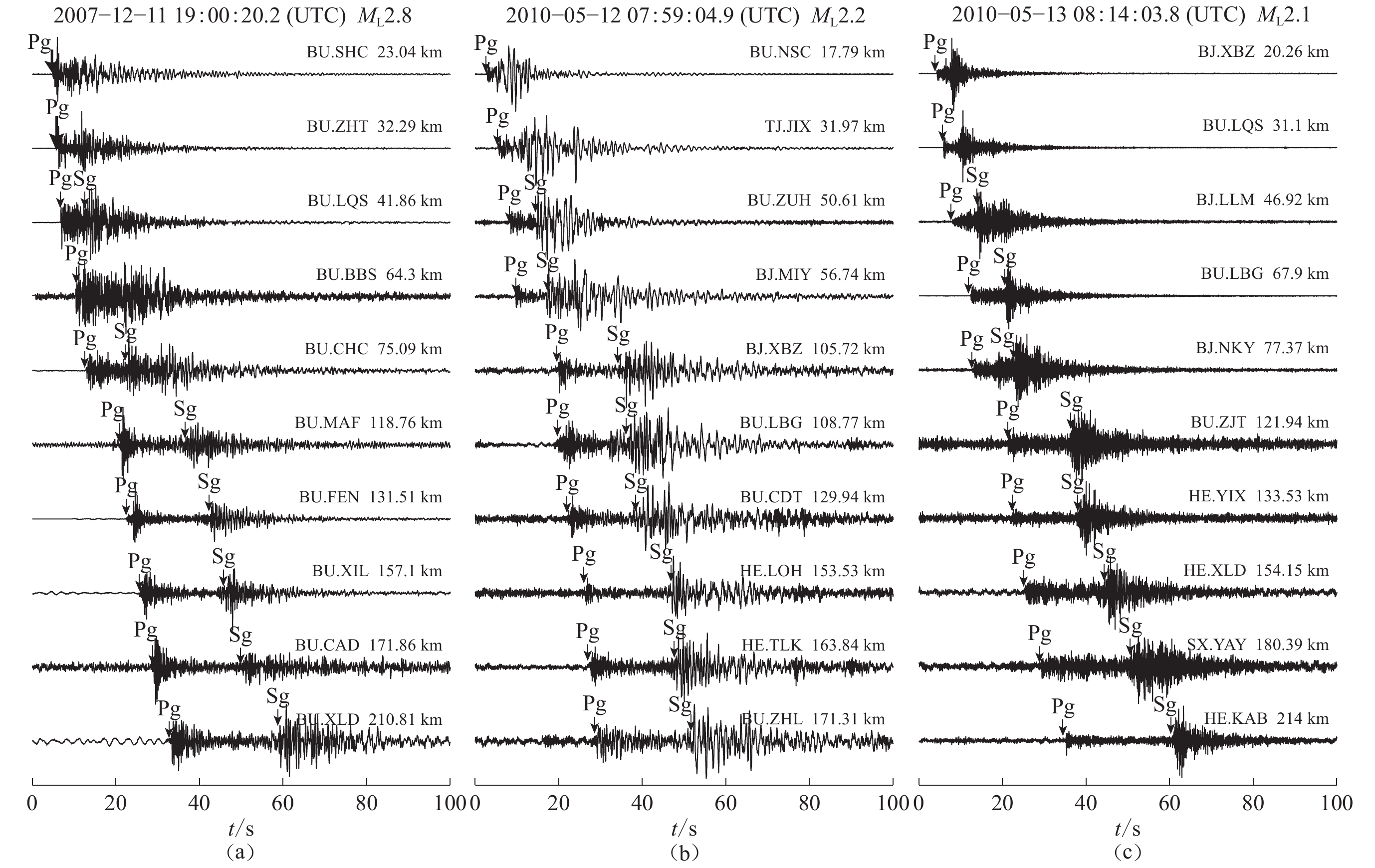
图 6 XBZ台站的不同事件地震波形记录(滤波频带为:0.5—25 Hz)
(a) 2004-03-02怀来爆炸;(b) 2005-03-12可疑事件;(c) 2010-07-10天然地震事件。左上角为事件震级和震中距
Figure 6. Seismic waveforms of different events recorded by XBZ (filtered:0.5—25 Hz)
(a) 2004-03-02 Huailai explosion;(b) 2005-03-12 Suspicious event ; (c) 2010-07-10 natural earthquakeThe magnitude and epicentral distance are on the top left corner of the wavforms
表 1 天然地震、怀来爆炸、三河爆炸主频分布
Table 1 The main frequency distribution of earthquake,Huailai explosion and Sanhe explosion
事件 P波主频分布/Hz S波主频分布/Hz 天然地震 2.5—13.2 2.5—9.0 怀来爆炸 2.5—7.2 2.0—3.8 三河采石场爆炸 1.5—5.8 1.0—2.0 表 2 三次对比事件参数
Table 2 Parameters of three comparison events
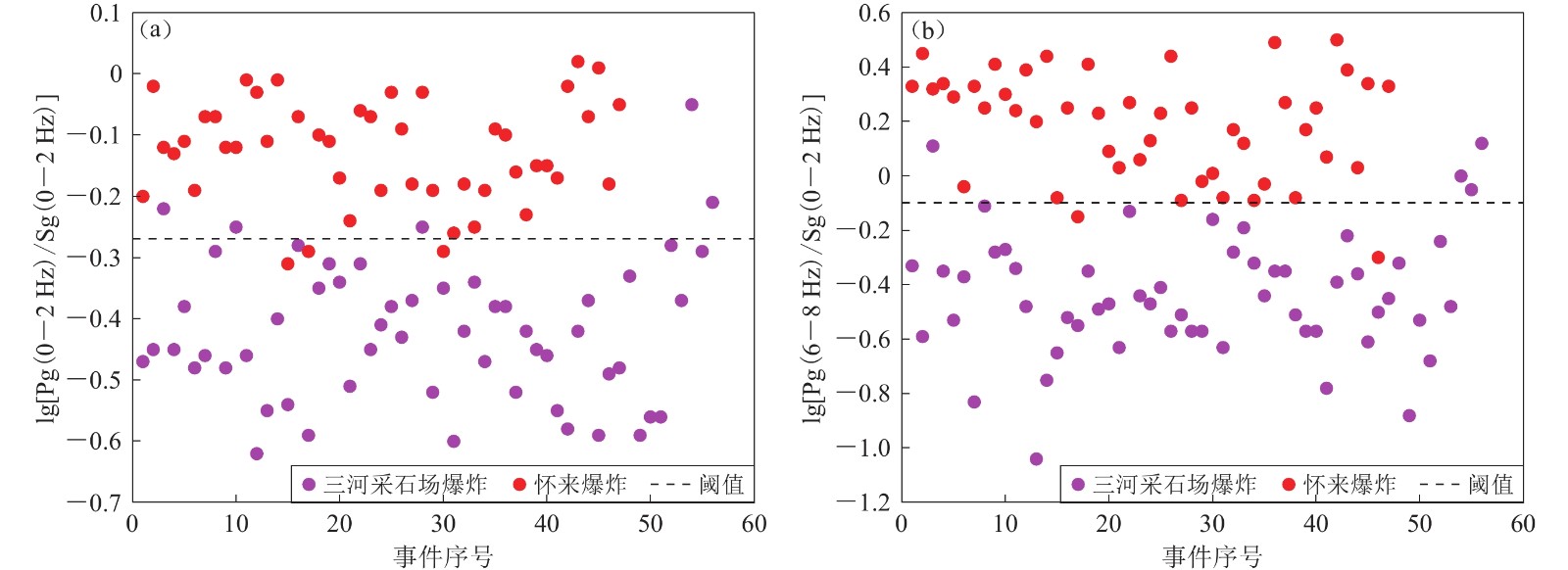
事件性质 发震时间 (UTC) 震中位置 ML 深度/km 年-月-日 时:分:秒 北纬/° 东经/° 怀来爆炸 2004-03-02 08:03:35.6 40.50 115.47 1.8 -- 可疑事件 2005-03-12 13:46:27.4 40.51 115.46 1.6 -- 天然地震 2010-07-10 09:53:43.0 40.47 115.55 1.8 7 表 3 怀来爆炸与三河采石场爆炸正确识别率大于85%的频带分布
Table 3 Frequency bands with the correct discrimination rate greater than 85% between Huailai and Sanhe quarry explosions
交叉频谱比 三河采石场爆
炸正确识别数怀来爆炸正
确识别数正确识
别率Pg (0—2 Hz)/Sg (0—2 Hz) 51 44 92% Pg (0—2 Hz)/Sg (4—6 Hz) 46 46 89% Pg (0—2 Hz)/Sg (6—8 Hz) 51 40 88% Pg (2—4 Hz)/Sg (0—2 Hz) 47 45 89% Pg (2—4 Hz)/Sg (4—6 Hz) 53 36 86% Pg (4—6 Hz)/Sg (0—2 Hz) 47 47 91% Pg (6—8 Hz)/Sg (0—2 Hz) 52 45 94% Pg (8—10 Hz)/Sg (0—2 Hz) 50 44 91% Pg (10—12 Hz)/Sg (0—2 Hz) 50 39 86% Pg (12—14 Hz)/Sg (0—2 Hz) 55 33 85% -
林大超, 白春华. 2007. 爆炸地震效应[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 70–78. Lin D C, Bai C H. 2007. Explosion Seismic Effect [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 70–78 (in Chinese).
潘常周,靳平,王红春. 2007a. P/S震相幅值比判据对低震级地震事件的适用性检验[J]. 地震学报,29(5):521–528. Pan C Z,Jin P,Wang H C. 2007a. Applicability of P/S amplitude ratios for the discrimination of low magnitude seismic events[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,29(5):521–528 (in Chinese).
潘常周,靳平,肖卫国. 2007b. 利用克里金技术标定新疆及附近地区P/S震相幅值比及其在地震事件识别中的应用[J]. 地震学报,29(6):625–634. Pan C Z,Jin P,Xiao W G. 2007b. Calibration of P/S amplitude ratios for seismic events in Xinjiang and adjacent areas based on a Bayesian Kriging method[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,29(6):625–634 (in Chinese).
孙海霞,杨选,林向东,侯丽娟,鲁跃. 2018. 北京及邻区Q值及台站场地响应分析[J]. 华北地震科学,36(3):1–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2018.03.001 Sun H X,Yang X,Lin X D,Hou L J,Lu Y. 2018. Analysis on the Q value and station site response in Beijing and its adjacent areas[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences,36(3):1–11 (in Chinese).
唐兰兰. 2018. 诱发地震检测及地震震源分类[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学: 35–44. Tang L L. 2018. Induced Seismicity Detection and Discrimination of Seismic Source[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China: 35–44 (in Chinese).
王婷婷,边银菊. 2015. 振幅衰减特性在地震与爆破识别中的应用[J]. 地震学报,37(1):169–179. doi: 10.11939/j.issn:0253-3782.2015.01.015 Wang T T,Bian Y J. 2015. Amplitude attenuation and its application to earthquake and explosion discrimination[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,37(1):169–179 (in Chinese).
王云专,王珊,董相杰,于承业. 2009. 多窗谱分析在Q值估算中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,24(6):2156–2162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.06.031 Wang Y Z,Wang S,Dong X J,Yu C Y. 2009. The application of the multiple tapers spectral analysis in the Q estimation[J]. Progress in Geophysics,24(6):2156–2162 (in Chinese).
徐锡伟, 吴卫民, 张先康, 马胜利, 马文涛, 于贵华, 顾梦林, 江娃利. 2002. 首都圈地区地壳最新构造变动与地震[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 5–10. Xu X W, Wu W M, Zhang X K, Ma S L, Ma W T, Yu G H, Gu M L, Jiang W L.2002. Recent Tectonic Changes and Earthquakes in the Capital Circle Area[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 5–10 (in Chinese).
赵爱华,郭永霞,孙为国,杨立强,刘哲. 2012. 华北地区矿山爆破活动的时空特征[J]. 地球物理学进展,27(3):917–923. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.03.012 Zhao A H,Guo Y X,Sun W G,Yang L Q,Liu Z. 2012. Spatio-temporal characteristics of mine blast activity in North China[J]. Progress in Geophysics,27(3):917–923 (in Chinese).
郑秀芬,傅瑀,许绍燮. 2006. 地震记录中小爆破的识别与判据研究[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,27(5):29–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2006.05.006 Zheng X F,Fu Y,Xu S X. 2006. The discrimination and criteria study between blasts and small earthquakes[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,27(5):29–33 (in Chinese).
朱新运. 2011. 衰减、场地响应等地震波传播相关信息综合研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所: 17–24. Zhu X Y.2011. Comprehensive Study of Seismic Wave Propagation Related Information Such as Attenuation and Site Response[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: 17–24 (in Chinese).
Bennett T J,Murphy J R. 1986. Analysis of seismic discrimination capabilities using regional data from western United States events[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,76(4):1069–1086. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0760041069
Bonner J L,Russell D R,Reinke R E. 2013. Modeling surface waves from aboveground and underground explosions in Alluvium and Limestone[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,103(6):2953–2970.
Chun K Y,Wu Y,Henderson G A. 2011. Magnitude estimation and source discrimination:A close look at the 2006 and 2009 North Korean underground nuclear explosions[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,101(3):1315–1329. doi: 10.1785/0120100202
Douglas A. 2013. Forensic Seismology and Nuclear Test Bans[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 340–368.
Fisk M D,Gray H L,McCartor G D. 1996. Regional event discrimination without transporting thresholds[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,86(5):1545–1558.
Fisk M D, Bottone S, McCartor G D. 2000. Regional seismic event characterization using a Bayesian Kriging approach[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd Annual DOD/DOE Seismic Research Symposium: Planning for Verification of and Compliance with the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty(CTBT). Louisiana: U.S. Government or Federal Rights: 1–11.
Fisk M D. 2006. Source spectral modeling of regional P/S discriminants at nuclear test sites in China and the former soviet union[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,96(6):2348–2367. doi: 10.1785/0120060023
Fisk M D. 2007. Corner frequency scaling of regional seismic phases for underground nuclear explosions at the Nevada test site[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,97(3):977–988. doi: 10.1785/0120060186
Fisk M D, Taylor S R, Patton H J, Walter W R. 2008. Applications of a next-generation MDAC discrimination procedure using two-dimensional grids of regional P/S spectral ratios[C]//Proceedings of 2008 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies: 583–592.
Fisk M D, Taylor S R, Walter W R, Randall G E. 2009. Seismic event discrimination using two-dimensional grids of regional P/S spectral ratios: Applications to Novaya Zemlya and the Korean Peninsula[C]//Proceedings of the 2009 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies: 465–474.
Hartse H E,Taylor S R,Phillips W S,Randall G E. 1997. A preliminary study of regional seismic discrimination in central Asia with emphasis on western China[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,87(3):551–568.
Kim W Y,Simpson D W,Richards P G. 1993. Discrimination of earthquakes and explosions in the eastern United States using regional high-frequency data[J]. Geophys Res Lett,20(14):1507–1510. doi: 10.1029/93GL01267
Kim W Y,Simpson D W,Richards P G. 1994. High-frequency spectra of regional phases from earthquakes and chemical explosions[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,84(5):1365–1386.
Kim W Y,Aharonian V,Lerner-Lam A L,Richards P G. 1997. Discrimination of earthquakes and explosions in southern Russia using regional high-frequency three-component data from the IRIS/JSP Caucasus network[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,87(3):569–588.
Kim W Y,Richards P G. 2007. North Korean nuclear test:Seismic discrimination low yield[J]. Eos,Trans Amer Geophys Union,88(14):158–161.
Kim W Y,Richards P G,Schaff D,Jo E,Ryoo Y. 2018. Identification of seismic events on and near the North Korean test site after the underground nuclear test explosion of 3 September 2017[J]. Seismol Res Lett,89(6):2120–2130.
Koper K D,Pechmann J C,Burlacu R,Pankow K L,Stein J,Hale J M,Roberson P,McCarter M K. 2016. Magnitude-based discrimination of man-made seismic events from naturally occurring earthquakes in Utah,USA[J]. Geophys Res Lett,43(20):10638–10645. doi: 10.1002/2016GL070742
McCoy E J,Walden A T,Percival D B. 1998. Multitaper spectral estimation of power law processes[J]. IEEE Trans Signal Process,46(3):655–668. doi: 10.1109/78.661333
Murphy J R,Bennett T J. 1982. A discrimination analysis of short-period regional seismic data recorded at Tonto Forest Observatory[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,72(4):1351–1366. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0720041351
Pomeroy P W,Best W J,McEvilly T V. 1982. Test ban treaty verification with regional data-a review[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,72(6):S89–S129.
Pasyanos M E. 2018. The coupled location/depth/yield problem for North Korea’s declared nuclear tests[J]. Seismol Res Lett,89(6):2059–2067.
Smith A T. 1993. Discrimination of explosions from simultaneous mining blasts[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,83(1):160–179.
Rodgers A J, Walter W R, Schultz C A, Myers S C,Lay T. 1999. A comparison of methodologies for representing path effects on regional P/S discriminants [J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,89(2):394–408.
Taylor S R,Denny M D,Vergino E S,Glaser R E. 1989. Regional discrimination between NTS explosions and western U.S. earthquakes[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,79(4):1142–1176. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0790041142
Taylor S R,Velasco A A,Hartse H E,Phillips W S,Walter W R,Rodgers A J. 2002. Amplitude corrections for regional seismic discriminants[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,159(4):623–650. doi: 10.1007/s00024-002-8652-8
Thomson D J. 1982. Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis[J]. Proc IEEE,70(9):1055–1096. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1982.12433
Walter W R, Taylor S R. 2001. A Revised Magnitude and Distance Amplitude Correction (MDAC2) Procedure for Regional Seismic Discriminants: Theory and Testing at NTS[R]. Livermore, CA: Lawrence Livermore National Lab: 1–13.
Willis D E,DeNoyer J,Pollack H,Wilson J T. 1963. Differentiation of earthquakes and underground nuclear explosions on the basis of amplitude characteristics[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,53(5):979–987. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0530050979
Xie J K,Patton H J. 1999. Regional phase excitation and propagation in the Lop Nor region of central Asia and implications for P/Lg discriminants[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,104(B1):941–954. doi: 10.1029/1998JB900045
Zanandrea A,Da Costa J M,Dutra S L G,Rosa R R,Saotome O. 2004. Spectral and polarization analysis of geomagnetic pulsations data using a multitaper method[J]. Comput Geosci,30(8):797–808. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2004.03.016
Zhao L F,Xie X B,Wang W M,Fan N,Zhao X,Yao Z X. 2017. The 9 September 2016 North Korean underground nuclear test[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,107(6):3044–3051. doi: 10.1785/0120160355
Zheng X F,Yao Z X,Liang J H,Zheng J. 2010. The role played and opportunities provided by IGP DMC of China national seismic network in Wenchuan earthquake disaster relief and researches[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,100(5B):2866–2872. doi: 10.1785/0120090257
-
期刊类型引用(25)
1. 孙喜文,鲁铁定,贺小星,黄佳慧. 顾及RMLE的GNSS时序噪声特性及环境负载修正. 导航定位学报. 2024(01): 21-27+42 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 余思,李辰风,唐婷婷,陈江贻. 顾及环境负荷的GNSS速度场分析. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2024(07): 732-736 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 余思,李辰风,唐婷婷. 赣鄂皖交界地区三维地壳运动特征分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(01): 44-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 金波文,王慧,刘玉龙,邓丽静,吕江华. 中国沿海海洋站GNSS坐标时间序列噪声模型的建立与分析(英文). Marine Science Bulletin. 2023(02): 63-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 任安康,徐克科,邵振华. GEONET网络GPS坐标时间序列噪声模型建立与分析. 导航定位学报. 2022(02): 141-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 郑博文,杜向峰,詹松辉,吴希文,王华. 中国大陆GPS连续站时间序列噪声分析. 广东工业大学学报. 2022(03): 70-76+82 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王力斌,潘鹏飞,薛蛟. 武汉市CORS坐标时间序列中共模误差分析. 地理空间信息. 2022(06): 96-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 高启平. 基于速率的Allan方差的GPS坐标时间序列噪声特性分析. 科学技术创新. 2021(02): 117-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 霍景焕,马进全,张睿. GPS时间序列分析尼泊尔地震震后位移. 测绘地理信息. 2020(01): 40-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 金波文,王慧,刘玉龙,邓丽静,吕江华. 中国沿海海洋站GNSS坐标时间序列噪声模型的建立与分析. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2020(05): 476-481 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 薛天云. 藏南地区GPS时间序列分析. 地理空间信息. 2020(09): 66-69+7 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 刘志平,朱丹彤,余航,张克非. 等价条件平差模型的方差-协方差分量最小二乘估计方法. 测绘学报. 2019(09): 1088-1095 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 常金龙,甘卫军,梁诗明,张克亮. 大华北地区GPS时间序列共模误差的确定与分析. 地震研究. 2018(03): 430-437+489 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 蔡琅,肖根如,王建强,田莎莎. 国产接收机在形变监测应用中的可靠性分析——以新丰江水库为例. 测绘与空间地理信息. 2018(11): 49-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 宋爱虎,马超,周宁. 有色噪声对东南极区域GPS测站三维速度估计的影响. 测绘通报. 2017(10): 18-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 张风霜,畅柳. 基于有色噪声模型的GPS速度场精度与时间序列长度相关性研究. 地震. 2017(01): 92-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 贺小星,花向红,鲁铁定,余科根,宣伟. 时间跨度对GPS坐标序列噪声模型及速度估计影响分析. 国防科技大学学报. 2017(06): 12-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 张风霜. 有色噪声模型下云南地区GPS基准站速度与周期估计. 地震研究. 2016(03): 410-420 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 丁开华,丁剑,李志才,王兰立. 川滇地区陆态网络基准站运动噪声模型分析. 测绘科学. 2014(12): 56-60+50 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 许颖,岳东杰,袁豹. 基于最大熵谱估计的GPS坐标时间序列噪声分析. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2014(02): 60-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 芦琪,张小红. 中国境内IGS跟踪站精密单点定位坐标时间序列频谱分析. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2014(05): 64-69+74 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 谢树明,潘鹏飞,周晓慧. GPS坐标时间序列共模误差空间特性分析. 地理空间信息. 2014(04): 44-45+54+9 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 谢树明,潘鹏飞,周晓慧. 大空间尺度GPS网共模误差提取方法研究. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2014(10): 1168-1173 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 王解先,连丽珍,沈云中. 奇异谱分析在GPS站坐标监测序列分析中的应用. 同济大学学报(自然科学版). 2013(02): 282-288 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 潘正洋,何建坤,卢双疆. 帕米尔高原现代地壳运动首期GPS观测及处理. 地球科学与环境学报. 2013(01): 103-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(17)




 下载:
下载: