Dispersion analysis for the finite element algorithm in acoustic wave equation numerical simulation
-
摘要: 针对有限元算法在地震波数值模拟中的数值频散问题,利用集中质量矩阵双线性插值有限元算法,推导了二维声波方程的频散函数.在此基础上采用定量分析方法,对比分析了网格纵横长度比变化时的入射方向、空间采样间隔、地震波频率以及地层速度对数值频散的影响.数值算例和模型正演结果表明:当采用集中质量矩阵双线性插值有限元算法时,为了有效地压制数值频散,在所使用震源子波的峰值频率对应的波长内,采样点数目应不少于20个;减小网格长度的纵横比可以有效地抑制入射角(波传播方向与z轴的夹角)较小的地震波的数值频散;地震波频率越高,传播速度越慢,频散越严重,尤其是当相速度与其所对应的频率比值小于2倍空间采样间隔时,不仅会出现严重的数值频散,还会出现假频现象.Abstract: This paper focuses on the dispersion problems of finite element algorithm in numerical simulation of seismic wave, and the dispersion function of two-dimensional acoustic wave equation is derived by employing lumped mass matrix and bilinear interpolation finite element algorithm. And, we compared quantitatively the effect of incident direction with the variable ratio of vertical to horizontal grid, spatial sampling interval, seismic wave frequency, and formation velocity on numerical dispersion. The numerical examples and the forward modeling indicate, if we want to suppress the numerical dispersion effectively, it should not be less than 20 samples within the wavelength corresponding to peak frequency of source wavelet; reducing the ratio of vertical to horizontal grid can suppress the numerical dispersion with small incident angle (the angle between the direction of wave propagation and the z axis) remarkably; the slower the propagation velocity of the seismic wave with higher frequency, the more serious its dispersion is; when the ratio of phase velocity to the corresponding frequency is less than twice of spatial sampling interval, not only the numerical dispersion becomes very serious, but also the aliasing phenomenon will happen.
-
引言
波动方程数值模拟是深入研究地震波传播规律的有效方法,而有限元法是模拟地震波在地球介质中传播最常用的方法之一,特别是对复杂介质进行数值模拟时.采用有限元法对连续介质进行空间离散会对地震波传播的数值解引入频散误差,这是因为用离散代替连续会引起精度上的误差,使得具有不同频率的地震波表现为不同的相速度,从而导致波场发生频散(董良国,李培明,2004),这类误差可以通过数值频散(网格频散)来描述.数值频散程度直接决定着地震波的数值模拟效果,因此压制数值频散对提高正演模拟精度具有非常重要的作用.为此,Mullen和Belytschko(1982)采用双线性四边形单元和线性三角形单元在网格布局、质量矩阵等方面对二维声波方程的频散问题进行研究,得出了矩形网格比三角形网格具有更高精度的结论;Abboud和Pinsky(1992)对三维声波方程有限元法数值频散进行相应研究,得到了最优网格离散的方法;Liu等(1994)分析了有限元不规则网格中波动的频散特性,结果显示当使用不恰当的单元时会导致相速度大于介质的真实速度; Christon(1999)研究了质量矩阵对频散的影响,并采用集中质量矩阵与一致质量矩阵的线性组合来压制数值频散;房营光和莫海鸿(2000)采用含有频率的高阶位移函数对有限元网格中波动的频散与稳定性条件进行了改进;De Basabe和Sen(2007)通过数值求解方法对高阶四边形谱元法进行了分析,并且证明高阶谱元法能够较好地压制数值频散;Seriani和Oliveira(2008)分析了弹性波谱元法数值模拟中的频散,结果表明高阶谱元法能够较好地压制数值频散;薛东川和王尚旭(2008)研究了一致质量矩阵和集中质量矩阵对数值频散的影响,并采用二者的组合形式来压制数值频散,最终得到当速度为2.5—4.0 km/s时最优组合系数为0.5.
在前人研究成果的基础上,本文将采用4节点四边形单元和集中质量矩阵得到二维声波方程的数值频散函数,以此来分析影响数值频散的因素,以期从理论和数值模拟实例上证明空间采样间隔、网格的纵横长度比、入射方向、地震波频率以及地层速度等因素对有限元法数值频散的影响,为提高声波方程有限元数值模拟精度及降低计算成本等提供参考.
1. 有限元算法频散的理论分析
1.1 集中质量矩阵双线性插值有限元算法声波方程数值模拟的频散函数
我们使用伽勒金(Galerkin)法求解二维标量波动方程,得到有限元方程组(杜世通,1982)为

式中,K e和Me分别为单元刚度矩阵和单元一致质量矩阵,ue为单元节点位移列向量.单元刚度矩阵和单元一致质量矩阵均为实对称且正定.计算出每一个单元的刚度矩阵和一致质量矩阵后,将其集成为总体的刚度矩阵 K和一致质量矩阵 M,得到整体有限元方程组

其中 u 为所有节点位移列向量.采用4节点四边形单元时,相应的形函数为

一旦确定了形函数,式(1)中单元刚度矩阵和单元一致质量矩阵的表达式可变为

式中,c为介质的真实速度,N T=[N1,N2,N3,N4].
采用等参单元和高斯(Gauss)数值积分,单元刚度矩阵和单元一致质量矩阵可具体表示为(Mullen,Belytschko,1982;徐世浙,1994)

其中γ=Δz/Δx,Δx为横向采样间隔,Δz为纵向采样间隔.
在采用有限元算法进行地震波数值模拟时,为了避免矩阵求逆的大量运算,一般采用单元集中质量矩阵代替单元一致质量矩阵.单元集中质量矩阵表示为

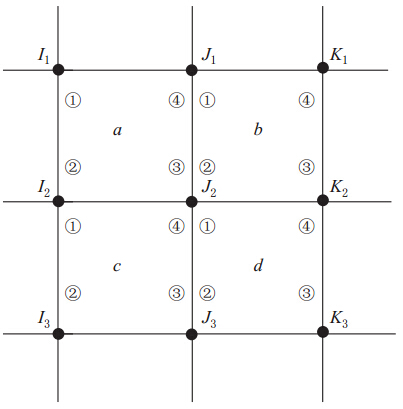
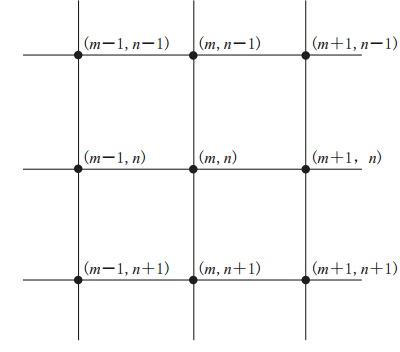
如图1所示,节点(m,n)处的坐标为(m>Δx,nΔz).根据平面波理论得到该节点(m,n)处的位移值为(孙成禹,2007)

式中,A为振幅,k为波数,ω为角频率,θ为平面波传播方向与x轴的夹角.相速度cp为

采用单元集中质量矩阵,得到节点(m,n)处的位移与周围相关节点的位移关系(推导过程,详见附录)为

将式(9)代入式(11),得到

其中

再将式(10)代入式(12),得到

式(13)即为集中质量矩阵双线性插值有限元算法声波方程数值模拟的频散函数.利用该式可以对集中质量矩阵双线性插值有限元算法在地震波数值模拟中的频散特征进行分析.显然,对同一频率而言,若cp/c值远大于或远小于1,则会发生严重的频散,若cp/c值为1,则不存在频散.
1.2 网格纵横长度比及地震波传播方向对频散的影响
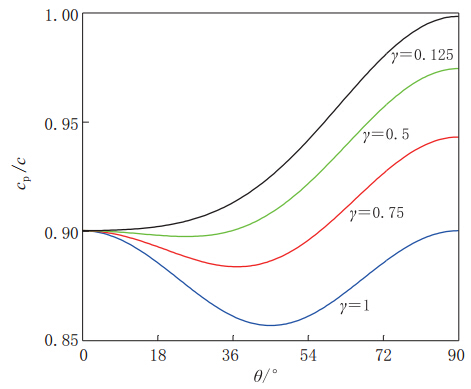
图2和图3分别给出了频散随平面波传播方向和网格纵横长度比γ的变化情况,且均假定kΔx=π/2.由图2和图3可见:① 当γ值小于或等于某一常数γ′时(图3中γ′约为0.4),随着θ的增加,频散逐渐减小;当γ值大于γ′时,随着θ的增加,频散先增加,后减小(图3);② 对同一入射角而言,单元网格纵横长度比越小,cp/c值越大,也就是说频散越弱;值得注意的是,当θ值为0°(即平面波沿水平方向传播)时,频散不随γ而改变(图3);③ 当单元网格纵横长度比值γ为1且θ为45°时,频散最为严重(图2);④ 减小γ值对压制大角度(波传播方向与x轴的夹角)传播的地震波的数值频散效果更为显著(图3);⑤ 采用集中质量矩阵进行地震波数值模拟时,相速度小于地层真实速度,即频散误差滞后于真实信号(图2,3);⑥ 在不同的传播方向上,相速度不相同(图2),这说明各向同性连续介质经离散化后会表现为频散各向异性,且其性质与单元尺寸的比值γ以及传播方向有关.
根据上述分析可知,减小网格的纵横长度比可以减弱数值频散,然而对于传播方向不同的地震波,其减弱程度是不一样的.
1.3 空间采样间隔对频散的影响
取奈奎斯特(Nyquist)频率时,kΔx的值等于π,因此当我们计算cp/c时,kΔx的取值范围为0—π(Liu,Sen,2009).
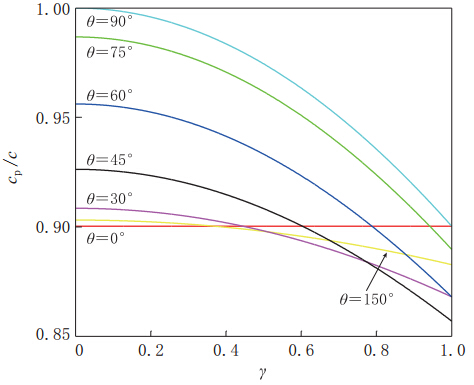
图4给出了θ取不同值时,cp/c随kΔx的变化情况.可以看出:① 频散随kΔx 的增加而增强,即网格越大,频散越严重;② 当kΔx≤0.333时,cp/c值大于0.995,此时可以忽略频散误差. 换言之,若要有效地压制数值频散,单元网格的最大边长应小于或等于λ/20(λ为震源峰值频率所对应的波长);③ 当kΔx值接近于0时,cp/c值接近于1,此时频散几乎不受波传播方向及单元网格纵横长度比的影响;④ 由图2可看出,在γ=1的情况下,当0°≤θ≤45°时,频散随θ值的增加而增强,当45°<θ≤90°时,频散随θ值的增加而减弱. 其中当θ=45°时,频散最为严重,并且频散以θ=45°为对称.因此,对于同一kΔx而言,θ取45°时数值频散最严重,然后依次为30°、20°、0°.由于其对称性,θ=30°与θ=60°以及θ=0°与θ=90°对应的曲线重合;⑤ 当γ=0.4时,频散随θ值的增加而减弱(图3),出现图4b所示结果. 因此在采用集中质量矩阵双线性插值有限元算法进行地震波数值模拟时,根据所选震源子波的峰值频率以及地层的速度来确定单元网格的大小,可以有效地压制数值频散.
1.4 地震波频率对频散的影响
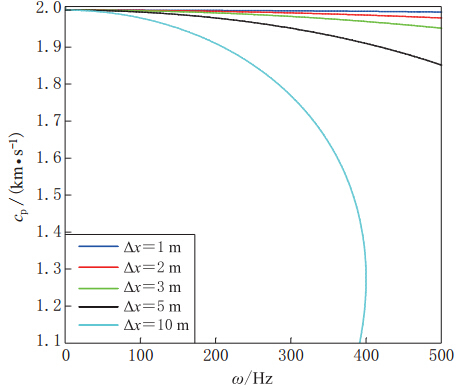
在实际介质中传播的地震波由不同频率分量组成,因此研究频率对地震波数值模拟频散的影响对提高地震波场正演模拟精度也具有指导意义.现假定地层的真实速度为2.0 km/s,单元网格纵横长度比为1,波传播方向与x轴的夹角为45°.将上述参数代入式(13)可以得到cp与ω的隐式关系.当分别采用1 m×1 m、2 m×2 m、3 m×3 m、5 m×5 m和10 m×10m的空间网格尺寸时,通过该隐式关系,得到cp与角频率ω的关系(图5).
由图5可看出:① 随着频率的增加,相速度减小,数值频散增强,零频率分量的传播 速度等于地层真实速度;② 在同一频率下,网格越小,相应的数值频散越弱; ③ Δx=10m的曲线形态与其它曲线有所不同,这是由于当角频率增大到某一特定值后,曲线朝着频率减小的方向发生逆转,出现“假频”现象所致.对这一现象,本文在后面将给出具体分析.总之,在相同网格间距的情况下,地震波频率越高,相应的相速度越低,频散越严重.因此高频地震波的频散对数值模拟的精度有很大影响.
1.5 速度变化对频散的影响
以网格为5 m×5 m,平面波传播方向与x轴的夹角为90°,介质速度分别为0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0 km/s为例来研究介质速度对频散的影响.将k=ω/cp代入式(13),得到cp与ω频散关系,这是一个隐式函数,通过其可以求出各个频率对应的相速度cp(ω).当速度不同时,cp/c与ω之间的关系如图6所示.可以看出,随着角频率的增加,相速度降低.当频率增大到某一特定值后,曲线朝着频率减小的方向发生逆转,使低频成分由于折叠作用而发生畸变.图中发生逆转的那个点所对应的频率即为折叠频率.总之,在相同单元网格尺寸下,地层速度越小,数值频散程度就越大,且对应的折叠频率越小.大于折叠频率的频谱成分被折叠到低频成分之上,使原始频谱被彻底改造. 引起频谱发生畸变的那部分频率统称为假频.
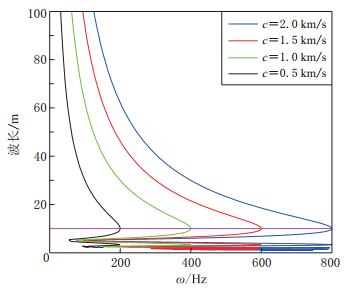
图7给出了不同频率分量的波长与角频率的关系.可见,随着角频率的增加,相应频率的波长减小.在波长为10m处,4条曲线均发生逆转,其所对应的频率即为折叠频率.根据奈奎斯特定理可知,不产生假频的条件是在一个波长的距离上至少采到2个样点(孙成禹等,2009). 由于我们使用的网格为5 m×5 m,因此不产生假频的必要条件是波长至少大于10 m.根据图6或图7,可以直接读出不同速度地层的折叠频率,其值与理论值相一致.
2. 数值模拟结果分析
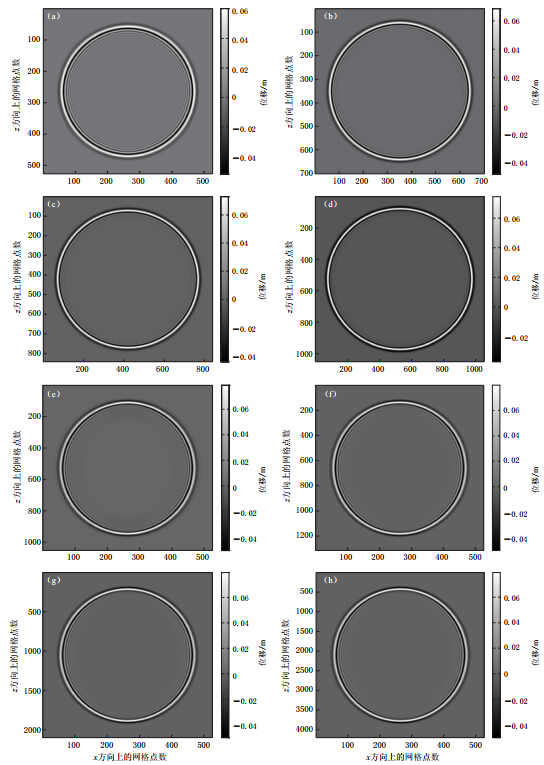
假设均匀介质模型的速度为2.0km/s,计算区域为2.1 km×2.1 km,基于此模型对上述定量分析结果进行验证.震源为40 Hz主频的雷克子波(发震时刻t0为10ms),位于模型中央,时间步长为0.2 ms. 从图8a-d中可以看到:网格越大,波前面的散开越明显,相应的数值频散越严重;网格越小,几乎只能看到一个波前面,则相应的数值频散现象越不明显.当采用3 m×3 m的网格(图8b)时,可以看到微弱的频散; 当采用2.5 m×2.5 m的网格(图8c)时,频散被有效地压制.在这个模型中,震源峰值频率对应的波长为50 m,所以当kΔx=0.333时,Δx的值约为2.5 m.该结果与上述分析结果一致.将图8a与图8e-h进行对比可看出,减小γ值可以显著地压制数值频散,其压制程度也与波的传播方向有关.
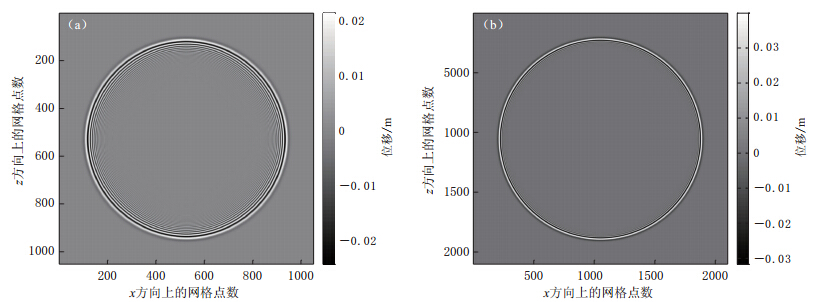
现将震源的主频改为100 Hz,其它条件保持不变,得到网格依次为2 m×2 m和1 m× 1 m的波场快照,如图9所示.对比图9a与图8d的波场快照可见,增大震源主频会增强波场的数值频散,减小网格尺寸会减弱波场的数值频散.因此,在进行地震波传播数值模拟时,合理选取震源的主频和网格大小均可以提高数值模拟精度及计算效率.
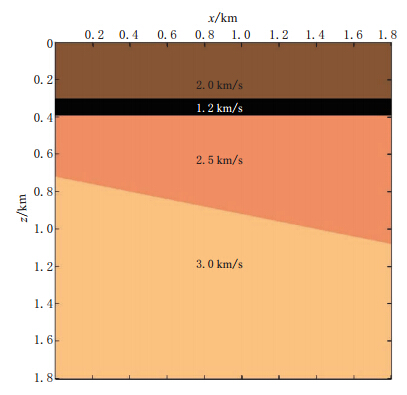
为了进一步验证有限元算法频散理论的准确性,我们又设计了含一低速夹层的介质模型.该模型宽度为1.8 km,纵深为1.8 km,薄层厚度为90 m,各层的速度由浅至深依次为2.0,1.2,2.5,3.0 km/s(图10).震源为40 Hz主频的雷克子波,位于(900 m,150 m)处,检波器与震源处于同一行,时间采样间隔为0.4 ms.分别采用3 m×3 m、3 m×1.5 m和1.5 m×1.5 m的网格进行数值模拟,得到如图11所示的单炮记录.
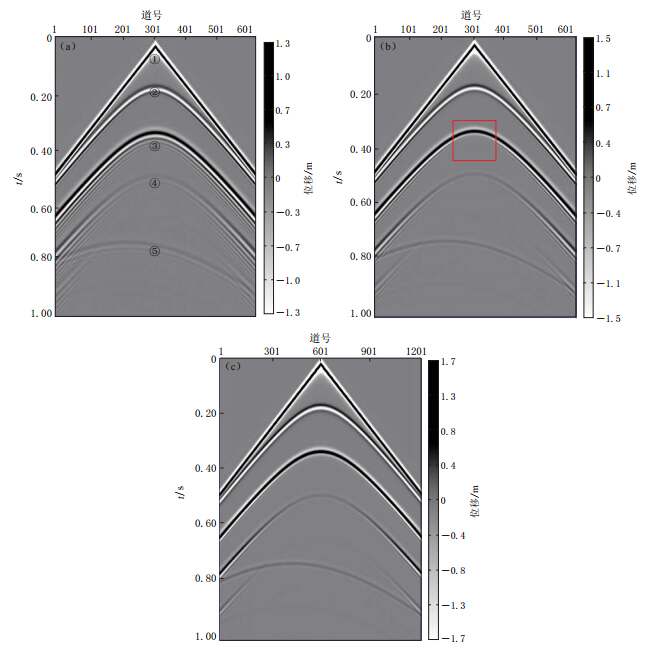
![]() 图 11 网格分别为3 m×3 m(a)、3 m×1.5 m(b)和1.5 m×1.5 m(c)情况下的单炮记录① 直达波; ② 薄层顶界面反射波; ③ 薄层底界面反射波; ④ 薄层内二次反射波; ⑤ 倾斜界面反射波Figure 11. Shot records with grid sizes of 3 m×3 m(a),3 m×1.5 m(b) and 1.5 m×1.5 m(c)① Direct wave; ② The reflection wave coming from the top of low velocity interlayer; ③ The reflection wave coming from the base of low velocity interlayer; ④ The re-reflection wave coming from low velocity interlayer; ⑤ The reflection wave coming from dipping interface
图 11 网格分别为3 m×3 m(a)、3 m×1.5 m(b)和1.5 m×1.5 m(c)情况下的单炮记录① 直达波; ② 薄层顶界面反射波; ③ 薄层底界面反射波; ④ 薄层内二次反射波; ⑤ 倾斜界面反射波Figure 11. Shot records with grid sizes of 3 m×3 m(a),3 m×1.5 m(b) and 1.5 m×1.5 m(c)① Direct wave; ② The reflection wave coming from the top of low velocity interlayer; ③ The reflection wave coming from the base of low velocity interlayer; ④ The re-reflection wave coming from low velocity interlayer; ⑤ The reflection wave coming from dipping interface对比图11中不同网格的单炮记录可见:当采用大网格时,由于低速层的影响(低速层内每个波长上的采样点过少),使得地震波经过低速层后出现严重的数值频散(如a图中③所示),并使低速层以下的高速层界面的反射波也出现严重的数值频散;减小单元网格的纵向长度,数值频散得到明显压制,特别是传播方向与x轴夹角较大的地震波的数值频散(如b图中方框所示部分),但由于单元网格横向尺寸过大,入射角(波传播方向与z轴的夹角)较大的地震波仍然会出现明显的数值频散;同时减小单元网格的纵向和横向尺寸,地震波传播的数值频散会得到较好的压制(c图).综上,在有限元法地震波数值模拟过程中,合理选取单元网格的横向和纵向尺寸,不仅可以保证数值模拟的精度,还可以提高计算效率.
3. 讨论与结论
采用集中质量矩阵双线性插值有限元算法对地震波进行数值模拟时,影响频散的因素主要有空间采样间隔、单元网格纵横长度比、传播方向、地震波频率及地层速度等.本文通过理论分析及数值模拟得到如下结论:
1)各向同性的连续介质经离散化后表现为频散各向异性,其性质与单元网格纵横长度的比值及传播方向有关.
2)为了有效地压制数值频散,震源子波主频对应的波长内所包含的采样点数目应不少于20个.
3)减小单元网格的纵横比,可在一定程度上压制数值频散,特别是对于入射角(波传播方向与z轴的夹角)较小的地震波,数值频散压制效果尤为明显.
4)在其它条件相同的情况下,地震波的频率越高,其数值频散越严重.因此,进行地震波数值模拟时,须根据实际情况合理选取震源子波的主频.
5)当模型含有低速地层时,如果按照高速地层的标准进行空间采样会导致严重的数值频散,因此合理选取单元网格的纵向和横向长度对提高正演模拟精度及减小计算量具有非常重要的作用.当地震波频率超过折叠频率后,会出现假频现象,这使得高于折叠频率的地震波成分与低频成分混合在一起,导致观测到的地震波的频谱被彻底改造.
本文的频散分析基于区域是均匀、无边界,且单元为周期单元的假设,但在实际地震波数值模拟中,为了较好地拟合起伏构造,一般采用不规则的四边形网格,因而只能通过本文已有的结论推测一般情况下频散的特征. 基于本文的核心思想,可以研究三角网格中波动的数值频散特性,以便进一步完善有限元法地震波数值模拟的理论基础.
附录
以节点J2为例,节点J2对应总体刚度矩阵的第J2行,该行的非零元素如下:

总体质量矩阵 M 的第J2行、第J2列为

式中,KI,J代表总体刚度矩阵的第I行、第J列,(Ke)ai,j代表第a个单元的刚度矩阵的第i行、第j列,质量矩阵的相关表达式类推.
图1中各个点的位移表达式与正文图1相对应,把正文式(2)进行第J2行的运算可以得到

将式(1)以及式(2)代入式(3)整理后即可得到正文中的式(11).
-
图 11 网格分别为3 m×3 m(a)、3 m×1.5 m(b)和1.5 m×1.5 m(c)情况下的单炮记录① 直达波; ② 薄层顶界面反射波; ③ 薄层底界面反射波; ④ 薄层内二次反射波; ⑤ 倾斜界面反射波
Figure 11. Shot records with grid sizes of 3 m×3 m(a),3 m×1.5 m(b) and 1.5 m×1.5 m(c)① Direct wave; ② The reflection wave coming from the top of low velocity interlayer; ③ The reflection wave coming from the base of low velocity interlayer; ④ The re-reflection wave coming from low velocity interlayer; ⑤ The reflection wave coming from dipping interface
-
董良国, 李培明. 2004. 地震波传播数值模拟中的频散问题[J]. 天然气工业, 24(6): 53-56. Dong L G, Li P M. 2004. Dispersive problem in seismic wave propagation numerical modeling[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 24(6): 53-56 (in Chinese).
杜世通. 1982. 变速不均匀介质中波动方程的有限元法数值解[J]. 华东石油学院学报, 6(2): 1-20. Du S T. 1982. Finite element numerical solution of wave propagation in non-homogeneous medium with variable velocities[J]. Journal of East China Petroleum Institute, 6(2): 1-20 (in Chinese).
房营光, 莫海鸿. 2000. 有限元网格中波动的频散与稳定性的一种改进方法[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 20(1): 21-26. Fang Y G, Mo H H. 2000. An improved method for dispersion and stability of wave motion in finite element meshes[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 20(1): 21-26 (in Chinese).
孙成禹. 2007. 地震波理论与方法[M]. 东营: 中国石油大学出版社: 31-37. Sun C Y. 2007. Theory and Methods of Seismic Waves[M]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum Press: 31-37 (in Chinese).
孙成禹, 宫同举, 张玉亮, 张文颖. 2009. 波动方程有限差分法中的频散与假频分析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 44(1): 43-48. Sun C Y, Gong T J, Zhang Y L, Zhang W Y. 2009. Analysis on dispersion and alias in finite-difference solution of wave equation[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 44(1): 43-48 (in Chinese).
徐世浙. 1994. 地球物理中的有限元法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 135-146. Xu S Z. 1994. Finite Element Method for Geophysics[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 135-146 (in Chinese).
薛东川, 王尚旭. 2008. 利用组合质量矩阵压制数值频散[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 43(3): 318-320. Xue D C, Wang S X. 2008. Using combined mass matrix to suppress numerical dispersion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 43(3): 318-320 (in Chinese).
Abboud N N, Pinsky P M. 1992. Finite element dispersion analysis for the three-dimensional second-order scalar wave equation[J]. Int J Numer Meth Engng, 35(6): 1183-1218.
Christon M A. 1999. The influence of the mass matrix on the dispersive nature of the semi-discrete, second-order wave equation[J]. Comput Methods Appl Mech Engng, 173(1): 147-166.
De Basabe J D, Sen M K. 2007. Grid dispersion and stability criteria of some common finite-element methods for acoustic and elastic wave equations[J]. Geophysics, 72(6): T81-T95.
Liu J B, Sharan S K, Yao L. 1994. Wave motion and its dispersive properties in a finite element model with distortional elements[J]. Comput Struct, 52(2): 205-214.
Liu Y, Sen M K. 2009. A new time-space domain high-order finite-difference method for the acoustic wave equation[J].J Comput Phys, 228(23): 8779-8806.
Mullen R, Belytschko T. 1982. Dispersion analysis of finite element semidiscretizations of the two-dimensional wave equation[J]. Int J Numer Meth Engng, 18(1): 11-29.
Seriani G, Oliveira S P. 2008. Dispersion analysis of spectral element methods for elastic wave propagation[J]. Wave Motion, 45(6): 729-744.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 武晔,赵晓燕,石砚斌,俞子钊,何欣娟,胡泊,熊仲华. 伪谱算法在声波数值模拟中的数值频散分析. 地震. 2017(02): 135-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曹丹平,周建科,印兴耀. 三角网格有限元法波动模拟的数值频散及稳定性研究. 地球物理学报. 2015(05): 1717-1730 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: